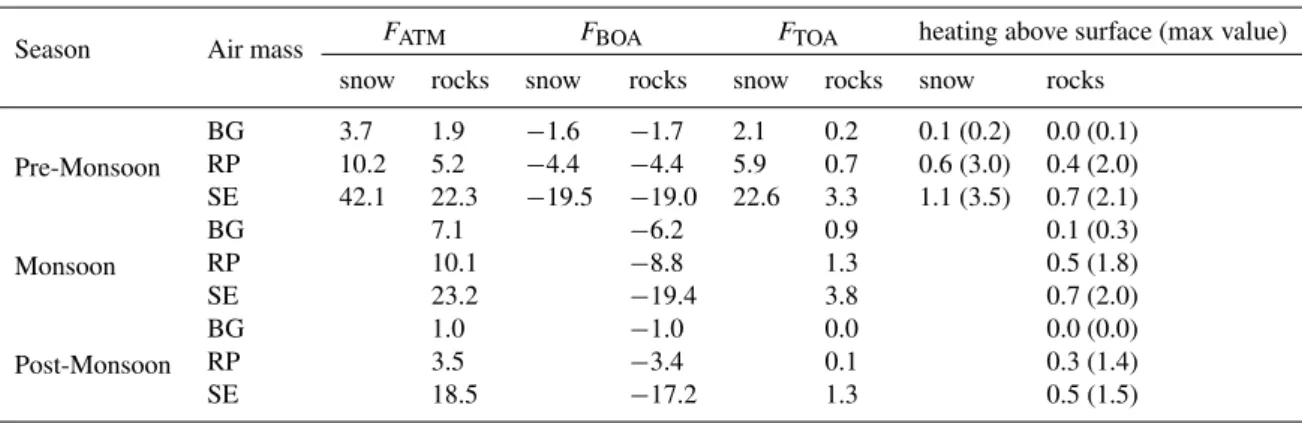
Aerosol optical properties and radiative forcing in the high Himalaya based on measurements at the Nepal Climate Observatory-Pyramid site (5079 m a.s.l.)
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
The well- predicted aerosol quantities, such as aerosol number, mass composition and optical properties, and the inclusion of full aerosol-cloud couplings lead to
changes in wind speed over the ocean on aerosols characteristics using collocated measurements of aerosol number size distribution, mass concentration, and spectral aerosol
To calculate radiative forcing and quantify the impact of varying sources of uncertainty, we need data including aerosol amount (e.g. optical depth) in both the present day and
Here we assess the aerosol optical depth ( τ ), direct radiative effect (DRE) by natural and anthropogenic aerosols, and direct climate forcing (DCF) by anthropogenic aerosols,
aerosol optical depth (AOD) of the atmosphere, acoustic sounding of the boundary layer, laser sensing of the aerosol content in the troposphere and stratosphere, mea- surement of
The spatial distribution of aerosol chemical com- position and the evolution of the Organic Aerosol (OA) fraction is investigated based upon airborne measurements of aerosol
(a) MODIS mean aerosol optical depth at 550 nm over Amazonia during the dry season (b) and mean direct aerosol radiative forcing of aerosols (DARF24h) during the peak of the
At the first stage of the measurements results analysis, the gear wheel cast surface image was compared with the casting mould 3D-CAD model (fig.. Next, the measurements results