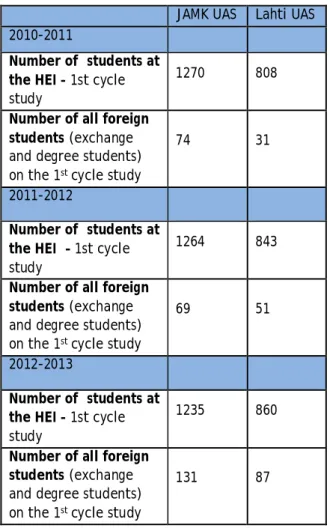
Internships are an essential part of higher education in the social and health professions. The number of social and health care students has increased in recent years due to the demand for social and health care.
Multicultural competence of UAS graduates in Finland
At both universities there are degree tutors who work with the degree students in the international programs and there are also international tutors who supervise the exchange students. Due to internationalization at home, students who do not have the opportunity to go abroad also have the opportunity to study during the academic year in the international intensive courses implemented at the universities or to participate in the English-taught academic courses during their studies.
Multicultural framework in Soulbus Project
International students want to belong and be valued in a new environment in different roles: as successful students, professionals, members of different social communities. The solution to these issues is based on changing the perception of international students from a problem to an advantage.
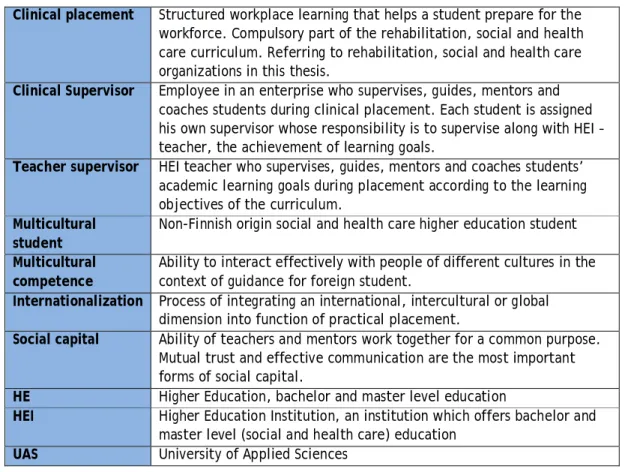
Clinical supervision
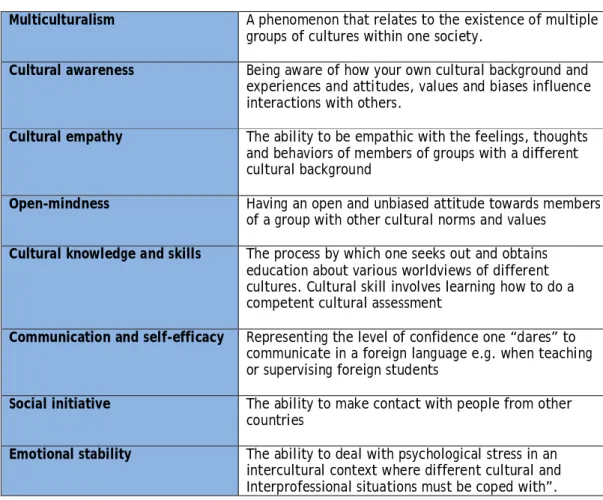
Cultural empathy The ability to be empathetic to the feelings, thoughts, and behaviors of members of groups of different cultural backgrounds. Emotional stability The ability to cope with psychological stress in an intercultural context where different cultural and interprofessional situations have to be faced”.
Supervision in social and health care Higher Education
Oinonen (1998) studied the supervision of practical practice of nursing students at different stages of study: at the beginning, in the middle and at the end of the study. In addition, students' expectations regarding the tasks and qualifications of tutors change during their studies as students acquire more professional competences.

Multicultural supervision
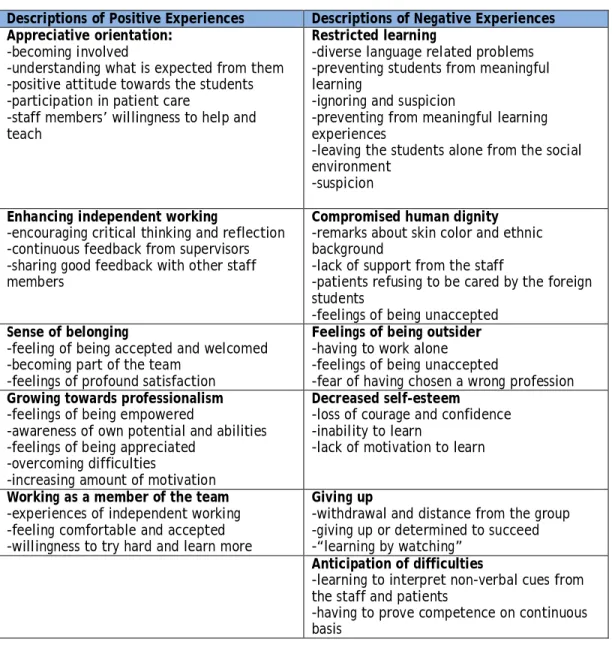
Their results indicated that value orientation, sense of belonging to a team, increased independent work, increased professionalism, and working as a team member were positive experiences for international nursing students. In WP 2 of the Soulbus Project, all participating countries of the Soulbus project with their working life partners had to learn about the current situation in the practical supervision of the practical placement of multicultural students in social and health care to be able to develop the module of e-learning for the use of work life mentors and HEI teachers.
Qualitative research approach and case study
The aim of this master thesis with a case study in Lahti UAS and Jyvaskyla UAS was to find out what are the good practices already in use in the Finnish higher education institutions and in practice. According to Metsämuronen, a case study can be understood as one of the essential data collection strategies as almost all approaches to qualitative research strategies use the case study method.
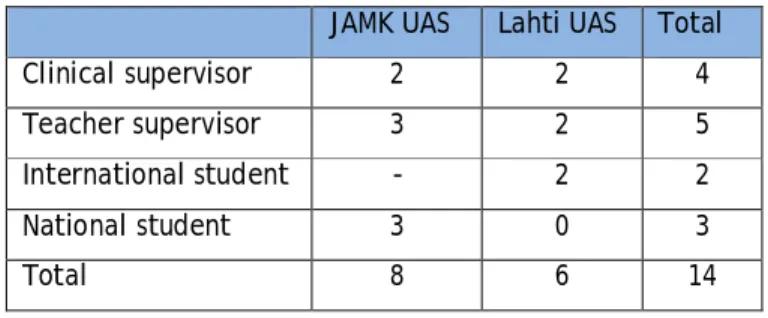
Participants
In the Soulbus setting, the case study meant that information and experiences were gathered from Jyväskylä and Lahti UAS teacher supervisors, work life partners (clinical supervisors) and students who have multicultural experience. The Soulbus project staff in Lahti and Jyväskylä had previous experience with work-life partners who provide clinical placements for multicultural HE students and with the help of the case study the understanding was to develop cooperation between work-life and HEI.
Data collection method
Data were collected by recording interviews and asking participants to complete a “Demographic Questionnaire” (Appendix 2) where relevant background information was provided. Basic data on internationalization in Lahti and Jyväskylä UAS were collected in order to understand the phase. All interviewees also received an "Information sheet for participants" (Appendix 3), where the purpose of the study was explained in detail.
The transcribed data consisted of 70 pages of text (Trebuchet MS, size 10) from the two interviews: 38 pages from the Lahti UAS interview and 32 from the Jyväskylä UAS interview.
Data analysis
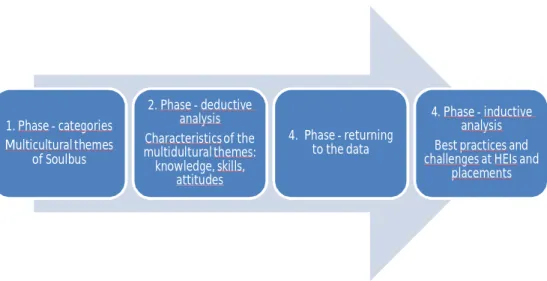
In the second phase of the data analysis process, the researcher returned to the transcribed data and it was analyzed again, now using inductive content analysis. The important element in inductive content analysis is to analyze the data with the informants' perspective in mind. After that, the data was reduced with the research question in mind to involve only the limited research area and all the non-relevant information was left out.
The two different methods of analysis ensured that the research questions were answered and the data were thoroughly analyzed taking into account different perspectives.
Multiculturalism
The deductive research results are categorized under knowledge, skills and attitudes that emerged clearly from the respondents' answers. Respondents described multiculturalism as respect and awareness of cultural differences, as well as understanding of its concept. Multiculturalism means that in a group there are people from different cultures and how to work with them.
What comes from culture and what comes from the other things?” (teacher supervisor, Lahti UAS).
Cultural awareness
According to the respondents, becoming and remaining culturally aware is related to a person's personal attitude, interest and experiences with other countries. It is of course extra work to take the international student with me, but I think I also learn a lot from the students” (Clinical supervisor, JAMK UAS). However, we are also active in organizing various kinds of leisure activities with international students to show them Finnish culture and traditions and also learn from their background cultures” (teacher facilitator, JAMK UAS).
Becoming and remaining culturally aware is connected to one's personal interest and experiences with other countries and ways of life.
Cultural empathy
The cultural background of the students was taken into account in one-to-one tutorials and practical placement interviews. The supervision of multicultural students was considered different and more demanding for the clinical and teacher supervisors. Discussions were experienced as positive and supportive, with topics ranging from students' own cultural backgrounds to international comparisons of nursing and healthcare systems.
Positive attitudes towards the students – such as cultural empathic welcome, interesting and discussed atmosphere at the school and placements – were considered important by the students.
Open-mindness
Most Finnish students see that they can learn more in the international groups” (teacher supervisor, Lahti UAS). I think there is added value in the international groups” (Teacher Supervisor, Lahti University). I have not seen any problems in group work, but the international students are not so willing to listen to the presentations or lectures.
Thinking about the language, I prefer to have some native English speakers from the US or UK in the group.
Cultural knowledge and skills
After the training we discussed the experiences with the students in class, where I noticed how stressed and tired many of my fellow students were. The evaluation process of multicultural students will also be included in the model” (Supervising teacher, JAMK UAS). Teachers wanted to work equally with international and local students, which was supported by their evaluation and student feedback.
I also received positive feedback from our exchange students in the evaluation sessions” (Supervisor teacher, Lahti UAS).
Communication and self-efficacy
Of course, language is very important in teaching, as is non-verbal communication and how to understand it. It is also important that you are interested, so it is also about attitudes” (teacher supervisor, Lahti UAS). The multicultural students mentioned the need for the facilitators and the internships to understand the different starting points and professional needs of local, degree and exchange students.
Degree students must learn Finnish to work in Finland, but exchange students are not required to do so.
Social initiative
Some supervisors had the willingness and ability to interact with multicultural students outside of neighborhood and placement settings. Now we have staff from Germany, Russia, Estonia…There are different ways to deal with patients and we have to learn from these colleagues with multicultural patients and students” (Clinical supervisor, JAMK UAS).
Emotional stability
Now we have more experiences, but sometimes they (problems) still happen” (Teacher Supervisor, Lahti UAS). Sometimes our workers tell about customers (to students) in English if the customer also wants or can speak English. We have only few workers who will speak English... I think people are ashamed of their language skills.
But if we have an international student in our office, for example ½ year, it is a good opportunity to acquire the language.
Best practices and challenges in multicultural supervision at Higher Education
Communication
Many of the respondents also emphasized the importance of continuous communication between supervisors and students and the courage to ask questions. The students also indicated that they needed more time, patience and explanation from the supervisors.
Co-operation between HEIs and placements
Structures supporting multiculturalism and supervision
Ethical consideration
When writing the theoretical framework for this thesis, I could not help but feel that I would have chosen a different approach to the multiculturalism theme: Standards of Multicultural Counseling Competencies (Sue et al. 1992) for counselor education e.g. These standards are one of the most widely used conceptual frameworks in multicultural counseling. They have also been one of the bases of the Jyväskylä University Counselor Training Program at the University of Jyväskylä, which has been running since 1996. This is also the form in which I presented my results of the multicultural themes in the deductive data analysis phase.
However, I decided to follow the framework of the Soulbus project as it had guided the group interview questions (Appendix 1).
Trustworthiness
In this thesis, many of the preconditions have already been determined in the Soulbus project. In addition, data analysis, data grouping, information categorization and most importantly, the conclusions and development ideas for the future were made based on the findings of the data. The reliability of qualitative research increases if the researcher accurately describes the phases of the research process.
This applies to all phases of the study: data collection, data analysis, research findings and the research report.
Discussion on the research findings
The data provided clear results and answers to the research questions, and development ideas for the collaboration were also found. The attitudes towards multicultural supervision showed that multicultural students add value to the supervisors' own work and to the professional environment. From the research findings of this study, it can be concluded that the communication between supervisors and multicultural students is a major challenge for both higher education and practical training staff.
However, it is very important that the clinical supervisors are chosen voluntarily, which is also useful for multicultural students.
Conclusion and development ideas for future cooperation
More research specifically on multicultural health and social care students. Supervision would be much needed in non-English speaking countries. The Multicultural Counseling Inventory: A measure for assessing social work students' and practitioners' self-perceptions of their multicultural competence. English-language degree programs in Health Care Faculties at Finnish Universities of Applied Sciences - Students' and teachers' conceptions of implementation.
A quantitative study to investigate whether lectures of the Faculty of Social Work and the Faculty of Health are known. A selective assessment of mental health nursing in New South Wales, Australia, in relation to clinical supervision. Accessed March 8, 2014. http://www.lamk.fi/english/studies/bachelor-degree-programmes/study-guide/Sivut/default.aspx.