Comparative analysis of the tissue inflammatory response in human cutaneous and disseminated leishmaniasis
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
A case-control study was conducted to examine the association among the Montenegro skin test (MST), age of skin lesion and therapeutic response in patients with cutaneous
In this study we review the clinical and epidemiological characteristics of the patients with diagnosis of cutaneous anthrax evaluated between 1969 and 2002 at the Hospital
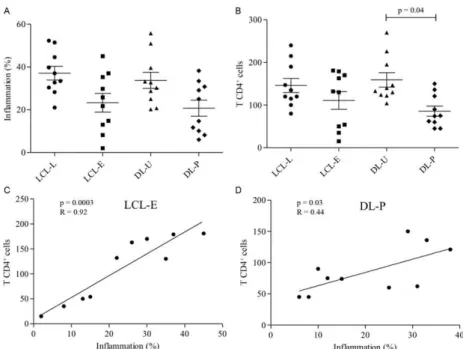
2: frequency of cytokine and iNOS producing cells in lesions from localized cutaneous leishmaniasis (LCL) and disseminated cu- taneous leishmaniasis (DL) patients. Mean is indicated
Therefore, we evaluated the expression of the chemokines CXCL10, CCL4, CCL8, CCL11 and CXCL8 and the chemokine receptors CCR3, CXCR3, CCR5 and CCR7 in the lesions of patients
In the present study, we evaluated the clinical characteristics and response to treatment with corticosteroids in adult patients with proteinuria and histological diagnosis of MCD
patients were evaluated, divided into groups of patients with different techniques of kinesiothera- py, TENS and Ultrasound. )t was observed that, at the end of the treatment,
The sample was divided in two groups according to the clinical presentation of the lesions: patients with exclusively reticular lesions (white lesions), and pa- tients
Although the analysis of the systolic wave on Doppler tissue imaging enabled the discrimination of patients in groups 1 and 3 and in groups 2 and 3 (chagasic patients with and