Chiseling and gypsum application affecting soil physical attributes, root growth and soybean yield
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
The lack of effect of gypsum on the leaf content of these nutrients reflected their behavior in the soil since they were not affected by gypsum application rates in any of the
Contents of water-soluble nutrients and electrical conductivity (EC) in the white oat extract at flowering as related to application or non-application of gypsum to the soil surface
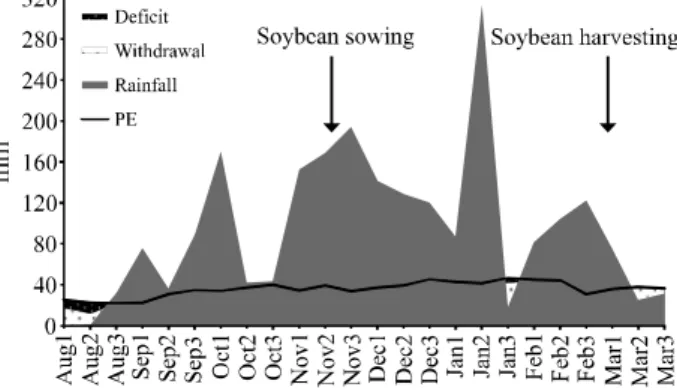
Soybean and wheat grain yield as related to soil penetration resistance at a matric potential of -33 kPa in the 0.10-0.20 m layer under the tillage systems: CT- conventional
Root length (A), root volume (B) and root fresh mass (C) of soybean plants, depending on the application form and concentration of manipueira, in the management of
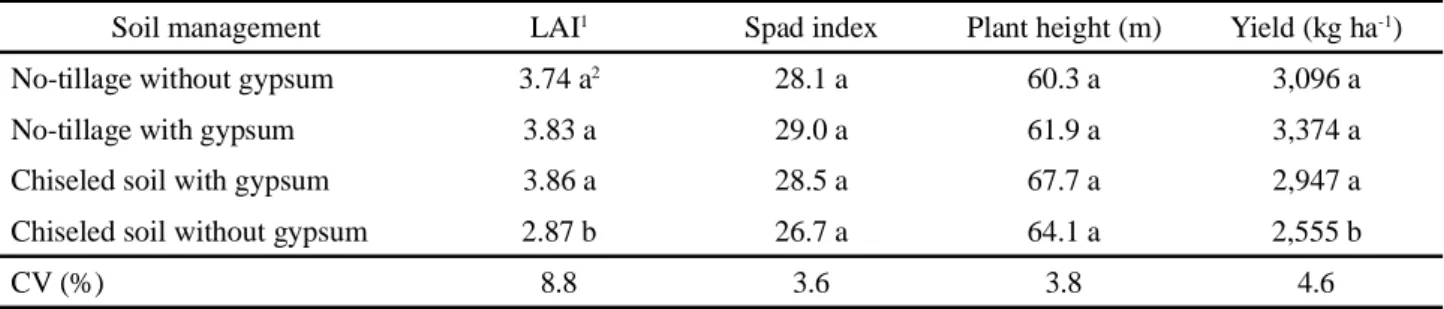
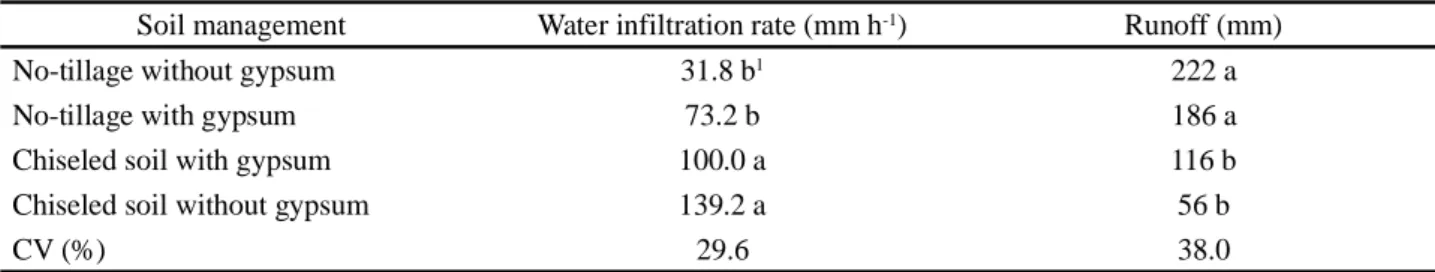
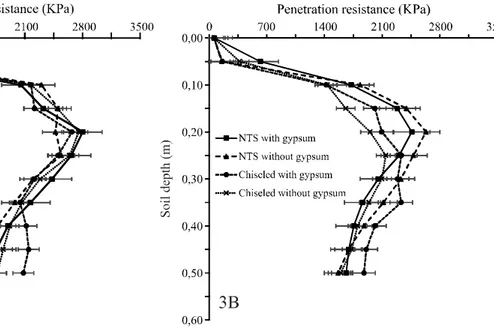
Soil chisel plowing reduced plant stand and soil resistance to penetration, enabling higher soybean plant growth and
Table 2 - Ryegrass dry mass and soybean plant population, number of pods per plantk, number of grains per plant, grain productivity, aerial part length (APL), root system
The application of both acidity-correcting materials increased N, Ca and Mg leaf concentrations, and all yield components and grain yield in soybean; but in maize, just silicate
(2007) used a mixture of sulfur inoculated with Acidithiobacillus and gypsum in equal proportions and observed excellent results in the attributes of the soil; however, the