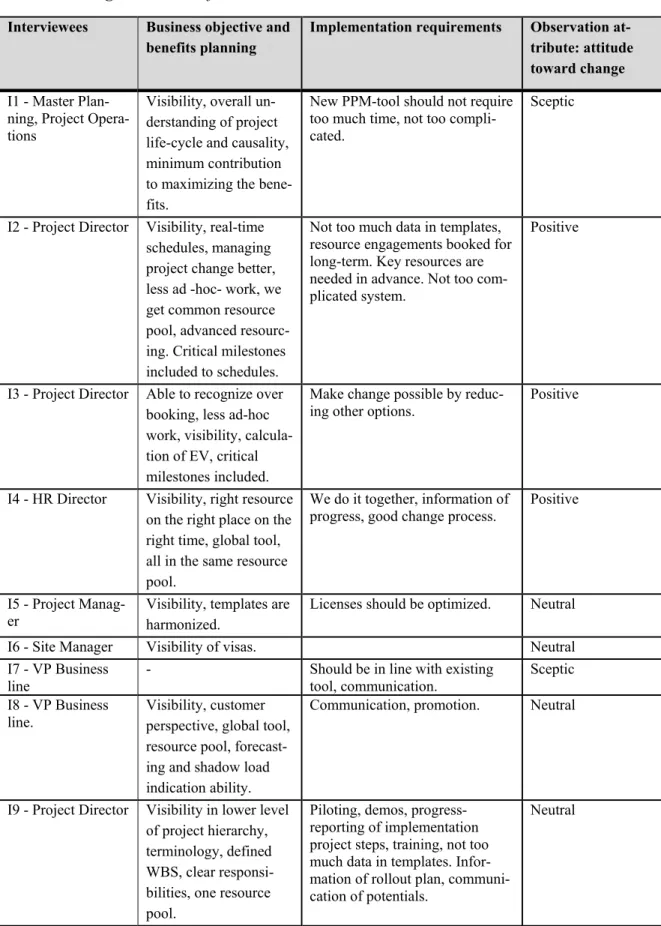
Through semi-structured interviews and observations, the current problems and goals of the case company were determined. The purpose of external interviews was to assess the validity and generality of the framework.
INTRODUCTION
- Motivation
- Case company
- Research problem, objectives and restrictions
- Theme of thesis
- Structure of thesis
This thesis aims to reveal these attributes in relation to the situation of the Case company. What should be included in the implementation framework to achieve the objectives of an information system implementation.

RESEARCH MATERIALS AND METHODS
Research approach and methodology
- Design science research
- Multi-method applied to Design Science framework
According to Hevner et al. 2004), design science creates and evaluates IT artifacts for the purposes of solving organizational problems. The usability, quality and effectiveness of the design must be rigorously demonstrated (Hevner et al. 2004).

Data collection
The data collection took place through primary observation (Saunders et al. 2009, p. 296), where the focus was on the participants' feelings about change. Participants were categorized in the way they felt that PPMs will affect their daily work after implementation.
Data analysis
INFORMATION SYSTEMS AND ORGANIZATIONAL TRANSFORMATION
- Value of organizational knowledge
- Digitalization impact on value adding
- Cloud software as a service
- Leveraging information systems for organizational transformations
- Sources, drivers and types of change
- Strategic alignment
- The role of business process re-engineering and management
- Business process walkthrough to describe a workflow
- Change as an important process
Recognition means that key people (top management) in the organization have a mutual agreement with the idea of change. In the first phase attention should be paid to the vision, the challenge of improvement and the deduction of the problem.

CRITICAL FACTORS IN CLOUD SYSTEM IMPLEMENTATION
Critical factors in cloud system implementation lifecycle
- Maintenance and service level agreement
- Cloud security
- Cracking knowledge barriers and blocks by implementation
The suppliers are expected to meet the quality and key performance indicators for services to enforce their agreed SLA terms (Fatema et al. 2014). Nevertheless, cloud computing is a relatively new paradigm and no common standards have been widely adopted by deployed systems (Aceto et al. 2013). Availability measures whether the cloud provides services according to the system design whenever users request them (Aceto et al. 2013).
Therefore, distribution practices must be aligned with company strategies (Markus et al. 2000) and they are critical to companies for many reasons. First, the company can decrease organizational resistance by undertaking fewer changes at a time (Robey et al. 2002). Companies that adopted the piecemeal approach seemed to have an easier time overcoming knowledge barriers than those that adopted a concerted approach (Robey et al. 2002).

Critical taxonomy and success factors of implementation
- Internal change promotion and communication
- Project management capabilities
Clear scope is critical, and the company must have a clear understanding of the desired end state (Handler et al. 2015). Ozguner and Ozguner 2014; Holbeche 2006, p. 380) Therefore, the implementation project team must be a combination of the right talented and motivated individuals (Handler et al. 2015). For example, research conducted by Themistocleous et al. 2001) raise the issues regarding the technical challenges and difficulties of the IS implementation project.
In the study by Robey et al. 2002), knowledge transfer from consultants to the company was seen as beneficial. Companies should have a solid understanding of the desired state at an early stage, including requirements, goals, processes and reports (Handler et al. 2015). Snider et al. 2009; Handler et al. 2015) Project management skills are therefore discussed in more detail.

Information system evaluation
- Success realization
- Benefits realization
However, there are difficulties that lie in many layers: the information system has an impact on social organization and people, and it is not just a technological activity. Another problem is that the information system is relied upon to improve decision-making, which is almost impossible to measure. RD57: Plan different variables to measure the success of information systems The framework developed by Smithson and Hirschheim (1998) is based on different zones: efficiency, effectiveness and understanding.
These dimensions focus on the information system and information quality aspects, such as how the decision maker perceived the value of information received from the information system. Irani (2002) highlighted that there is a correlation between the concept justification of an information system to operational stakeholders and their increased level of commitment to project success. A study by Irani (2002) argues that there is evidence to support the proposition that IT/IS benefits can be classified as strategic, tactical and operational benefits with financial, non-financial and intangible characters. 2008) emphasizes that benefits should be the central focus of IS implementation: focus on benefits rather than technology.

EMPIRICAL RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Problem identification in the case context
Information was in silos with limited access, and each project manager and resource manager had their own methods of obtaining resources, despite the statement that in project-based organizations, the comfortable certainty of climbing the ladder up the functional silo does not exist (Huemann et et al. 2007). The relevance of the issue of resources is shown in the description of the process in Figure 18. Current management of project resources in the project implementation organization As Figure 18 tries to illustrate the challenges in the project implementation organization and in resource management: the flow of information between individuals is hierarchical. and requires many points of contact, although some of the files were publicly available.
This landscape was considered to complicate project management in a global environment where the organization must have shared resources to access. 11 out of 20 interviewees felt that overall project resource management was a major problem and many resource owners had their own ways and methods of securing resources. However, some interviewees felt that resource acquisition was not a problem due to dynamic resource management or the existing resource management system in the line organization.

Objectives identification in the case context
Most of the interviewees, 17/20, mentioned that the visibility in the project management was weak and therefore the relevance of the instrument in the organization is accepted, as most of the project managers emphasized this fact during the interviews. There should be no black box in the delivery process” (I18: VP of Business line). However, internal IS requirements are tailored to the limitations of MS Project Server.
The centralized development was one of the critical goals from a management perspective, because it provides harmonized methods for system management and thus saves resources. As the vice president of the business line project management said: "You cannot overcommunicate in this project". The purpose of the research was to find a way in which the goals and the desired state are achieved in the company with a plan that is introduced in the next chapter.
Building artefact design
- Rollout process
- Communication process
In the case of Case company's situation, the need to support the decision-making (RD1) and project management visibility was part of digitization requirements (RD7), resulting in the need for harmonization of the project's internal and customer reporting (RD2, RD6) had. In the Case company's situation, the chosen type was to adapt strategic alignment adopted from Henderson and Venkatraman (1999) who supported the idea of dynamic model where change is as an interaction of technology, structures, people and tasks (RD11). In the case of the company's situation, the plan proposed a phased rollout, where few changes at the.
Architecture validation and the software test plan were recognized by Case as important factors in the configuration phase. In addition, it allows control over whether the new methods are actually understood and used in the organization. Communication through organizational changes is supported by various authors in the literature.

Artefact evaluation
- Internal validation interviews in Case company
- External interviews Partner company C1 and C2
The next management communication event was the Steering Group review where the goal was the progress of the implementation project. While evaluating the benefits, he pointed out that long-term planning and real-time data are one of the main benefits for him. Otherwise, I probably won't practice myself, was one of the comments made during the interviews.
Based on the general feedback from the interviews, the feeling seemed to be positive. External interviews were considered a critical factor in the evaluation of the implementation framework. The problems are at the structural level of goals and benefits: how, for example, to consider the personal level.
Combining the empirical results
Since the correction was necessary, evaluation was beneficial and added rigor to the research, thus most likely increasing the framework's ability to achieve its goal (validity, effectiveness), consistency with organization, and the clarification and completion of structure. The result of the interviews of how the framework's evaluation characteristics should be weighted in the case organization's context is presented in Figure 23. The colors indicated whether the framework met some of the dimensions and criteria.
The third important evaluation criteria was consistency with the organization, as the purpose of the framework was to create consistency with the organization, IT and processes. There, the completeness was not quite achieved as the experimentation of the framework was underway. If the goals of the implementation are fully successful, the artifact fulfills its purpose (Hevner et al. 2004).

CONCLUSIONS
Key results
The purpose of the criteria was to evaluate the feasibility of the artifact's design, its ability to achieve its objectives given the short time it takes to cover an entire implementation project. Therefore, the evaluation of the framework showed that the evidence of its ability to guide the organization to the desired location is still incomplete. Evolution is considered the second least important attribute, but its relevance should be higher as the framework is evolving and designed to include iterative work.
-5) during complex projects, instead of sticking to elaborate plans that will change, it is often better to create options through iterative methods: try a little, review the results and adjust, then take the next steps based on the experience. As a result, the research still lacks evidence to fulfill its purpose and requires a full case study after the completion of the implementation project.
Recommendation for actions
Assessment of research
Therefore, the case study of this research was only partially feasible and experiments should be continued. In addition, the results of the evaluation are only indicative, which is why it will be relevant to examine the evaluation criteria and their order again in the future.
Assessment of the utilized methods
The effect an individual feels of being observed changes his/her behaviour, therefore a time error is relevant. However, the subject of information technology quickly evaporates as new technology is developed and new research results are discovered. Therefore, this thesis attempted to use a wide range of different types of literature and placed value on currently relevant articles.
However, the literature on strategic alignment has developed over time and conceptualizations have expanded over time, and research recognizes many points of alignment between business and IT, as stated by Chan and Reich (2007). Therefore, it is important to argue that the approximation built in this thesis has been adopted in a sophisticated, moderated way and will probably be continuously developed.
Recommended future researches
Strategic Alignment: Leveraging Information Technology to Transform Organizations. 2004), Design science in information systems research, MIS Quarterly 28(1). Human Resource Management in the project-oriented company: A review, International Journal of Project Management 25. Oxford Surveys in Information Technology 4, pp Explaining information systems change: a punctuated socio-technical change model", European Journal of Information Systems, volume 17(4 ).
Communications of the Association for Information Systems (CAIS A Design Science Research Methodology for Information Systems Research, Journal of Management Information Systems 24(3). Learning to Implement Enterprise Systems: An Exploratory Study of the Dialectics of Change, " Journal of Management Information Systems 19(1 ), pp. RD2: Plan how the information system should support the reporting and analysis needs RD3: Design and visualize methods of information knowledge creation, sharing and capture with IS.