Human Mixed Infections of Leishmania spp. and Leishmania- Trypanosoma cruzi in a Sub Andean Bolivian Area: Identification by Polymerase Chain Reactionhybridization and Isoenzyme
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
Proteins (kDa) recognized by immunoblotting in serum samples of six groups of patients using antigens of Leishmania (Leishmania) amazonensis (A) and Leishmania (Viannia)
and drimane sesquiterpenes isolated from the stem bark against strains of Leishmania amazonensis and Leishmania braziliensis promastigotes and Plasmodium falciparum
In 2005, draft sequences of the genomes of Trypanosoma brucei, Trypanosoma cruzi and Leishmania major, also known as the Tri-Tryp genomes, were published.. These protozoan parasites
Nesse contexto, o presente trabalho teve o objetivo de estudar o potencial de reúso de águas residuárias de laboratórios de análises químicas, para fins não potáveis, no
Ocular conditions, anti- Leishmania antibodies and total protein of the aqueous humor were studied in dogs naturally infected by Leishmania ( Leishmania ) chagasi.. Fifty dogs
and Leishmania (Leishmania) infantum in horses from a VL endemic area in the state of São Paulo, Brazil by PCR on DNA extracted from blood samples and conjunctival swab (CS) and
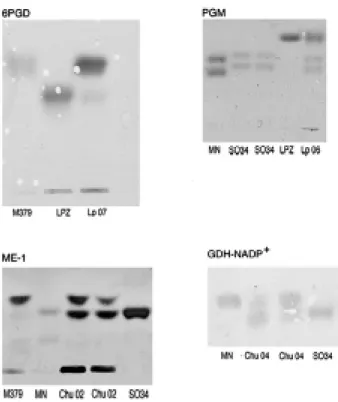
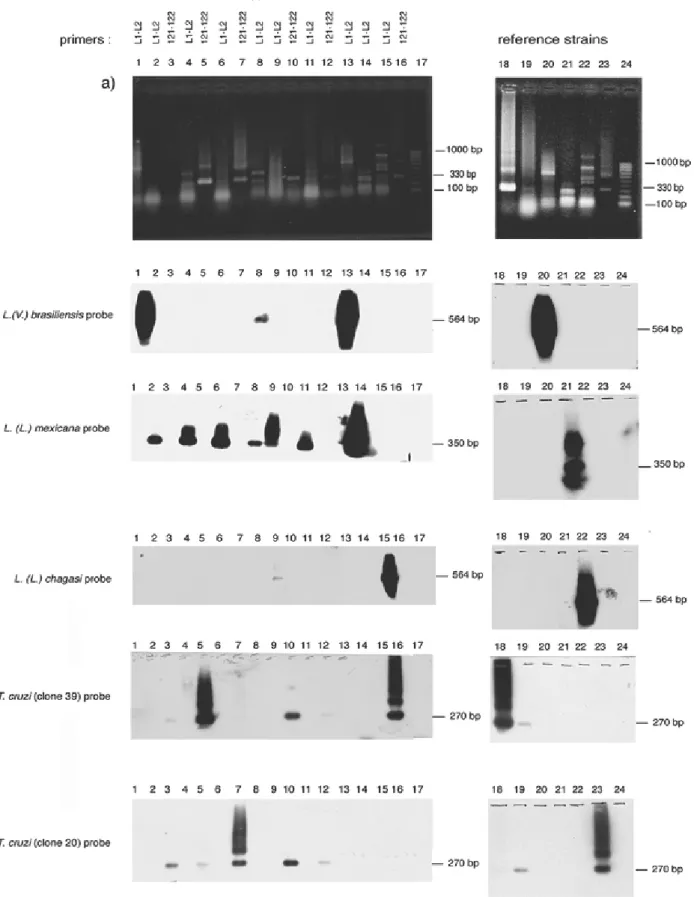
Identification of Leishmania was carried out by the analysis of amplified DNA with specific primers belonging to the Leishmania subgenus and by dot blot positive hybridisation
Activity of cinnamic acid analogs against Leishmania spp., Trypanosoma cruzi , and Plasmodium falciparum was evaluated in the interest of identifying new