Prostate Cancer: The Role of Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Texto
Imagem



Documentos relacionados
Conclusions: Pre-biopsy pelvic phased array dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging is an accurate technique for detecting and quantifying intracapsular transition
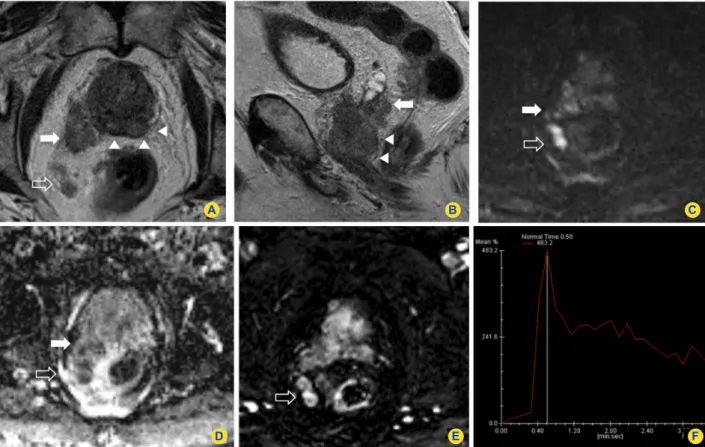
magnetic resonance imaging studies are of value for adequate characterization of local recurrence of prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy. Recurrent prostate cancer appears
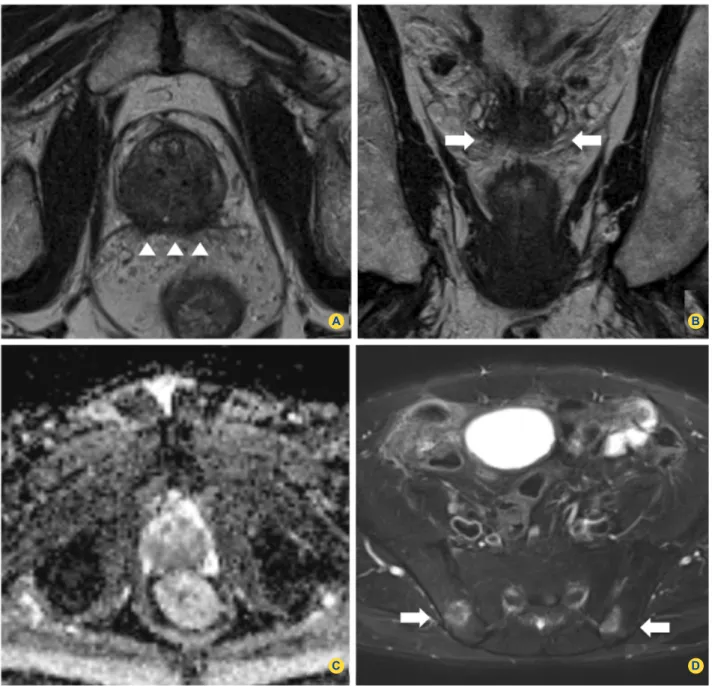
Purpose: To retrospectively determine the accuracy of diffusion-weighted (DW) magnetic resonance (MR) imaging for identifying cancer in the prostate peripheral zone (PZ)
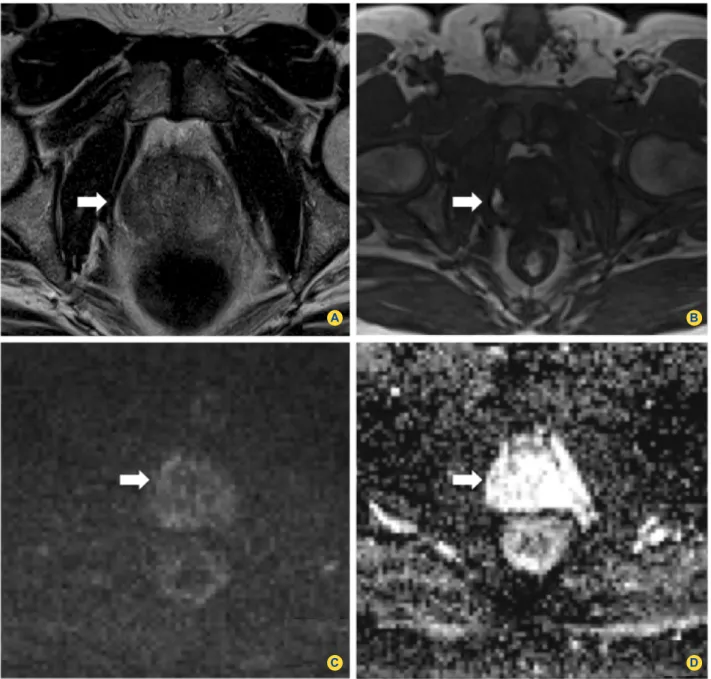
Purpose: To assess the diagnostic accuracy of endorectal magnetic resonance (MR) imaging and MR spectro- scopic imaging for prediction of the pathologic stage of prostate cancer and
The electronic medical records were searched for all contrast material-enhanced magnetic resonance (MR) imaging exami- nations performed during the post-guidelines adoption
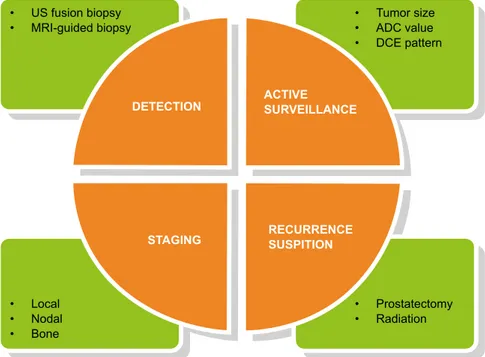
Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging guided diagnostic biopsy detects significant prostate cancer and could reduce unnecessary biopsies and over detection: a prospective
The predictive value of endorectal 3 Tesla multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for extraprostatic extension in patients with low, intermediate and high risk prostate
Magnetic resonance imaging: dynamic contrast enhancement and diffusion-weighted imaging to identify malignant cervical lymph nodes..