Responsiveness of glycogen breakdown to cyclic AMP in perfused liver from rats with insulin-induced hypoglycemia
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
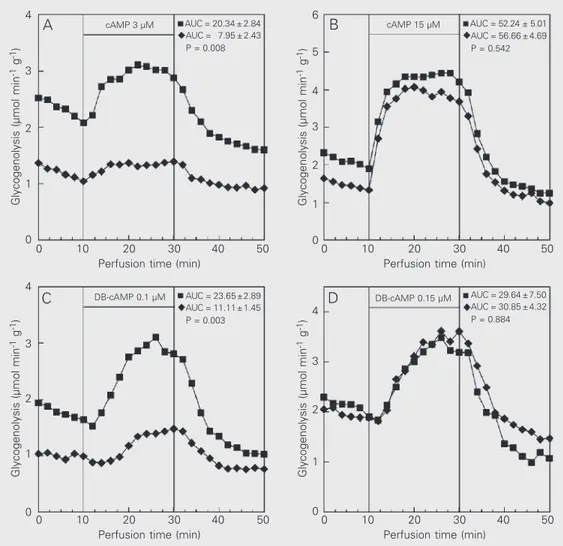
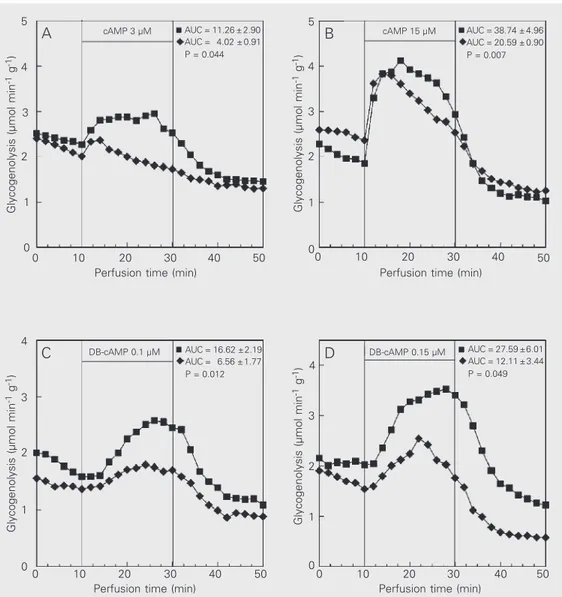
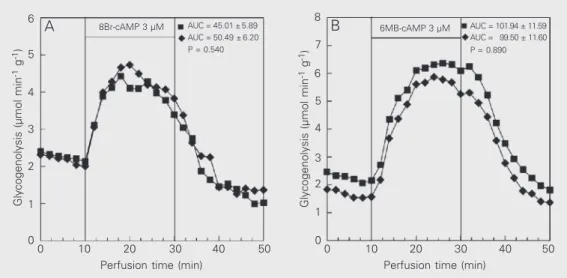
The data re- ported are the mean of 4 indi- vidual liver perfusion experi- ments performed 120 min after injection of saline (CN group, squares) or insulin (IN group, dia-
Consequences of cerebroventricular insulin injection on renal sodium handling in rats: effect of inhibition of central nitric oxide
To explore the effect of exendin-4 on macrophage- secreted in fl ammatory cytokines mediated insulin resistance, we tested the insulin-stimulated glucose uptake using 3T3- L1
concentration of 50 nM insulin showed maximum up regulation of mRNA expression of G6Pase and PEPCK, and the 150nM insulin treatment group has the strongest effect on the increase
Starting with L-alanine and L-lactate that entered in the gluconeogenic pathway at pyruvate step, the present results suggested that the treatment with glucose
The intramuscular injection of Epi caused significant elevation in blood sugar level, while liver glycogen and insulin were decreased as compared to the control
Streptozotocin treatment (150 mg/kg body weight) induced the decrease of GSH level, antioxidant enzymes activities, glycogen content in liver, HDL-C content and