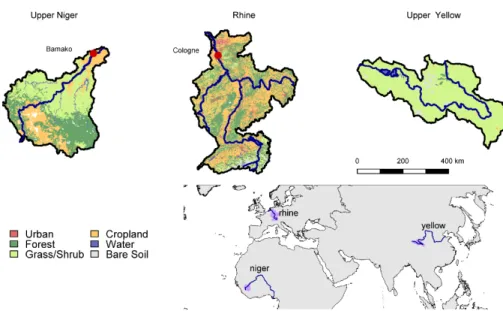
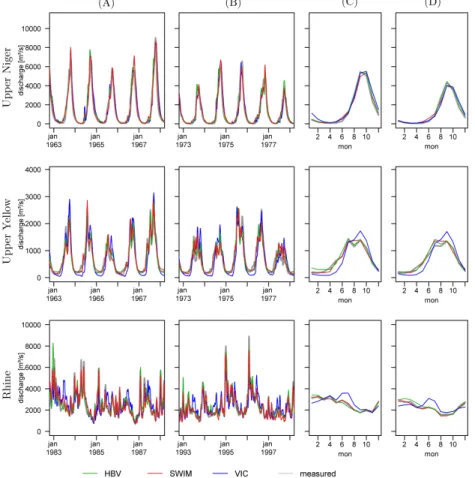
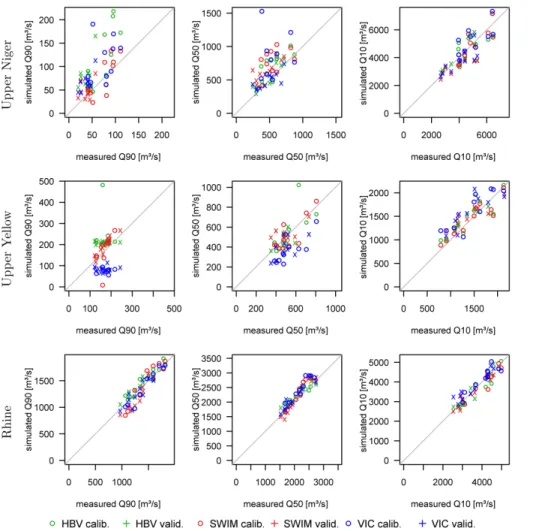
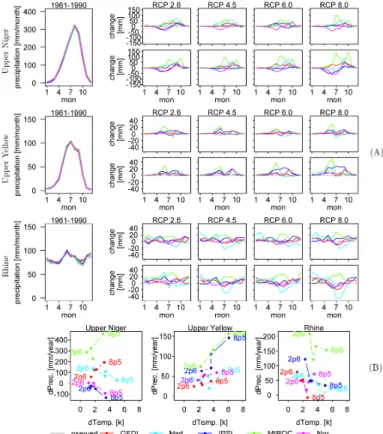
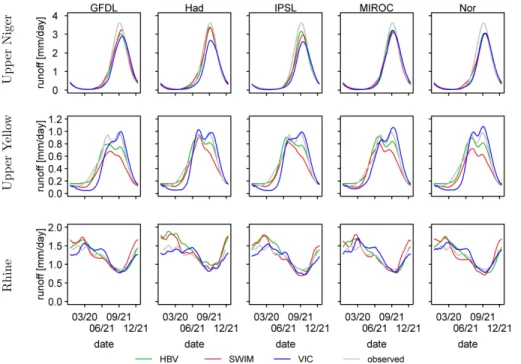
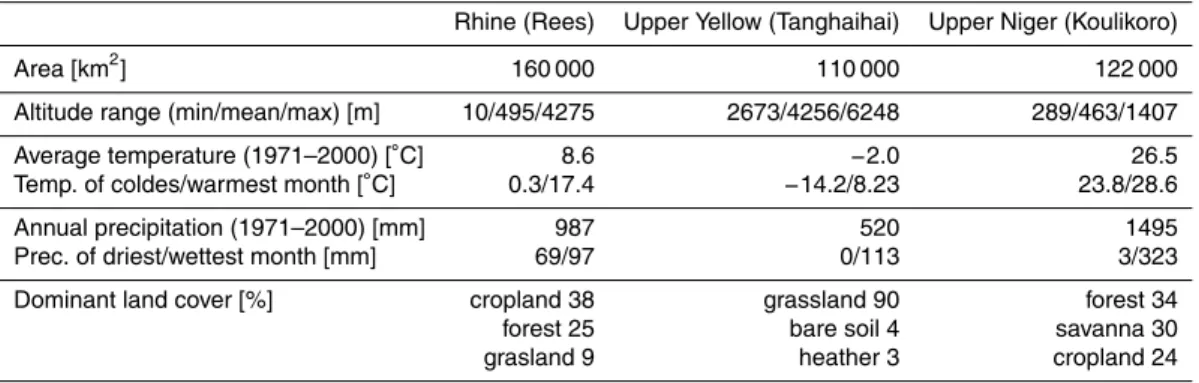
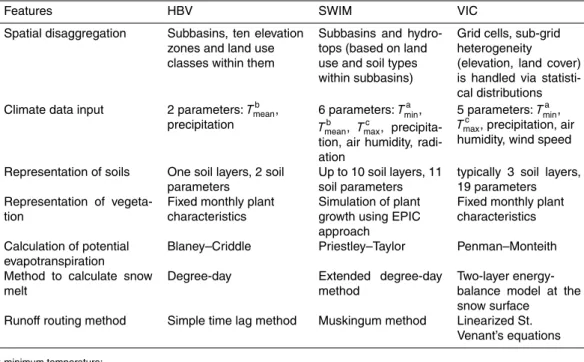
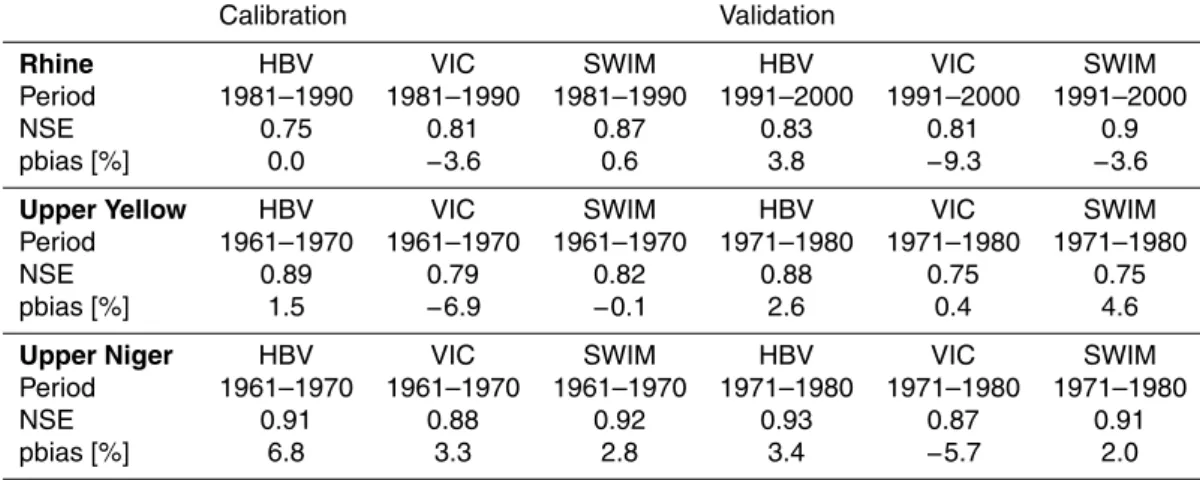
Multi-model climate impact assessment and intercomparison for three large-scale river basins on three continents
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
An increase in the number of consecutive dry days and in the maximum 5-day precipitation amount in the region of the Tibetan Plateau for the monsoon season, as well as large
This study presents an analysis of the long-term evolution of two denudational escarpments, the Cristiano Otoni and the São Geraldo steps, which divide the river basins of the
Firms with older and more experienced CEOs have, on average, lower variability of firm.. performance, as measured by the standard deviations of the firm
We tested the contribution of the phylogenetic and specific components to the ecomorphological structure of stream fish from the upper Paraguai River and upper São Francisco
Consequently, the methodology used to analyze the dynamics of land use and occupation in the upper Teles Pires River basin was appropriate, and could make a viable
At the first stage of the measurements results analysis, the gear wheel cast surface image was compared with the casting mould 3D-CAD model (fig.. Next, the measurements results
the Schoof (2007) results, an intercomparison e ff ort compared the behaviour of the GL evolution on a flowline of 26 di ff erent models, as part of the Marine Ice Sheet
Furthermore we analyse the separate impact of changes in stomatal conductance, leaf area index and vegetation dynamics on climate and we find that di ff erent