Hydrocarbon Pneumonitis; Clinical and Radiological Variability
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
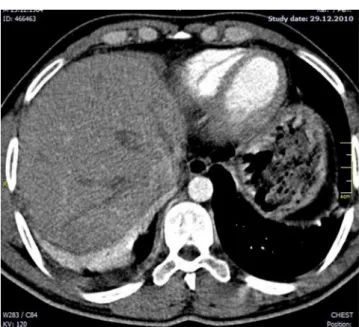
Figure 2 - A) Computed tomography scan of the chest showing free bilateral pleural effusion, greater on the right and atelectasis by compression of the lower lobes, greater on
At that point, the patient was submitted to a computed tomography scan of the chest, which revealed that the areas of consolidation, although smaller in size, persisted in both
A computed tomography scan of the chest revealed atelectasis of the right upper lobe (caused by occlusion of the upper lobe bronchus) that extended up to the juxtacarinal portion of
Figure 2 - Computed tomography scan of the chest showing an extensive mediastinal lesion (arrow) in contact with the right tracheal wall and causing anterior deviation
Computed tomography of the chest revealed consolidation with interposed cavitation in the right upper lobe.. Fiberoptic bronchoscopy revealed purulent fluid within
Figure 4 - In A, chest X-ray showing bilateral pleural opacities and enlargement of the cardiac silhouette; in B, chest CT scan showing an opacity in the left lower
In B, a chest CT scan taken prior to treatment with itraconazole showing an opacity with a ground-glass halo in the right upper lobe.. In C, a Cladosporium cladosporioides colony
A chest CT showed branching opacities, which characterize the tree-in-bud (TIB) pattern, in the middle lobe and the left lower lobe, as well as left lung volume reduction