Thanks to Jarmo Harju, examiner on this thesis, also for the great support and quick replies to e-mails. Of course, thanks must also go to all Ericsson PSIRT members for their support in the tasks in connection with the thesis and the actual implementation of ISMS. My father Juha I would like to thank for the advice regarding the future working career.
Introduction
This thesis will go through different types of information security frameworks and the background of ISO 27000 standard family. A comparison between ISO 27000 standard family and SIM3 Security Incident Management maturity model is also presented in this thesis. Finally, there are conclusions of the whole implementation procedure at the end of this thesis.
Computer Emergency Response Team
Background
Responsibilities
Ericsson PSIRT
Information Security Frameworks
- TCSEC
- ITSEC
- Common Criteria
- COBIT
- ITIL
- SIM3: Security Incident Management Maturity Model
- ISO 27000
The focus of the COBIT framework is to meet the business requirements placed on an organization's IT. The maturity requirements are therefore in the hands of the executing organization. It is a way to assess the effectiveness and suitability of the ISMS for a CERT.
![Table 3.2 Maturity level descriptions [23]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/9pdfco/1890653.266819/16.892.150.814.111.264/table-maturity-level-descriptions.webp)
ISO 27000 standard family
- History of the International Organization for Standardization
- ISO 27001
- ISO 27002
- ISO 27005
- Comparison between SIM3 model and ISO 27000 standard family
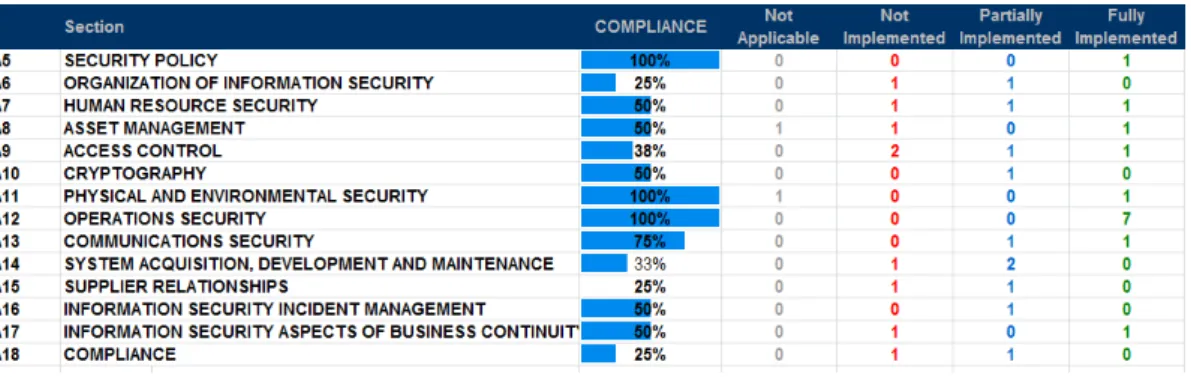
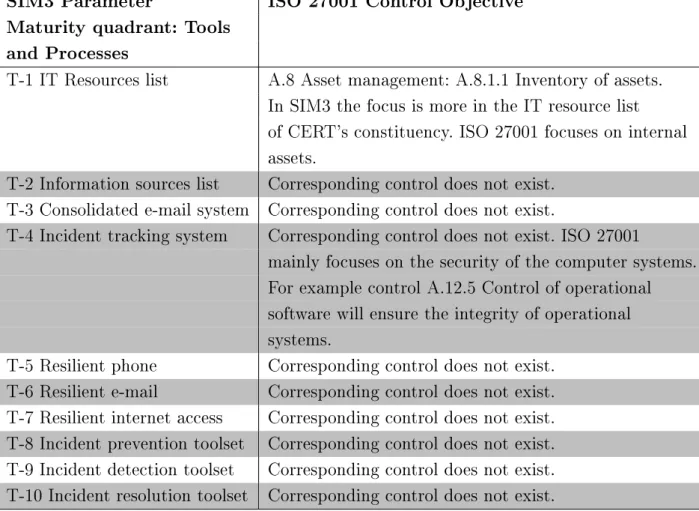
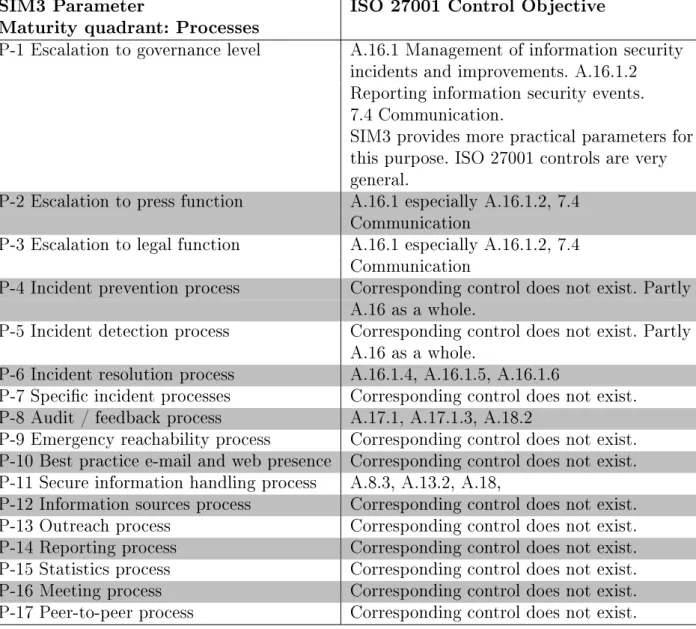
The target organization must review all ISO 27001 and ISO 27002 control objectives to have full control of the assets related to information security. However, these two models have many similarities and there is a correlation between some parameters and the control objectives from ISO 27001. As can be seen in Table 4.1, ISO 27001 covers almost all organizational parameters of the SIM3.
Parameters O-5 and O-7, service description and service level description are not requirements in ISO 27000, which is understandable since ISO 27001 is focused on information security management. The difference between the human parameters of SIM3 and the control objectives of ISO 27001 is more obvious. This is because ISO 27001 does not make any specific recommendations or requirements for specific organizations.
ISO 27001 has a clause for monitoring and measuring ISMS performance, but it is not what the SIM3 model requires. This can be seen from the comparison and correlation between ISO 27001 security objectives and SIM3 parameters. ISO 27001 will provide the basis for the ISMS and SIM3 will complete the control set from the CERT aspect.
The SIM3 model is also a good example of how much tailoring ISO 27001 requires when implementing ISMS for a CERT.
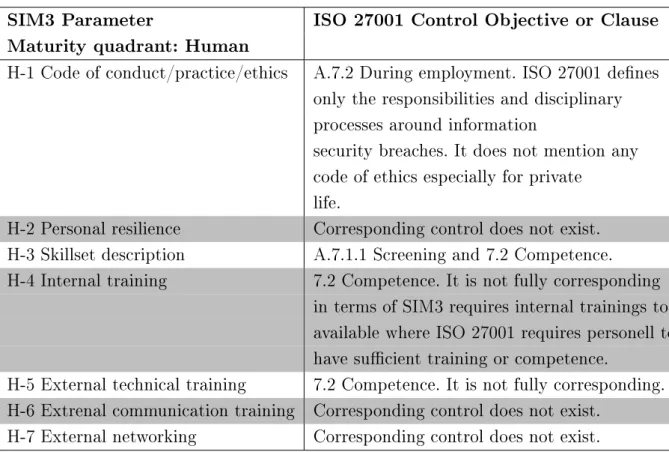
ISMS implementation process
Establishment
- Management commitment
- Dene scope
- Risk assessment
- Plan the risk treatment
- Statement of Applicability
In this phase, most of the documents required by the ISO standard will be created. Once the management commitment is achieved, the scope of the ISMS will be denied. The scope must be tailored to the target organization and is highly dependent on the nature of the target.
Therefore, it must be approved and signed by the top management of the organization. If the identification of assets is done improperly, the risk assessment will not have sufficient input and the effectiveness of the ISMS will be unsatisfactory. Evaluation criteria should be created taking into account the criticality of the information assets identified in the previous step.
Risk assessment criteria will be part of the risk assessment and methodology document in the ISMS. That is a very important and subjective choice of scale and should be carefully analyzed by the ISMS organization. A control is an example of the risk and the mitigation plan for that specific risk.
SoA must be updated and it must always represent the current state of the ISMS.
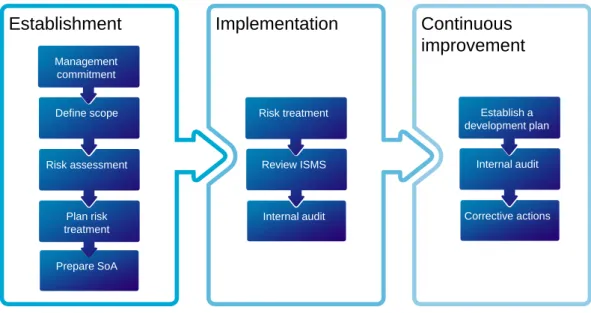
Implementation
- Execute risk treatment plan
- Review ISMS
- Internal audit
This review is conducted by the ISMS organization to see if anything significant is missing, such as required documentation. In the review, all necessary documents are checked and published for the channel, most often a documentation system used to communicate the ISMS. The purpose of the review is to verify that the risk management plan is effective, that it is executed correctly and that there are no major deficiencies in the ISMS.
This audit will be done by the persons within the organization, but in such a way that the objectivity of the audit will be guaranteed [1]. Persons conducting the audit may be people outside the specific organization that is in the scope of ISMS, but still within the company or higher organization. The ISMS organization must take responsibility for creating and executing the audit program.
The ISMS manager is responsible for monitoring the program's execution and ensuring the auditors' objectivity. Individuals performing the audit cannot be the same as those who reviewed the ISMS in the previous step. The standard also requires management to review the ISMS at set intervals.
Through these audits, management is able to ensure the suitability, appropriateness and continued effectiveness of the ISMS [1].
Continuous improvement
- Establish a development plan
- Periodical audit of the ISMS
- Corrective actions
- Maintenance
The responsible persons have a documented list of the updated list of ISMS organizations and will determine the responsible persons for the design, planning and implementation of the development plan. The objective of the periodic review is to update, evaluate and improve the state of the ISMS. This review is based on the risk assessment and takes into account the risks identified in the previous risk assessment.
If past risks have not been mitigated as planned, the mitigation plan must be escalated higher up the management chain. As the previous risks are surely mitigated, new risks are supposed to be found. After the new round of risk assessment, a new round of internal audit will be done.
Each time the risk assessment is performed, a risk treatment plan is created and corrective actions are documented and implemented by the risk owners. After the corrective actions have been implemented for the first time and the risks have been mitigated, the organization can start following the ISMS development plan. After completing these three main steps of the continuous improvement phase, the organization can move to the ISMS maintenance phase.
Risk assessment, risk treatment and internal audits must be carried out on a regular basis to keep the ISMS up to date and fully functional.
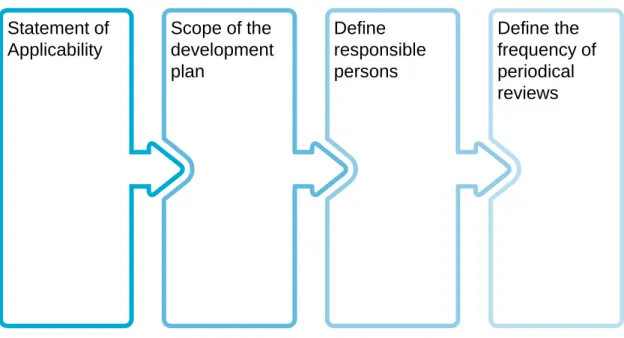
Establishing an ISMS in Ericsson PSIRT
- Management commitment
- The scope denition
- Risk assessment
- Risk treatment plan
- Statement of Applicability
The ISMS organization consists of the ISMS manager, internal auditors and current PSIRT members selected to be part of ISMS activities. They also act as risk owners and are therefore responsible for maintaining the ISMS. RA (Risk Assessment) leaders were external to ensure the objectivity of the risk assessment.
The person sitting at the top of knowledge may feel intimidated and afraid of losing their edge in the organization. Risks are assessed on the basis of the probability of the danger materializing and its impact on business operations, i.e. A risk management plan for each risk identified in the risk assessment was implemented in a risk management workshop.
Some controls were selected because they acted as input for new risks. The risk management plan and selection of controls were made in several separate workshops with Ericsson PSIRT members. Several control objectives were excluded because they were not part of the ISMS scope.
A summary of the statement of applicability document was created below the actual document and the state of the ISMS was further communicated to the ISMS steering group.
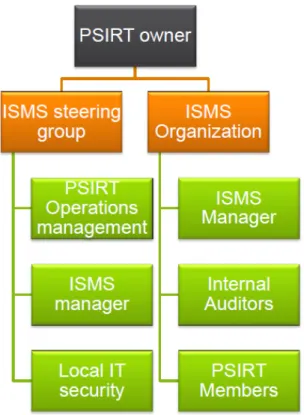
ISMS from a CERT organization aspect
- Advantages of the ISMS
- Problems and limitations
- Cost estimation
- Certication process
The greatest advantage of ISMS to a CERT is to highlight the risks associated with operations, services and ways of working. The biggest problem with the ISO 27000 family of standards is that it is a very general standard. If one has to implement an ISMS and start work based on ISO 27000 standards, the implementation will require a lot of time.
It can also be difficult to even deny the scope of the ISMS if the organization does not have experience on the ISO 27000 standard. It is possible to create documents required by the ISO 27001 without a correlation with the real world. If a SERT needs to demonstrate compliance with ISO 27001 or such requirement is presented to a SERT in another way, the certification process will be started.
This certification body will perform a gap analysis between the ISMS of the target organization and the requirements of the ISO 27001 standard. had to be implemented to be fully compliant with the standard. By choosing an accredited certification body, the organization can ensure the competence of the external auditor.
If the ISMS requirements are met, the certification body will certify you as an ISO 27001 compliant organization.
Conclusions
The biggest advantage of ISMS is having a systematic overview of CERT's information security risks. Although CERT is an information security team, this does not mean that the internal information security posture is sufficient. 2] ISO/IEC Information technology - Security techniques - Code of practice for information security controls, International Standardization Organization, 2013.
4] ISO/IEC Information Technology - Security Techniques - Information Security Risk Management, International Standardization Organization, Second Edition, 2011. 6] Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation, available: http://www.commoncriteriaportal.org /filer/ccfiles/CCPART1V3. 9] COBIT 4.1, Executive Summary, Framework, IT Governance Institute, 2007, available: http://www.isaca.org/Knowledge-Center/cobit/.
Beckers, Objective-Based Establishment of an Information Security Management System Compliant with ISO27001, The Ruhr Institute for Software Technology, University of Duisburg-Essen, Germany, 2014. 16] ISMS Implementation Guide, atsec information security corporationm, 2007, Available: http:// www.atsec.cn/downloads/documents/. 18] Friendship among equals - Memories from ISO's first fifty years, 1997, Available: http://www.iso.org/iso/2012_friendship_among_equals.pdf [19] Using oence to inform defence.
22] Information Security Management Systems Auditor/Lead Auditor Training Course (BS ISO/IEC Course Notes, British Standards Institution, 2007.
![Table 5.1 List of minimum set of mandatory documents required by the ISO 27001:2013 [1], [20]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/9pdfco/1890653.266819/26.892.153.790.688.1066/table-list-minimum-set-mandatory-documents-required-iso.webp)
![Figure 5.2 Risk management process according to ISO 27005:2011 [4]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/9pdfco/1890653.266819/33.892.273.688.150.690/figure-risk-management-process-according-iso.webp)
![Figure 5.3 Risk level matrix [4]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/9pdfco/1890653.266819/34.892.167.784.497.707/figure-risk-level-matrix.webp)