J. bras. pneumol. vol.43 número4
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
Despite the limitations of this systematic review (e.g., few randomized clinical trials, low methodological quality of many of the included studies and the absence of
This study consists in a systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials to as- sess the use of Omega 3 fatty acids for the treat- ment of hypertriglyceridemia
Não sendo possível indagar em profundidade as aprendizagens atitudinais, procedimentais e concetuais das crianças do estudo, por escassez de tempo e meios, o meu intento
This systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized studies involving patients requiring cardiac valve replacement revealed similar mortality between patients who underwent
Objectives: The objectives of this systematic review of randomized controlled trials were to determine the relative clinical effectiveness of hand instrumentation versus
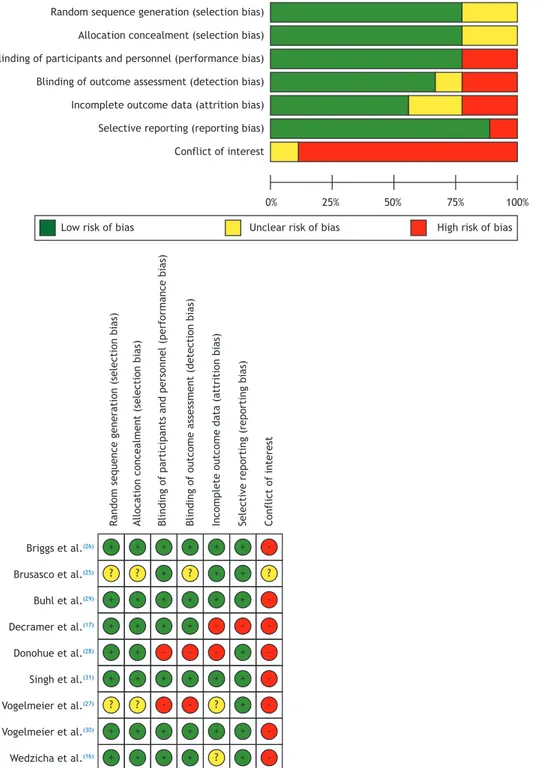
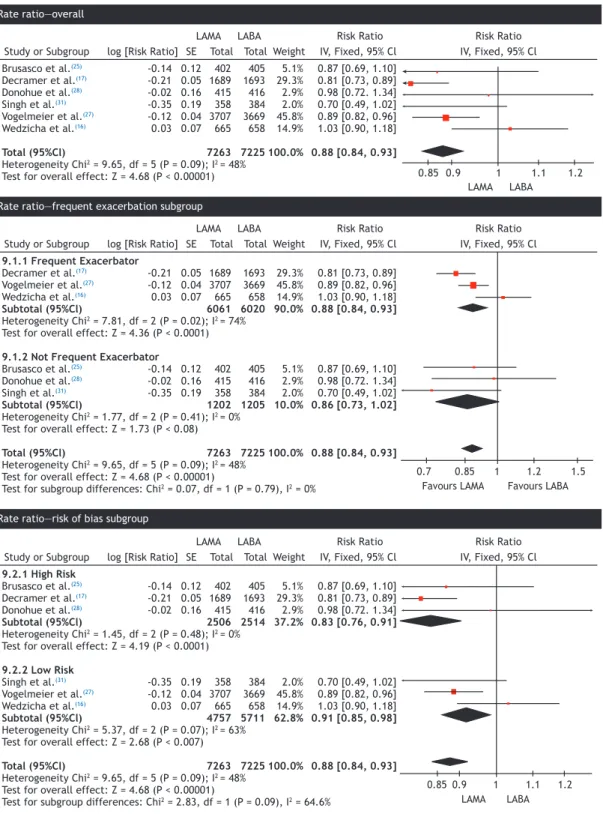
Methods: This was a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials involving patients with stable, moderate to severe COPD according to the Global Initiative
perform a systematic review and meta-analysis on the efficacy of all randomized controlled trials evaluating the efficacy of all avail- able endoscopic treatments when compared to
The objective of this systematic review is to evaluate published randomized clinical trials on oral medications used to treat symptoms of BPS, analyzing group of
![Figure 4. Proportion of patients with at least one exacerbation and subgroups.4.1.1 High RiskBrusasco et al.(25) 129 402 142 405 4.8% 0.92 [0.75, 1.11]Decramer et al.(17) 632 1689 712 1693 24.1% 0.89 [0.82, 0.97]Donohue et al.(28) 79 415 72 416](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_br/15132575.516302/8.765.64.672.84.1057/figure-proportion-patients-exacerbation-subgroups-riskbrusasco-decramer-donohue.webp)
