Different feeding habits influence the activity of digestive enzymes in freshwater fish
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
Com este trabalho pretende-se explorar a relação entre experiências de vitimação e bem-estar na infância e adolescência. Considerando que, a saúde mental não envolve apenas
Capitulo 6 Conclusão e Desenvolvimentos Futuros 6.1 Conclusão No presente estudo descrevem-se as características construtivas dos edifícios antigos - em particular das
The fermentation experiments for the simultaneous production of alkaline protease and alpha amylase from Bacillus subtilis were carried out in a laboratory scale 7.5 L
Com o presente trabalho pretende-se relacionar as medidas antropométricas com a idade e o sexo numa amostra representativa da população adulta Portuguesa proveniente do
A statistical approach for the enhanced production of alkaline protease showing fibrinolytic activity from a newly isolated Gram- negative Bacillus sp. Bafibrinase:
Compared with the native protease, the activity, pH ranges and thermostability of mutant protease was improved significantly, probably due to the modification of
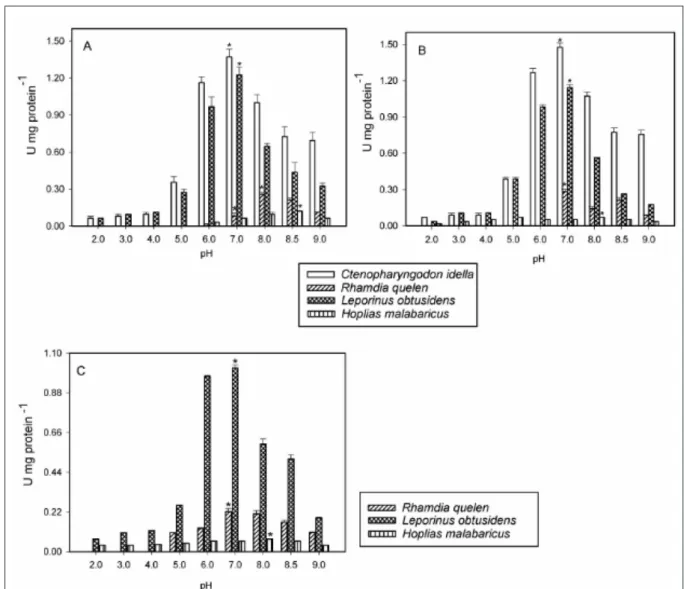
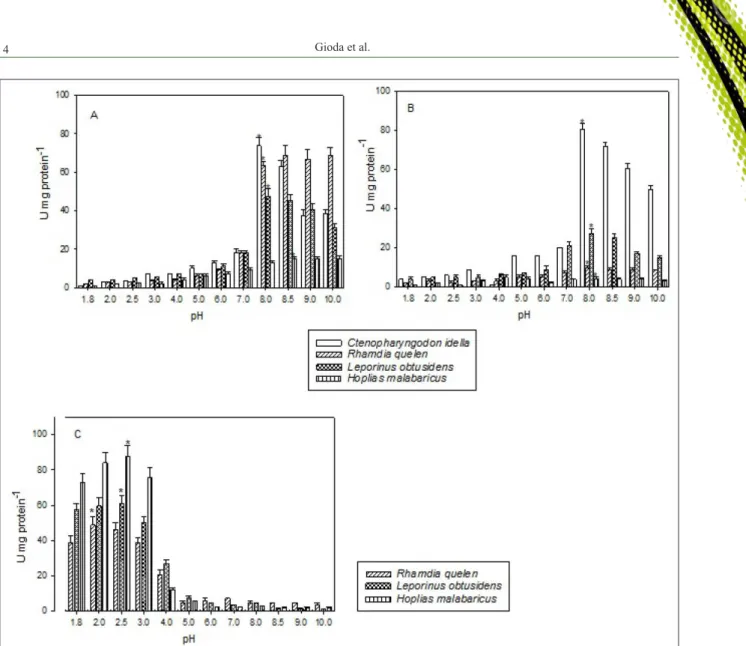
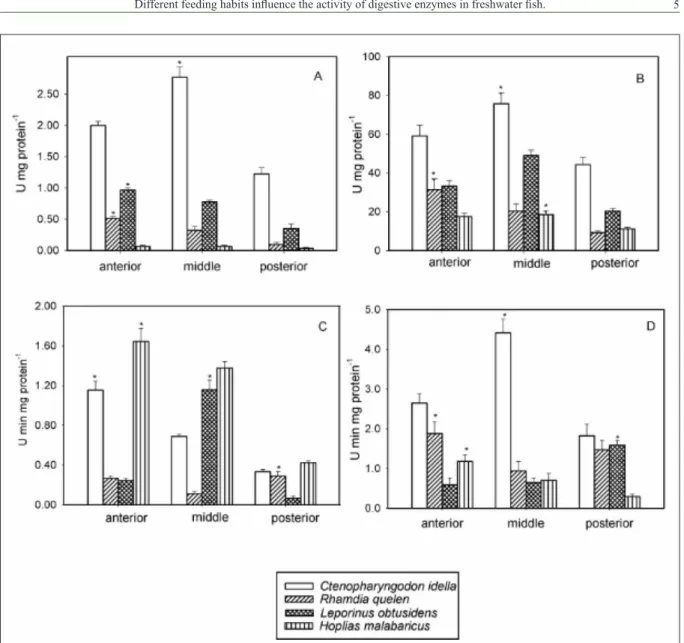
Differences in the development of the digestive system are related to different feeding habits among fish species, with functionality emerging at different stages of life,
probatocephalus , acid protease activity is lost at neutral and alkaline pH, this process is not reflected, where the loss of activity is compen - sated by the hydrolysis of