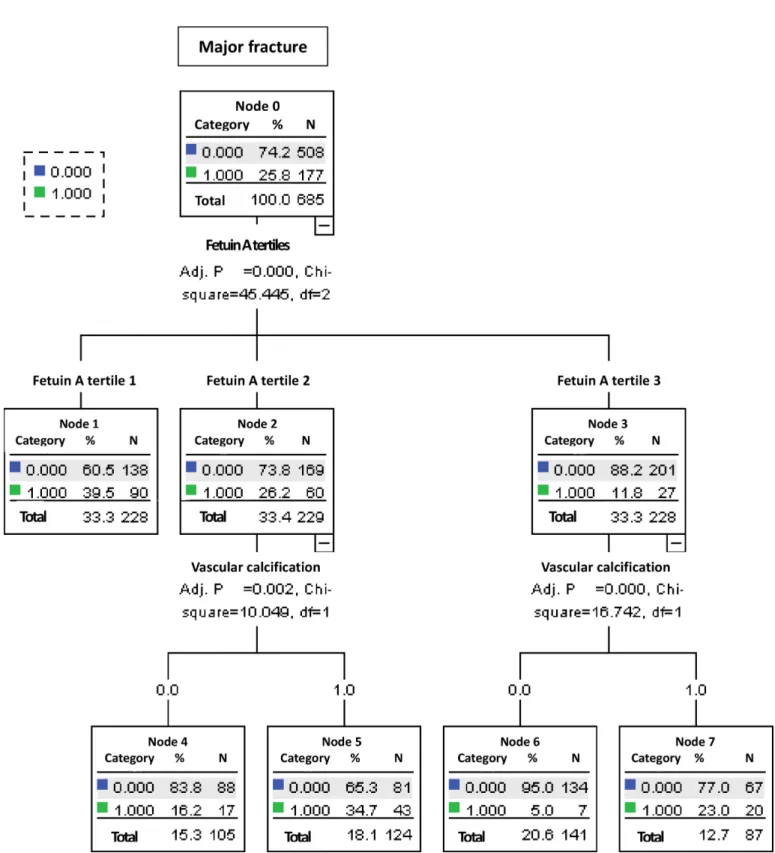
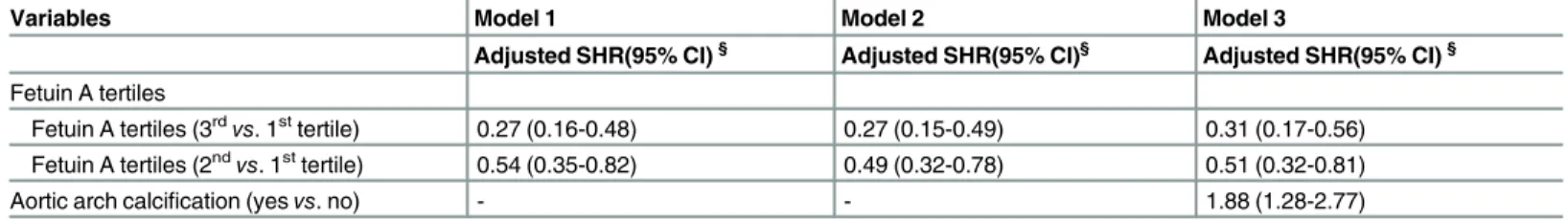
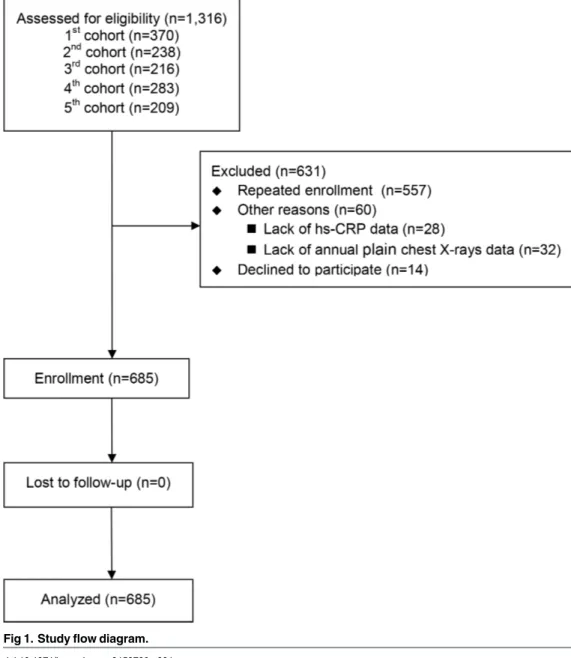
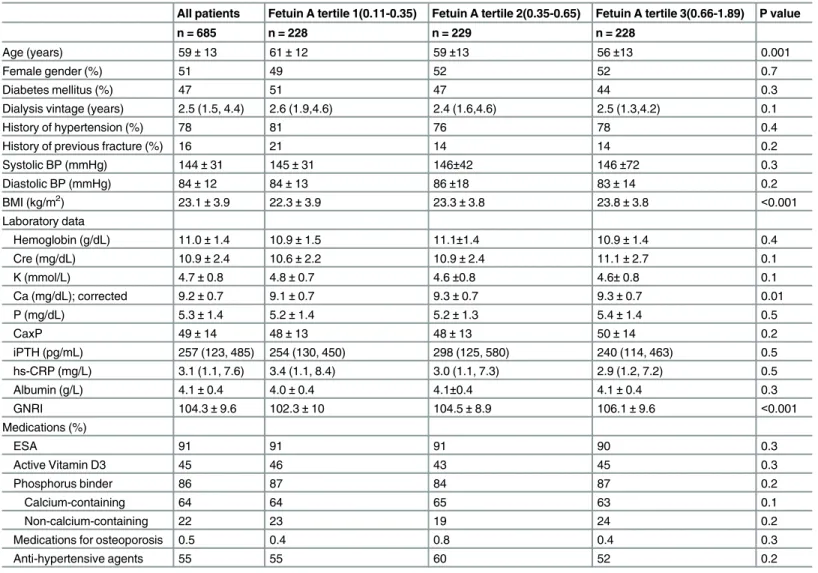
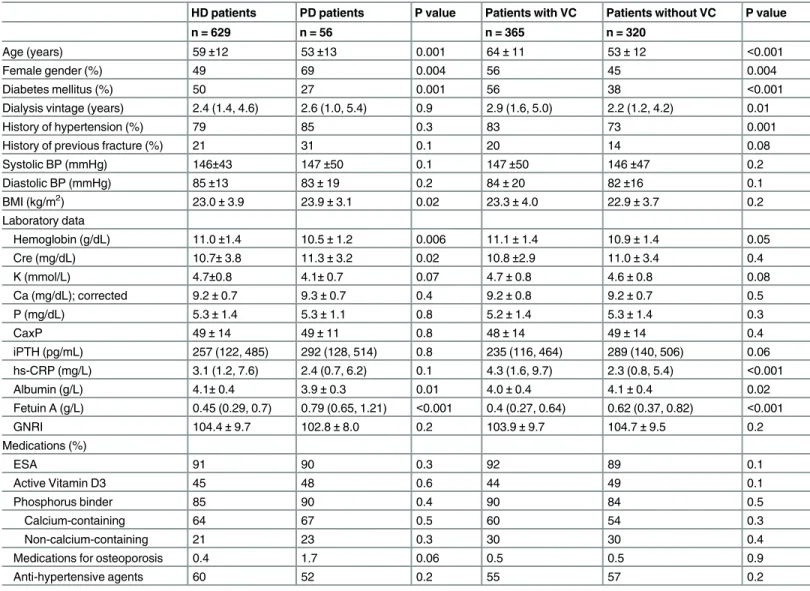
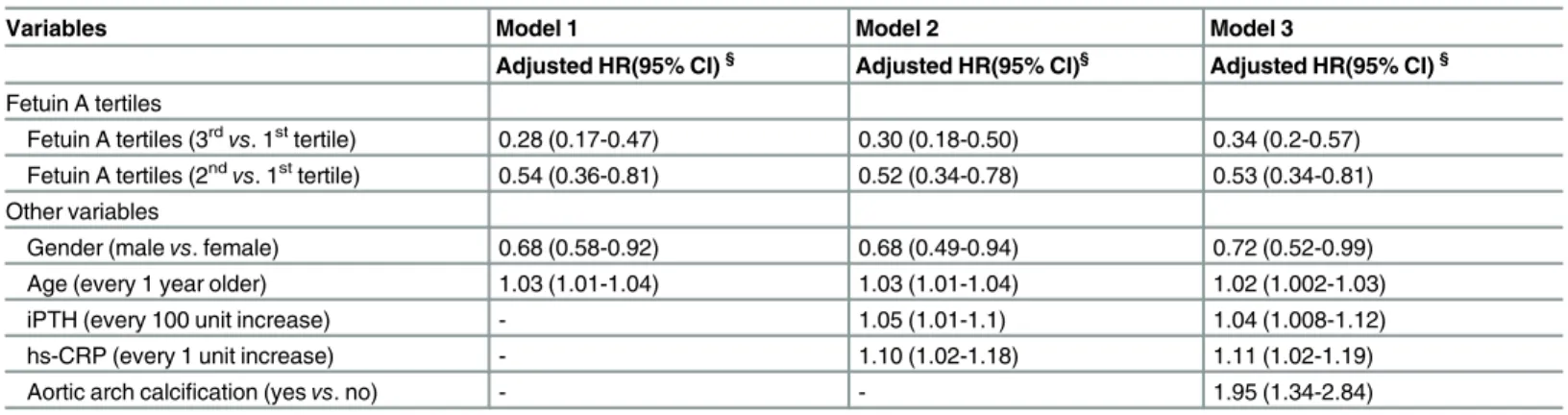
Relationship between Fetuin A, Vascular Calcification and Fracture Risk in Dialysis Patients.
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
The increased levels of D-dimer and tPA in CRF patients, particularly in those using central venous dialysis catheters, led us to propose a relationship between the type of
Background: In patients with type 2 diabetes, the presence of retinopathy is associated with increased cardiovascular disease, regardless of known risk factors for vascular
Como já referimos, esta investigação centra-se na análise da prática emergente de dois contextos formativos distintos: formação contínua e inicial de
The main finding of this study was that chronic re- nal failure patients on hemodialysis had lower muscle thickness of the pectoralis major and rectus abdomi- nis. Compared to
Body size and longitudinal body weight changes do not increase mortality in incident peritoneal dialysis patients of the Brazilian peritoneal dialysis multicenter study.. Overweight
Acampa et al demonstrated that patients with a negative scintigraphy for ischemia had a lower risk of heart events in the long term than patients who presented ischemia,
This study shown that serum TSH level was associated with risk of stenosis, detected during the CA, especially for patients with older age, higher levels of HbA1c and presence
In the present study, patients treated with radial approach for coronary procedures had lower baseline risk of bleeding as compared with the femoral access group.. This