Convective Flow of Sisko Fluid over a Bidirectional Stretching Surface.
Texto
Imagem
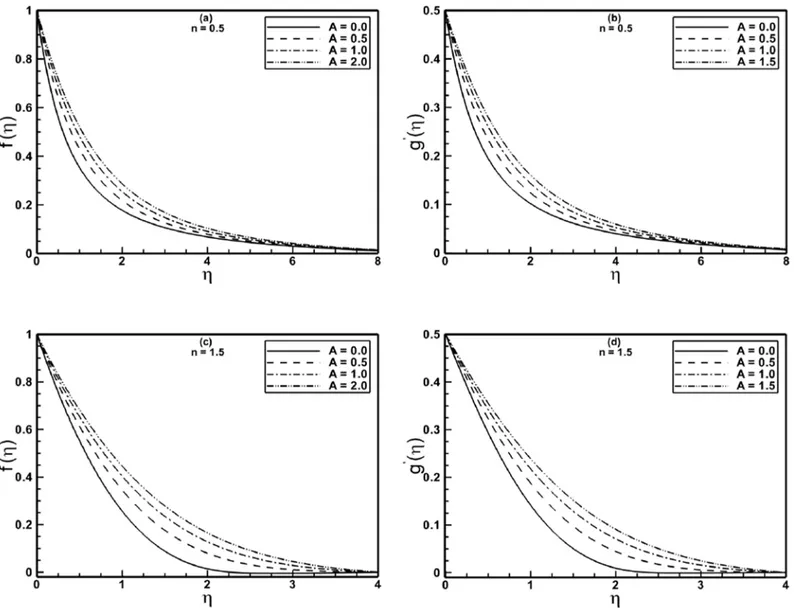
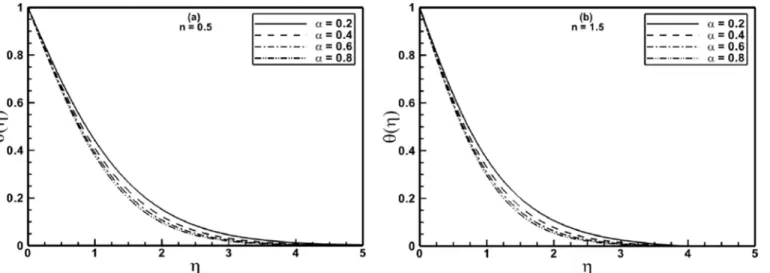
Documentos relacionados
Hayat T, Yasmin H, Alsaedi A (2014) Convective heat transfer analysis for peristaltic flow of power-law fluid in a channel.. Parsa AB, Rashidi MM, Hayat T (2013) MHD boundary-layer
Further Nandy (2013) studied the hydromagnetic boundary layer flow and heat transfer of a non-Newtonian Casson fluid in the neighborhood of a stagnation point over a stretching
An efficient method to obtain semi-analytical solutions of the nano boundary layers over stretching surfaces, International Journal of Numerical Methods for Heat &
Effects of Thermal Radiation and Chemical Reaction on MHD Free Convection Flow past a Flat Plate with Heat Source and Convective Surface Boundary
In the presented analysis, we have explored the characteristics of melting heat transfer in the MHD stagnation point flow of Jeffrey fluid induced by an impermeable
This article examines the non-aligned stagnation point flow and heat transfer of an Ethylene- Glycol and water based Nano fluid towards a stretching surface utilizing hematite
Effects of thermal buoyancy and variable thermal conductivity on the MHDflow and heat transfer in a power-law fluid past a vertical stretching sheet in the presence
Consider a steady, laminar boundary layer flow of a viscous, incompressible and electrically conducting fluid in the presence of a strong magnetic field B(x)