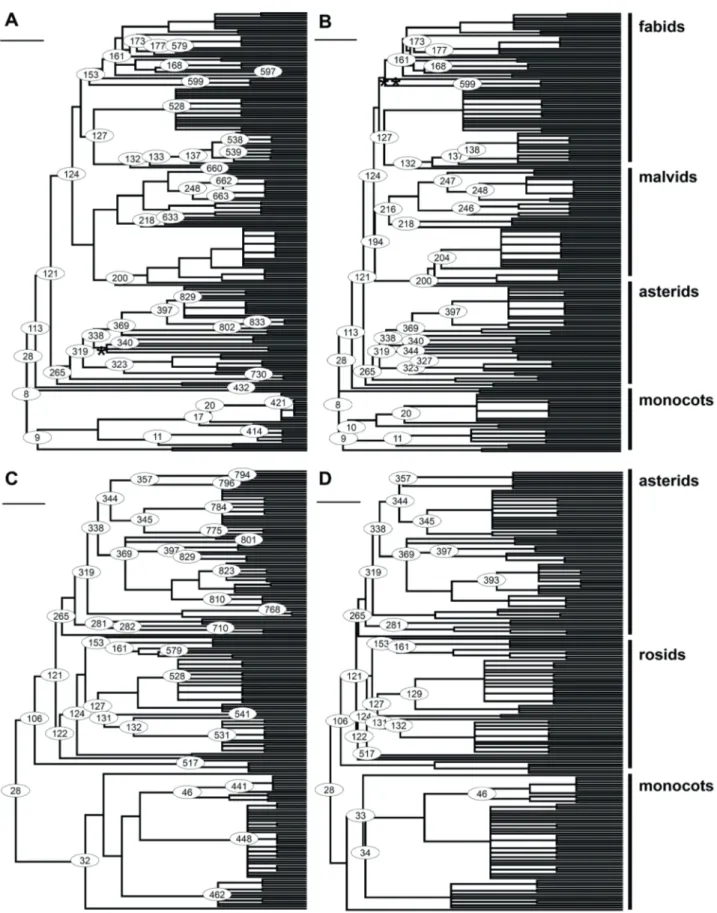
Updated angiosperm family tree for analyzing phylogenetic diversity and community structure
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
A igualdade entre homens, mulheres e escravos era, assim, menos encarada por Platão como um direito do que como um meio de melhorar o governo da cidade. Historicamente, o segundo
5.5 MAC-MPRR protocol: optimal values of w and p for different number of nodes, as well as the optimal throughput, the average number of nodes successfully transmitting an RTS packet,
Table 2 – Mean numbers of productive nodes, number of leaves, and distance between nodes in branches located in the upper, middle, and lower thirds of coffee cultivars, in subplots
Face às mais recentes orientações publicadas, sobre a melhor evidência científica para sustentar e guiar as equipas que prestam cuidados perioperatórios a clientes idosos
done between track analysis and phylogeny of the studied group is important as the generalized tracks and biogeographical nodes formed by phylogenetically-related species are
The proposed model is represented by a weighted semantic network composed of two kinds of nodes – one for presenting the concepts (concept nodes) and the other for
As some methods are more sensitive to variation in deeper phylogenetic nodes (COMDIST) while others capture variation mostly associated with shallower nodes (COMDISTNT, UniFrac
ML methods of ancestral state reconstruction treat the character states at internal nodes of the tree as parameters and attempt to find the parameter values that maximize