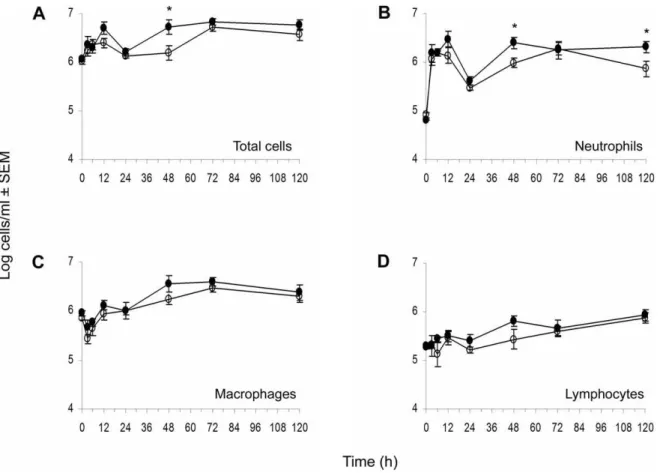
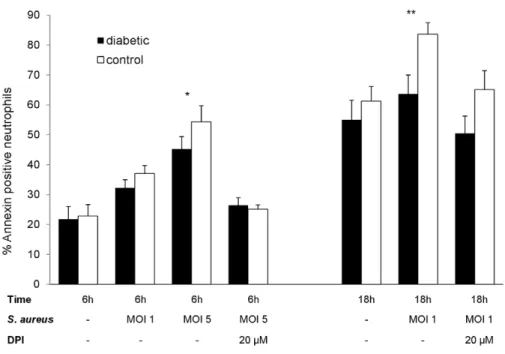
Reduced neutrophil apoptosis in diabetic mice during staphylococcal infection leads to prolonged Tnfα production and reduced neutrophil clearance.
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
In conclusion, SLE patients receiving immunosuppressive treatment presented with elevated systemic levels of IL-6 and IL-10, reduced neutrophil phagocytic capacity, and
Stem cell factor protects against neuronal apoptosis by activating AKT/ERK in diabetic
Spontaneous NBT levels, as well as spontaneous IFN- γγγγγ and TNF- αα αα α production, were significantly higher (p<0.001) in HTLV-1 infected subjects than in
No perfil fenólico de várias espécies da família Asteraceae, com relevância na flora portuguesa, foram identificados diversos compostos, entre os quais flavonoides
Macrophages from Schistosoma mansoni- infected mice showed depressed capacity to increase the phagocytosis in the presence of a high bacterial load, due to a reduced involvement
As shown in Figure 7, cholesterol and triglyceride levels in renal and hepatic tissues were markedly increased in diabetic db/db mice than non-diabetic db/m mice, and
Following infection with Leishmania major, T cell activation and apoptosis can be detected in draining lymph nodes of C57BL/6-infected mice.. We investigated the mechanisms involved
Probiotics fed, Giardia -infected mice, showed a significant increase in the levels of antioxidants (reduced glutathione and superoxide dismutase) and intestinal