Brain Energy Metabolism in Chronic Hepatic Encephalopathy: an in vivo and longitudinal Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy study on a rat model of Biliary Cirrhosis
Texto
Imagem

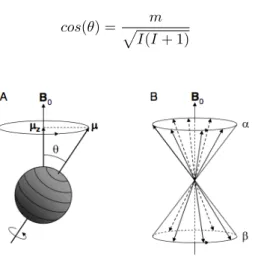
Documentos relacionados
Lactulose is highly potential in prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis and upper gastrointestinal bleeding: results of a controlled randomized
In order to study metabolic changes within the brain, the authors performed a magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) study in a 1- year-old girl with merosin-positive CMD (MP-CMD)..
Abstract – In two children with near drowning hypoxic encephalopathy and normal-appearing structural MRI, acute proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy ( 1 H MRS) showed
In fact, the availabil- ity of functional magnetic resonance imaging for in vivo analysis of the normal brain has revolutionized the study of language. Another unexpected ind in
In the hope to clarify the contribution of fructose on the pathomechanisms of brain damage observed in HFI patients, the aim of the present work was to investigate the in vivo and
Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) of the human brain has proven to be a useful technique in several neurological and psychiatric disorders and benefits from higher
Evidence for cellular damage in normal-appearing white matter correlates with injury severity in patients following traumatic brain injury: A magnetic resonance spectroscopy
31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy in dilated cardiomyopathy and coronary artery disease: altered cardiac high- energy phosphate metabolism in heart failure. Contributions