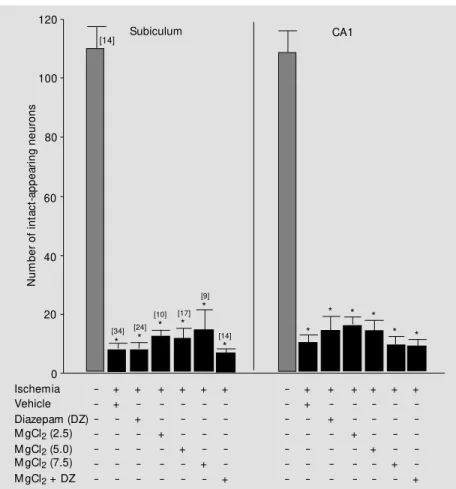
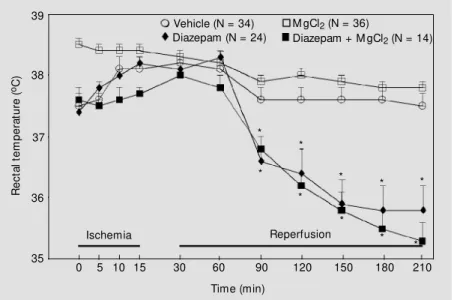
Magnesium chloride alone or in combination with diazepam fails to prevent hippocampal damage following transient forebrain ischemia
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
The present study, in which focal ischemia was in- duced without reperfusion, demonstrated no signiicant differences in ATP, MDA or caspase-3 levels between the right and left
GFAP versus S100B in serum after traumatic brain injury: relationship to brain damage and outcome. Piazza O, Storti MP, Cotena S, Stoppa F, Perrotta D, Esposito G
The results from animals reperfused after 10-min ischemia indicate that there is a rela- tionship between plasma oxidative damage and brain reperfusion when this injurious
In the present study, we demonstrated that post-injury treatment with CBD was able to decrease kidney oxidative damage and inlammation in an animal model of ischemia-
Tal circunstância, além de ser vista como penosa para os próprios AO’s (responsáveis pelo transporte e distribuição deste tipo de produtos pelas várias unidades do
This study was conducted to investigate the effect of Anchusa italica extract on hippocampal injury induced by transient global cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in the rat.. To
Evidence for cellular damage in normal-appearing white matter correlates with injury severity in patients following traumatic brain injury: A magnetic resonance spectroscopy
130 reported its neuroprotective effect in a model of focal ischemia with 70% xenon administration during ischemia induced by cerebral artery occlusion in rats and showed a