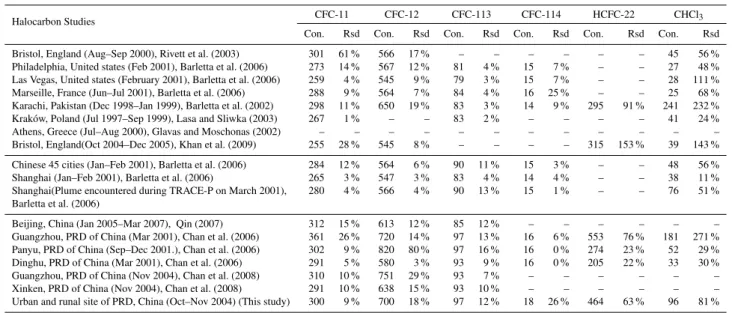
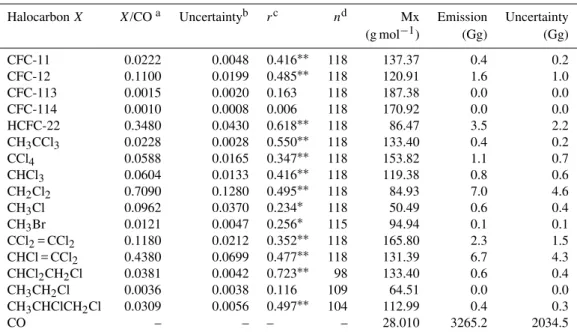
Estimate of anthropogenic halocarbon emission based on measured ratio relative to CO in the Pearl River Delta region, China
Texto
Imagem




Documentos relacionados
All diets were isonitrogenous and had the same ratio of essential amino acids in relation to lysine, except threonine, and 100, 25, 85, 92, 102, 124, 31, 67 and 120% to
Finally, the inequalities obtained in the proof of Theorem A permit us to give, modulo Omori's theorem, a simple proof of a recent result by Jorge and Xavier [8]
To estimate the impact of aldehyde emissions at an airport on the air quality, formaldehyde and acetaldehyde concentrations were measured in the idle and taxiway areas of
Bias of using odds ratio estimates in multinomial logistic regressions to estimate relative risk or prevalence ratio and alternatives.. Viés da razão de chances estimada
The uncertainty assessment indicates that the fuel-related combustion sources such power plants and boilers are more reliable compared with the other source categories, because
transport model and a minimum variance Bayesian inverse method was used to estimate annual emission rates using the measurements, with a priori estimates from the Emis- sions
PSC microphysical properties were retrieved by comparison of the measured particle depolarization ratio and PSC-averaged lidar ratio to theoretical optical data obtained for
During co-combustion, the blending ratio of biomass and coal had a significant impact on emission of gases. In order to optimize blending ratio of coal and biomass, different