Adaptive Majority-based Re-routing for Differentiated Delay in Wireless Sensor Networks
Texto
Imagem
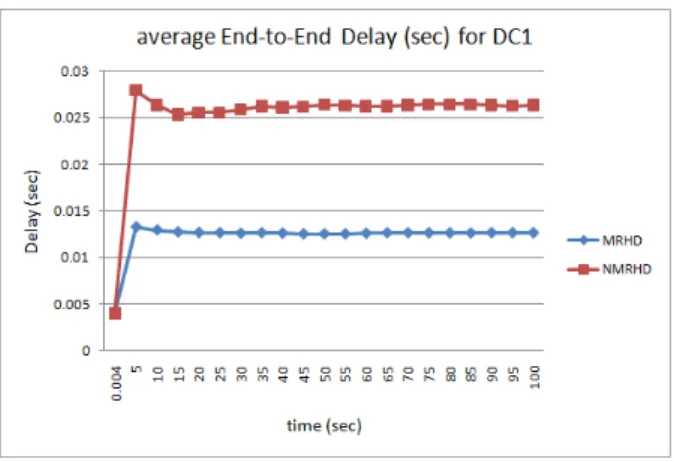
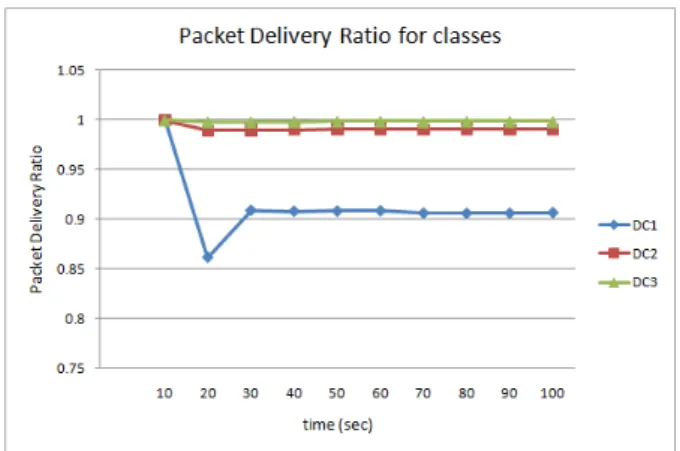
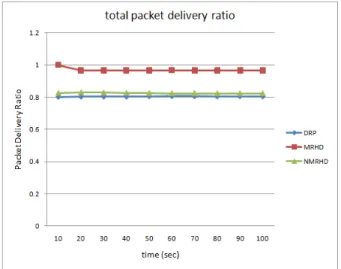
Documentos relacionados
In this paper, we will review the routing protocol in delay tolerant networks and compare the routing protocols that have been proposed specially for Vehicular Delay
Earlier on-demand routing protocols[3,4,5,6,7] were based on flooding the routing packets in all directions irrespective of the location of the destination node, resulting
The network life time of MIN-RC is broken down into a number of rounds, and each round starts with the setup phase, where each node sends its Id, location and current level of
This algorithm adjusts the cluster-head radius considering the residual energy and distance to the base station parameters of the sensor nodes.. This helps to
In this paper, we propose a model for the detection of denial of service attack in wireless networks using dominance based rough set. The proposed model is analyzed with the help of
Topology Based routing approach has Route instability, this is because an established route consists of a set of nodes between the source and the destination that are affected
Routing is the critical issue in the MANET and focus based on routing protocols such as Ad hoc On-demand Distance Routing Protocol (AODV), Dynamic Source Routing (DSR),
Key words: Delay tolerant networks, routing protocols, prioritization of messages, delivery ratio, delivery latency, epidemic routing, simulation results,