Dental Press J. Orthod. vol.16 número6 en a17v16n6
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
These include embryonic stem cells, pancreas- derived multipotent precursors, pancreatic ductal cells, hematopoietic stem cells, mesenchymal stem cells, hepatic oval cells, and
Increased proliferation of human synovial mesen- chymal stem cells with autologous human serum: compari- sons with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and with fetal bovine serum.
O objetivo do presente estudo foi realizado com o pressuposto de determinar a relação entre o rendimento académico (reprovação escolar) e o consumo de substâncias tóxicas
Transplantation of Bone Marrow – Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improves Diabetic Polyneuropathy in Rats.. Transplantation of Bone Marrow-Derived Mononuclear Cells Improves
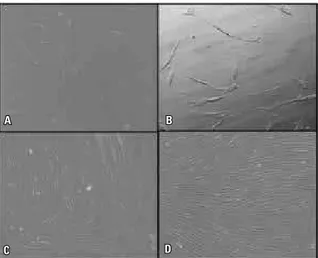
In another work, the feasibility of dental pulp from deciduous teeth as an eventual source of stem cells for pulpal tissue engineering has been studied.. 4 Mesenchymal stem
COSTA (2000) trabalhou com 3 doses de nitrogênio na semeadura (30, 60 e 90 kg ha -1 de N) e 3 doses de nitrogênio em cobertura (30, 60 e 90 kg ha -1 de N) na cultura do milho
In this context, the objective of this study was to evaluate in vitro resistance of Enterococcus faecium (ATCC 8459) and Lactobacillus helveticus (ATCC 15009) against
A new population of human adult dental pulp stem cells: a useful source of living autologous fibrous bone tissue (LAB). A three-dimensional nanofibrous scaffold for