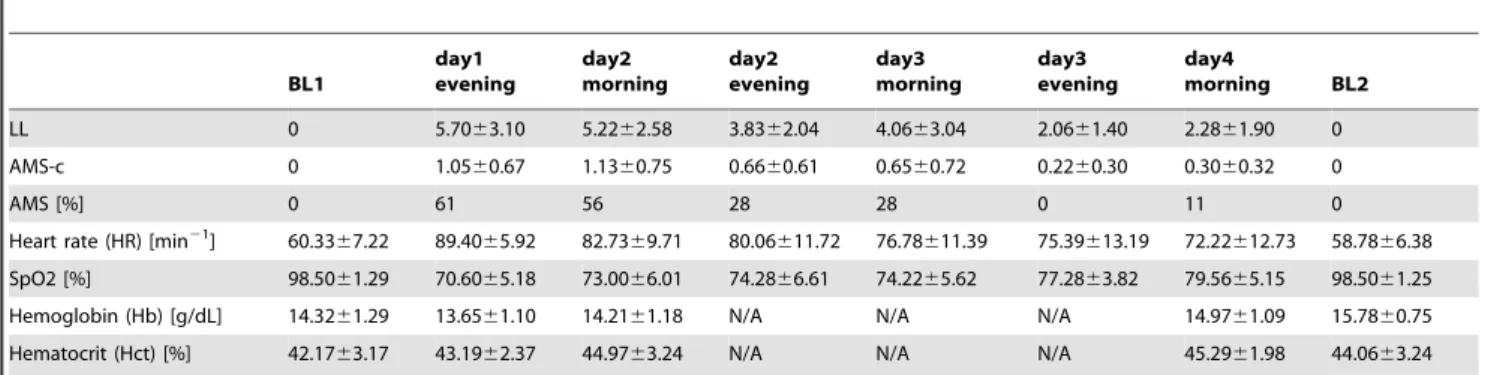
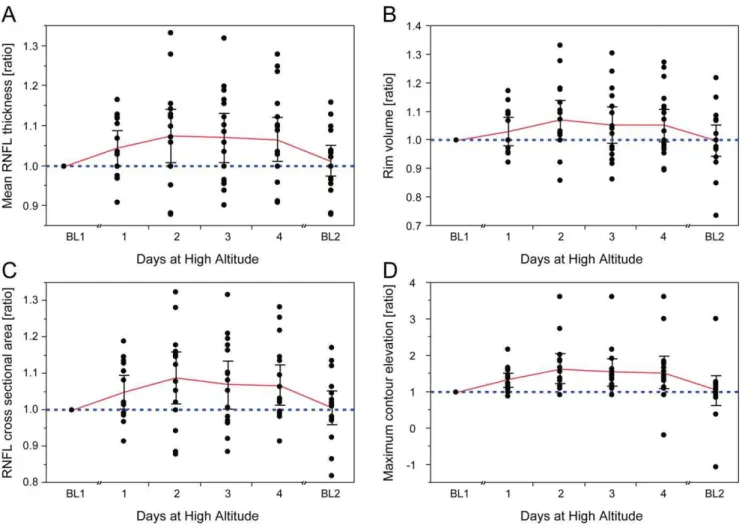
Quantification of optic disc edema during exposure to high altitude shows no correlation to acute mountain sickness.
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
(1996) found significantly higher numbers of globule leucocytes/mucosal mast cells in the intestinal mucosa in resistant than in susceptible lambs that were naturally infected
Objective: To demonstrate the prevalence of stress hyperglycemia in a cohort of patients with acute coronary syndrome and to determine the correlation of stress hyperglycemia
The purpose of this study is therefore to evaluate the optic disc area of patients with NA-AION or A-AION and in normal controls in order to define whether optic disc areas tend to
Thus, our study shows that the tendency to produce greater mea- surements in normal eyes and to some extent in eyes with reduced RNFL is not uniform but appears to be dependent on
Purpose: This study was performed to evaluate the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) and peripapillary choroidal thickness in eyes with tilted optic disc in order to
There was no correlation among the presence of visual symptoms, the mean interocular retinal layer thicknesses and volumes (inner and outer, parafoveal and perifoveal), the
Partial correlation analysis to investigate the relationships among anterior segment and optic nerve head parameters, controlling for age and optic DA, showed that corneal
Variables – For correlation with patients’ evolution, in addition to gender, age and left ventricular ejection fraction, the following pre-operative characteristics were