Involvement of the caudal raphe nuclei in the feeding behavior of rats
Texto
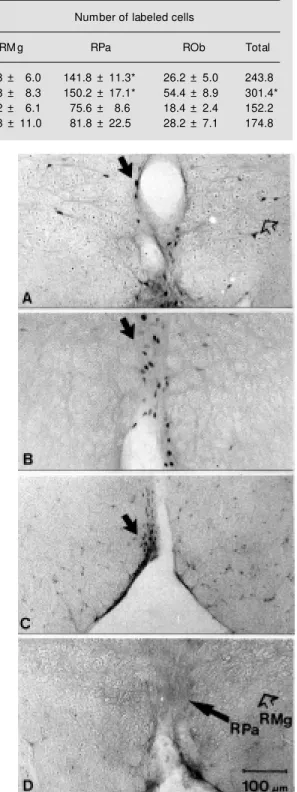
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
Although these animals have a relatively simple buccal apparatus, they demonstrate various different types of feeding behavior (capture by suction, mandibular apprehension,
Regularity of cell discharge during quiet waking was determined by calculating the interspike interval coefficient of variation (standard deviation/mean). 3) Neuronal dis- charge
a) Number of spikes per 10 s, digastric muscle rectified and integrated activity (over 10 s) and masseter muscle rectified and inte- grated activity (over 10 s) were calculated for 60
Effect on mean arterial blood pressure (M AP; panel A) and heart rate (HR; panel B) of bilateral microinjections of cere- brospinal fluid (CSF, 200 nl) or kynurenic acid (Kyn, 2.7
5-HT 1A autoreceptor modulation of locomotor activity induced by nitric oxide in the rat dorsal raphe
Effect of dietary capto- pril treatment (1 mg/g of food) on chronic ingestion of 0.3 M NaCl (A) and water (B) by rats with excitotoxic lesion of the dorsal raphe nucleus produced
Microinjections of L-glutamate (0.18 M, 50-100 nl with 1% Pontamine Sky Blue) were performed within the DRN or the MRN with glass micropipettes. At the end of the experiments the
ebellar form, MSA-C, usually causes pontocerebellar atro- phy and a “hot cross bun” sign in the pons, due to selective loss of myelinated transverse pontocerebellar fibers and