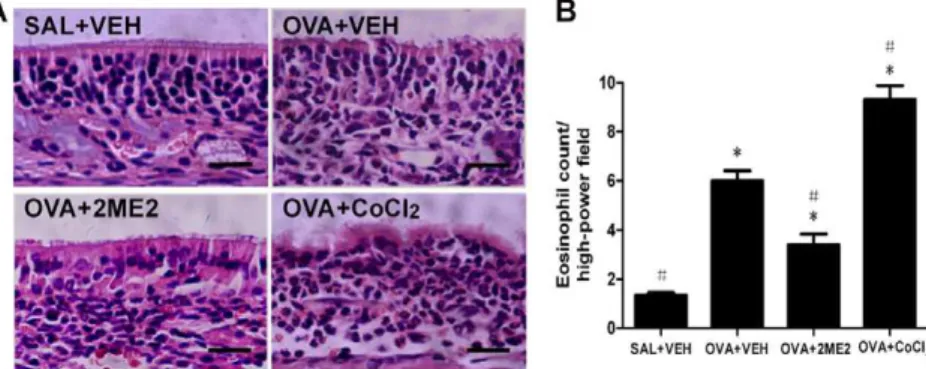
HIF-1α inhibition reduces nasal inflammation in a murine allergic rhinitis model.
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
An analytical expression is developed to define the critical angle for the case of single storey buildings and a special category of multi storey buildings under constant
HMGB1 has a role in the pathogenesis of chronic nasal mucosa in fl ammatory diseases such as allergic rhinitis, chronic rhino- sinusitis, and nasal polyposis. HMGB1 inhibition might
The volunteers were evaluated in terms of nasal patency, with a peak nasal inspiratory low (PNIF) meter, and obstruction symptoms, by a Nasal Obstruction Symptom Evaluation
Evaluation of treatment response in patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis using domiciliary nasal peak inspiratory flow. Clin
IgE-dependent cytokine generation by mast cells - Contrary to the inhibition of allergic airway inflammation observed when rmIL-10 was given by intra-nasal route, its
crassiceps NCC infection in C57BL/6 mice triggers an inflammatory response, a predominance of Th2 type in situ profile, with mononuclear inflammatory cell infiltration,
Conclusions: Single dose intravesical hyluronic acid instillation reduces inflammatory cell infiltration and the severity of bladder inflammation in the rat model of bladder
study, compared mucociliary clearance and the total score of nasal symptoms before and 10 min after the use of hyper- tonic versus 0.9% saline in 81 children with allergic rhinitis,