A qualitative comparison of secondary organic aerosol yields and composition from ozonolysis of monoterpenes at varying concentrations of NO<sub>2</sub>
Texto
Imagem



Documentos relacionados
(The Alternative Trading System operated by Bond Spot was launched six months following the opening of Catalyst, i.e. on 11 January 2013).The architecture of
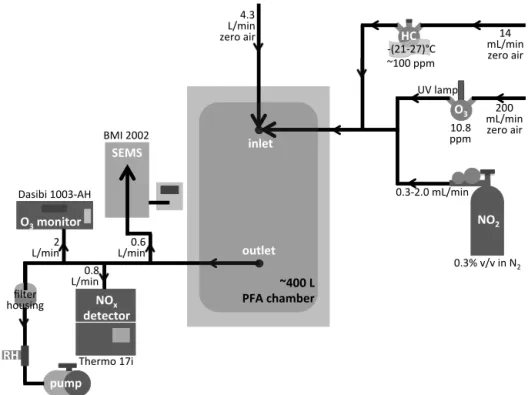
A wide range of smog chamber results obtained at various conditions (low/high NO x , presence/absence of UV radia- tion, dry/humid conditions, and temperatures ranging from 15–40 ◦
In an e ff ort to retrieve the m r s of SOA closely resembling ambient aerosol, this work explores the e ff ect of parent hydrocarbon ( α -pinene, limonene and toluene) and
T.: Particle mass yield in secondary organic aerosol formed by the dark ozonolysis of alpha-pinene, Atmos. T.: Loading-dependent
Aerosol mass loading was calculated from the FMPS measurements by applying the determined aerosol density after taking into account the aerosol deposition on the chamber wall
Time traces of aerosol volume as a result of SOA growth from OH oxidation of α -pinene followed by injection of ammo- nium sulfate seed (black) or ammonium sulfate and sulfuric
a smaller diameter for longer times, more particles are lost to the wall before and during SOA growth in ∼ 10 ppbv initial alkane experiments than in those with 60–80 ppbv
The known chemistry of the monoterpenes and their measured abundance of 0.4–27.9 % of non-methane organic compounds (NMOCs) and ∼ 21 % of organic aerosol (mass basis) suggests that
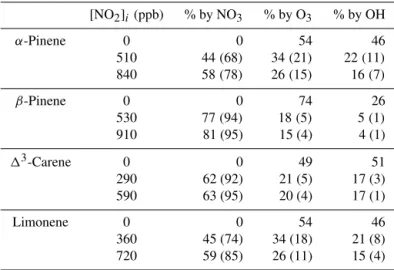




![Table 5. Minimum [NO 2 ] / [BVOC] value reported for each monoterpene studied at which NO 3 is expected to dominate night-time oxidation.](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_br/18271471.344557/12.918.163.356.161.269/table-minimum-reported-monoterpene-studied-expected-dominate-oxidation.webp)