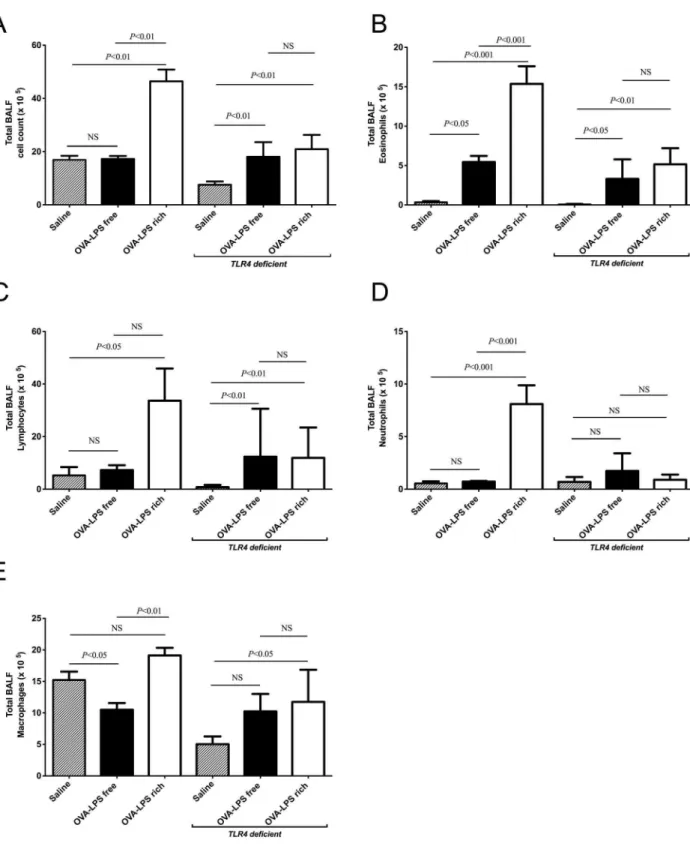
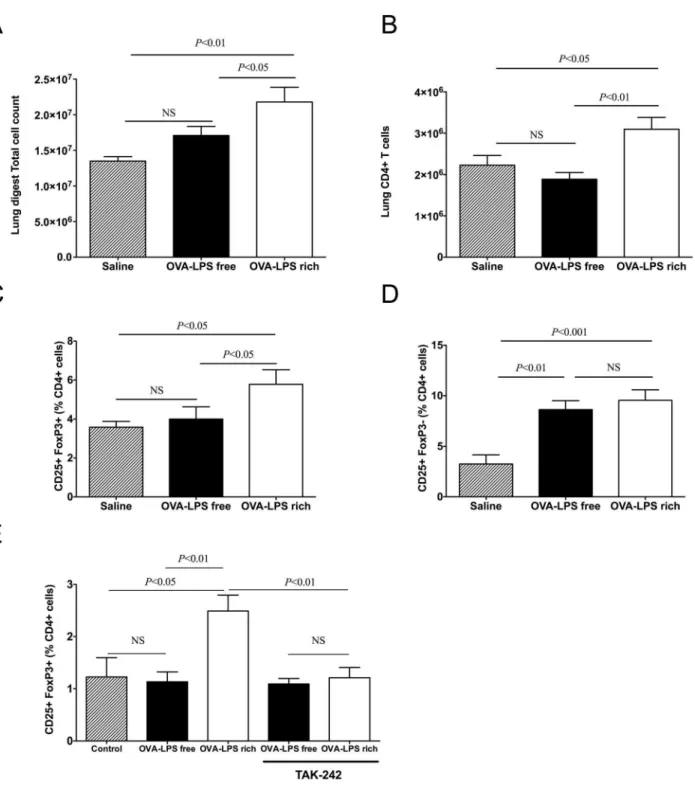
Concomitant exposure to ovalbumin and endotoxin augments airway inflammation but not airway hyperresponsiveness in a murine model of asthma.
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
Mice missing functional caspase 1/11 or caspase 11 had equivalent airway inflammation after LPS challenge compared to the wild type control mice suggesting these proteins are
NR OVA/PBS = well- nourished group immunized with ovalbumin and challenged with phosphate buffered saline; NR OVA/OVA = well-nourished group immunized and challenged
As expected, serum IgE levels significantly increased following OVA sensitization and challenge in both the CC10 controls and the transgene ++ group when compared to littermate
Upon OVA allergen challenge, sensitized WT mice displayed robust allergic inflammatory responses, including macrophage and eosinophil dominated cell infiltration in the airway and
In the mouse model of OVA-induced asthma, the number of white blood cells (WBCs) in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) was significantly increased compared with that of mice
Results: High fat diet resulted in obesity in both wild-type and RAG mice and significantly impaired lymphatic fluid transport and lymph node uptake; interestingly, obese wild-type
To determine whether skin-derived TSLP could cause airway hyper-responsiveness in RBP-jCKO mice, we used the OVA-induced model of allergic inflammation and challenged the lung
When viewed together, epicutaneous sensitization of wild type mice with superantigen SEB enhanced epicutaneous Ova-induced lung inflammation, airway mucus metaplasia, AHR and Th2