Retrieval of aerosol optical depth in vicinity of broken clouds from reflectance ratios: case study
Texto
Imagem



Documentos relacionados
Once a high cloud is detected by ODS, its altitude and optical depth can be estimated by searching the optimal values of these parameters that provides the best fit between
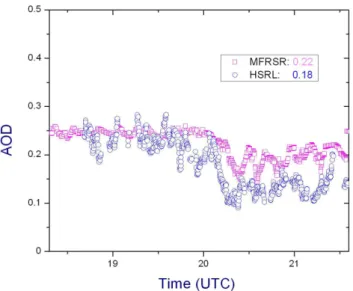
aerosol optical depth (AOD) of the atmosphere, acoustic sounding of the boundary layer, laser sensing of the aerosol content in the troposphere and stratosphere, mea- surement of
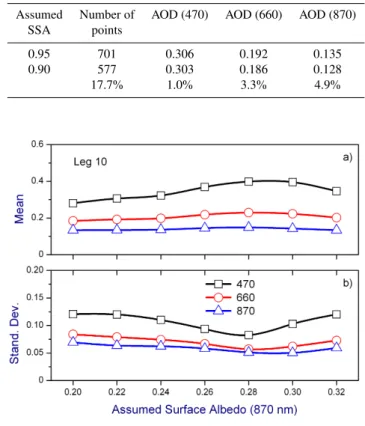
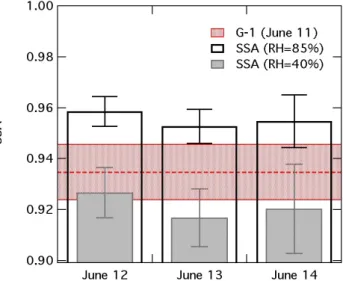
In this paper, numerous key uncertain factors in the retrieval of aerosol optical depth (AOD) are articulated for some widely used and relatively long satellite aerosol
Measurements of aerosol chemical composition and aerosol optical depth in the Nepal Himalaya have clearly shown the build up of aerosols in the pre-monsoon season during the winter
A multiple linear regression is performed to identify the dependence of α in cloudy scenes on cloud liquid water path (LWP) and aerosol optical depth (AOD), using the
this study, we take advantage of this well-calibrated set of measurements by applying a newly-developed aerosol optical depth (AOD) retrieval algorithm over land and ocean
The comparison of aerosol optical depth (AOD) from HAC against MODIS shows larger HAC AOD values over regions with higher aerosol loads and smaller HAC AOD values than MODIS for
Aerosol optical depth at 355 nm obtained from the Ra- man inversion is shown as a function of the optical depth from the elastic inversion for 4435 nighttime cloud-free 1 min