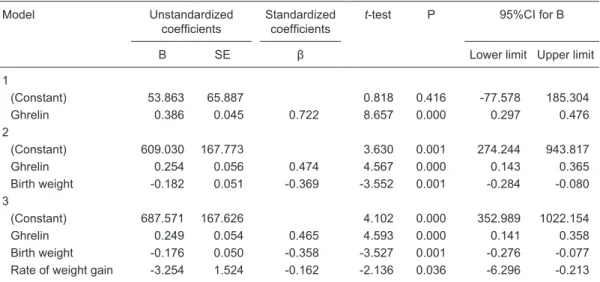
Correlations of circulating peptide YY and ghrelin with body weight, rate of weight gain, and time required to achieve the recommended daily intake in preterm infants
Texto
Imagem



Documentos relacionados
Photoperiods affect the variables weight gain, feed intake, feed conversion, total and standard length, height, specific growth rate, protein efficiency ratio and daily weight
BP - blood plasma; YE - yeast extract; W21 - initial weight; W35 - final weight; DFI - daily feed intake; DWG - daily weight gain; FCR - feed conversion rate; CV - coefficient
Soybean in the diet resulted in poorer animal performance for final weight, total weight gain and daily weight gain, empty body weight, feed conversion, carcass compactness, and hot
Average daily gain, stocking rate, live weight gain per hectare, body weight, body condition score, weight-to-height ratio and reproductive tract score of the heifers kept on
Inclusion of increased levels of SPC in pre-starter and starter diets did not affect the final body weight, body weight gain, feed intake, feed conversion ratio and viability
In a prospective randomized study involving 170 very low birth weight preterm infants, who received diet including at least 80% of maternal milk, the authors found daily weight gain
the high daily gain of the body weight standardized on the 180th day of life were younger and obtained generally higher body weight and higher performance test selection index and
The findings in this study question other work that both self- reported height bias and self-reported weight bias contribute equally to BMI underestimation in large population