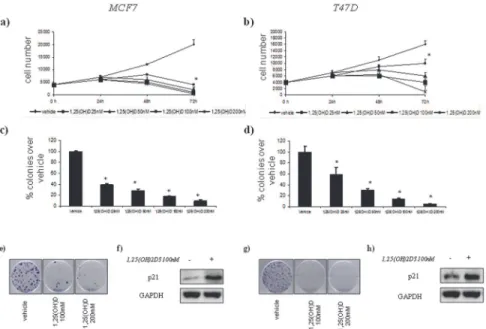
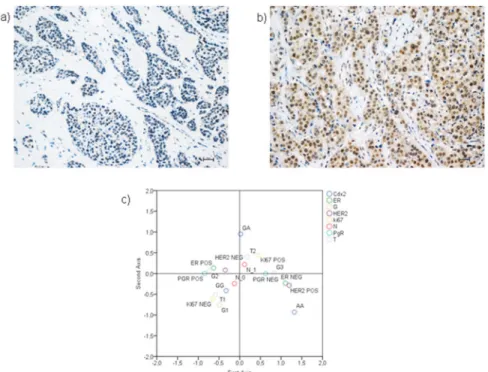
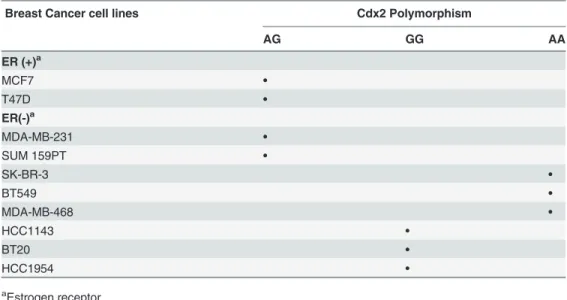
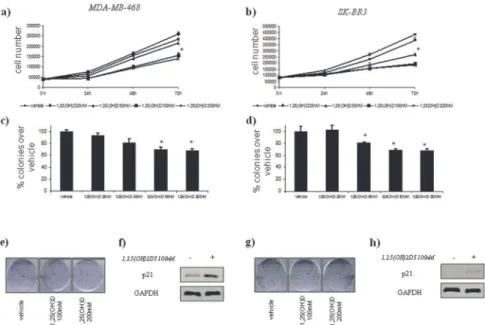
Cdx2 polymorphism affects the activities of vitamin D receptor in human breast cancer cell lines and human breast carcinomas.
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
These variables were used in the construction of the combined index STAN; STAN responded adequately to noxious stimuli, with a more pronounced response to
Assim, utilizando uma amostra de conveniência, foram constituídos 12 grupos focais: profissionais da Saúde (com seis pessoas de diferentes serviços de saúde e com distintas
Our findings indicate that Brb and Dox, alone and in combination, exhibit antiproliferative effects against human breast cancer T47D and MCF7 cell lines, and this
Phase 2 randomized trial of primary endocrine therapy versus chemo- therapy in postmenopausal patients with estrogen receptor- positive breast cancer. Chemotherapy (CT)
Sendo assim, é melhor tirar as fantasias do armário, decorar o sambaenredo da escola favorita e cair na folia, esperando que 2015 não traga mais surpresas ne gativas para o
Influence of estradiol and triiodothyronine on breast cancer cell lines proliferation and expression of estrogen and thyroid hormone receptors.. Efeito do estradiol e
The objective of this study was to evaluate the expression of basal biomarkers such as p63, p-cadherin and CK5, as well as estrogen re- ceptor (ER) and Human Epidermal Receptor
Grow th inhibition of both M CF- 7 and Hs578T human breast cancer cell lines by vitamin D analogues is associated w ith increased expression of insulin-like.. grow th factor