Je remercie également Morgan pour ses conseils et son humour, Julien pour avoir toujours été la meilleure compagnie et Fatou pour ses encouragements constants qui m'ont fait du bien. En 2000, l'Organisation mondiale de la santé (OMS) a publié pour la première fois un classement des systèmes de santé de ses 191 États membres (OMS, 2000).
Le système de soins en France
Les objectifs de la médecine de ville
Cependant, le nombre de médecins généralistes (au centre de l'organisation de la médecine de ville) diminue et la pratique libre se raréfie (Anguis et al., 2021). Cela peut se faire par la réglementation du remboursement des médecins, dont on sait qu'il affecte le volume et la qualité des soins dispensés.
Au cœur du système de soins : des médecins et des patients
De plus, lorsque les patients consultent ces médecins conventionnés, ils sont remboursés d'une partie des frais de consultation. Plus de la moitié des médecins exerçant en tant que généralistes libéraux ont une activité libérale ou mixte contre seulement 48 % des spécialistes (Anguis et al., 2021).
Un système de santé en tension
Selon des études récentes, cette forme d'exercice pourrait être une réponse efficace pour lutter contre les « déserts médicaux » (Chevillard et Mousquès, 2021) et améliorer l'accès aux soins des patients tout en augmentant les revenus des médecins (Cassouet al., 2020). La littérature montre que le système de rémunération des médecins (rémunération à l'acte, head money ou salaire) a une influence majeure sur l'organisation des soins primaires (des études comparatives sont régulièrement publiées ; voir la plus récente par Espinosa-González et al. , 2021 ; Jia et al. al., 2021 ; Quinn et al., 2020).
La rémunération des médecins libéraux
La prédominance du paiement à l’acte
La rémunération des médecins joue donc un rôle majeur dans la performance du système de santé en matière de prestation de soins. Toutes ces innovations sont mises en œuvre dans une logique de diversification des modes de rémunération des médecins.
La pratique des dépassements d’honoraires
La liberté tarifaire, défendue par les médecins libéraux, est encore aujourd'hui source d'inégalités d'accès aux soins. Ces contrats incitent les médecins à réduire leurs dépassements et à augmenter leur part d'activité à des tarifs applicables en échange d'un gain financier.
La régulation de l’offre de soins par la rémunération
L'effet du gel du secteur 2 sur la proportion de médecins s'installant en secteur 2 n'a été que temporaire : les médecins spécialistes ont de plus en plus accès aux titres leur permettant de s'établir en secteur 2. En 2014, le « Contrat d'accès aux soins » (CAS) a incité les médecins à réduire leur taux de ticket modérateur et à développer leur activité à des tarifs opposables.
Objet de la thèse
Chapitre 1
A partir d'un panel de médecins généralistes libéraux observés avant (2005 et 2008) et après (2011) sa mise en place, nous estimons un premier modèle de changement avec une variable instrumentale pour corriger les biais endogènes liés au fait que l'adhésion au CAPI est un choix. Nous montrons que le CAPI a significativement influencé les pratiques des médecins généralistes qui les ont rejoints dans un sens compatible avec une amélioration de la qualité des soins : les membres du CAPI n'ont pas, contrairement aux autres médecins, diminué le nombre de consultations de patients ni le nombre de prescriptions par patient.
Chapitre 2
Enfin, le CAPI a entraîné une augmentation des honoraires collectés par patient, ce qui a entraîné une augmentation des coûts des soins pour l'assurance maladie.
Chapitre 3
Rapport sur la santé dans le monde 2000 : pour un meilleur système de santé. Soins de santé primaires : Rapport de la Conférence internationale sur les soins de santé primaires, Alma-Ata (URSS, 6-12 septembre 1978).
The Introduction of Pay-for-Performance
Literature Review
Their results suggest that CAPI has a significant but small impact on achieving this objective. To the best of our knowledge, no assessment of pay-for-performance from this perspective of the impact on the structure of care delivery has been carried out in either the French or the international literature.
The CAPI system, Data and Descriptive statistics
- The Data: an exhaustive panel of French self-employed General Practitioners 22
- Variables of interest
- Descriptive statistics
Bonus = level of achievement × number of patients as médecin traitant × e7 The bonus received is an increasing function of the number of patients treated as médecin traitant and the level of achievement of objectives. Notes: CAPI bonus decile and average number of patients treated as médecin traitant are read on the left axis.

Empirical Strategy
A change in the family situation (such as a birth) can also have a negative impact on the doctor's activity (∆Yi0811 < 0) and at the same time encourage him to join CAPI (to earn a bonus that will allow him to negative effect of working less on their income). The instrument used, Zi05, is the logarithm of the density of GPs observed in 2005 in the municipality where the doctor works.
Estimation of the Impact of CAPI
- The context: changes in the practices of General Practitioners between
- First Stage: signing up to CAPI
- Impact of CAPI on the practices of General Practitioners
This is positive for most level variables (volume of care, number of patients), but negative for most of them measured in ratios per patient (consultations per patient, prescriptions per patient, costs per patient). Activity structure per patient. i) Depending on the result of the Hausman test, OLS estimates (variables "number of consultations" and "number of total procedures") or instrumental variable estimates are used.

Discussion and Conclusion
Pay-for-performance in the United Kingdom: impact of the quality and outcomes framework: a systematic review. The true impact of the French pay-for-performance program on physicians' benzodiazepine prescribing behavior. The European Journal of Health Economics.
Objectives of CAPI
Sampling frame
French physicians’ responses to overbilling restrictions 47
The regulation of ambulatory care in France
- Physicians’ payments
- The "Sector-2 freeze" reform and the regulation of overbilling in France . 52
- An exhaustive dataset on physicians in France
- Outcomes considered in the analysis
- Descriptive statistics
Moreover, since the choice of sector is endogenous, this reform, which is the only attempt in France to regulate drastically overcharging, can be used to look at the care of sector 1 doctors. In general, the total fees of sector 1 doctors are lower, except for general practitioners: their lower prices are not compensated by higher workload7. These are not the doctors' incomes, defined as total fees excluding expenses (office rent, secretary's pay, etc.).
Empirical strategy
- Fuzzy Regression Discontinuity Design
- Validity checks
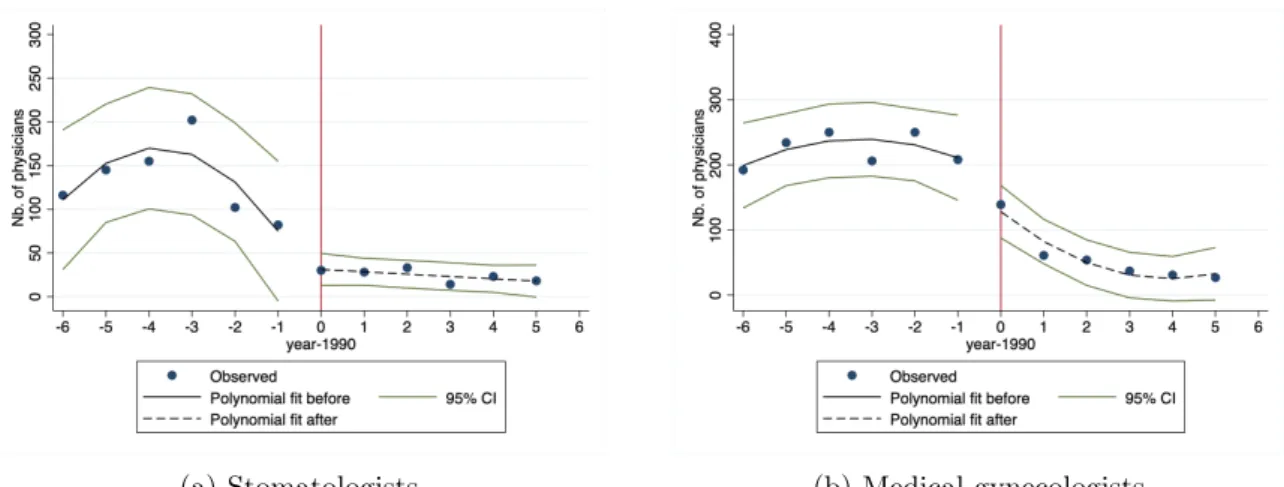
However, as noted by Imbens and Lemieux [2008] and Lee and Card [2008], adjusting for covariates (especially covariates defined before the reform) can help eliminate small sample biases in the specification and improve the precision of the estimates. First, the expectations of possible outcomes conditional on X must be continuous in the first quarter of 1990. First, we graphically check the continuity of the number of doctors who start practicing each year: there is no discontinuity in this number, and above all no increase in the year before the reform (Figure 2 .B.4).
Results
- Main Results
- Robustness checks
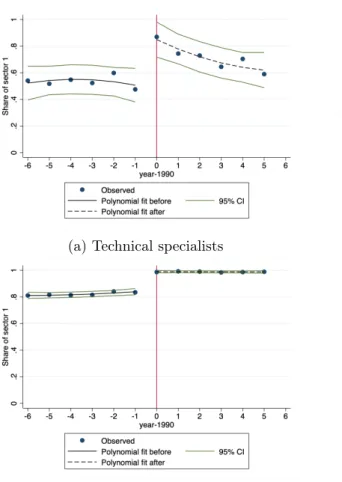
Therefore, technical specialists who increased their number of operations either increased their total work time (by keeping the time of each consultation constant) or maintained it (by reducing the duration of each consultation). Only 48% of these procedures were aimed at their new patients, the rest being an increase in the number of (potentially unnecessary) procedures performed on their regular patients. The improved access to care leads to an increase in the number of reimbursements that are reimbursed, as well as strategic behaviors that we identified.

Data: Choice of the different specialties and sample used for the estimates
Excluded are doctors who do not have a contract with the National Health Insurance, are employed full-time in private hospitals and are aged 60 or over and receiving an old-age pension. The second-order polynomials are obtained with function specifications before and after the reform date (1990). We exclude physicians who were not matched to the DGFiP dataset, who did not have an NHI contract, who worked full-time in the private sector or in a hospital, who were 60 years of age or older and who were retired, who had zero fees, zero prescriptions and zero performed actions.

Validity of the regression discontinuity set up
Columns (1-3-5) report estimates obtained using a first-order polynomial function of trimester-year of practice setting. Estimates are obtained using a bandwidth of 6 years around the reform for technical specialists, medical specialists and general practitioners. Columns (1-3-5) report estimates obtained using a first-order polynomial function of trimester-year of practice setting.

RD estimates with 95% confidence intervals
Results for each specialty
Sensitivity checks
Columns report estimates obtained with a bandwidth of 5, 6, or 7 years around the reform and a first-order polynomial function of the year of training onset. Regressions are performed with control variables (physician gender, age at thesis defense, female/male life expectancy and mortality rate in the medical practice department in the year of thesis defense. Estimate regressions with a bandwidth of 6 years around the reform for technical specialists, medical specialists and general practitioners.

Falsification test
Do conditional financial incentives improve access to care?
The regulation of overbilling in France
- The practice of overbilling in France
However, the large number of doctors who started charging additional fees put the principle of access to care for all at risk. Additional charges are not reimbursed by NHI or are partially reimbursed if the patient agrees to supplementary health insurance. This regulation has reduced the average amount of additional fees per performed procedure, without reducing the total fees for self-employed specialists in sector 2.

Empirical Strategy
- Difference-in-Differences framework
- Construction of a comparison group
It allows controlling for time-invariant individual heterogeneity that affects the CAS or OPTAM membership decision. Therefore, a represents the average effect of CAS on Yit for doctors who only joined CAS and (a+g) is the average effect of CAS on yit to always treat (doctors who joined CAS and OPTAM) compared to never treat (doctors which did not join either CAS or OPTAM). It means that in the absence of CAS or OPTAM, both the treated group (physicians signing CAS and/or OPTAM) and the control group (never treated by either CAS or OPTAM) would have experienced the same trends in outcomes (Rubin, 1974; Angrist and Pischke 2009).

Data
- Administrative data on all French self-employed physicians
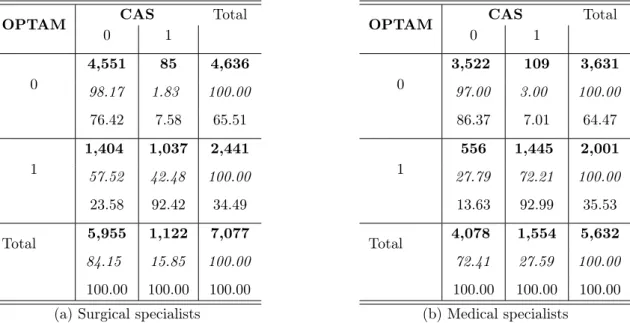
- Who chose the CAS and the OPTAM?
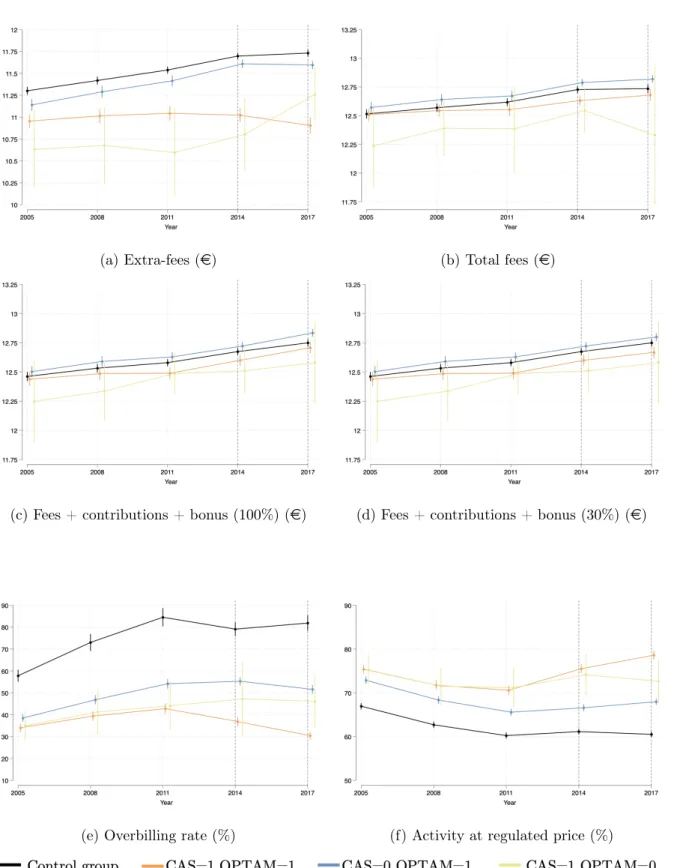
As for surgical specialists, the effect of OPTAM is stronger than CAS on the activity of doctors. Finally, both CAS and OPTAM influenced the activity of medical specialists, but OPTAM provided more incentives. Finally, CAS and OPTAM encouraged doctors to see more patients (including the poorest).
Additional robustness analyses
- Average treatment effects on subgroups
- Estimations with Callaway and Sant’Anna [2021] method
However, CAS (assuming that all doctors met their targets) increased for NHS expenditure by 11.7%. For surgical specialists, we have the same results for the CAS effect as in Equation 3.3. Both CAS and OPTAM affected the activity and income of medical specialists: overall activity increased (larger patient lists led to more procedures).

Discussion and Conclusion
Therefore, the introduction of financial incentives has led to a transfer of the payment of extra fees from the patients to the community (the NHI). This paper estimates a short-term effect of the CAS and the OPTAM on physician activity. Furthermore, I only estimate the effect of the programs on the volume of care instead of on the quality.
Social contributions calculations
Sociodemographic characteristics of CAS and OPTAM physicians
Self-employed doctors operating in sector 2 work full-time as self-employed under the age of 70.

Trends in outcomes of interest
Self-employed doctors practicing in sector 2, working full-time as self-employed, under 70 years of age.
Additional analyses trends
- Pistes de recherche
- Recommandations de politiques publiques
- Proportion of the CAPI bonus in total fees and lump-sum payments of general
- Share of physicians in sector 1 by year of practice beginning
- Adhesion rate of the CAS and the OPTAM according to overbilling rate
- Changes in the different variables of interest between 2008 and 2011 over the
- First stage estimation - equation ()
- Effects of signing up for CAPI on the provision of care by General Practitioners 38
- Descriptive statistics of care supply variables between sector 1 and sector 2
- First stage estimates for practicing in Sector 1
- RD estimates
- RD estimates - Mechanism variables
- RD estimates - physicians’ behavior around year 1990
- Description of the CAS and the OPTAM
- Simulations of physicians’ benefits from the CAS and the OPTAM
- Treated and non treated physicians’ socio-demographic characteristics in 2011
- Physicians’ status according to CAS and OPTAM in 2017
- Mean outcomes difference between CAS and non CAS physicians before and
- Mean outcomes difference between OPTAM and non-OPTAM Surgical physi-
- Mean outcomes difference between OPTAM and non-OPTAM Medical physi-
- Average effect of the CAS and OPTAM adhesion on matched physicians’ ac-
- Average effect of the CAS and OPTAM adhesion on matched physicians’ fees 126
- Additional estimations on subgroups of treated versus the never treated group 132
Plus précisément, au chapitre 1, une estimation est faite de l'effet de la rémunération incitative sur l'activité des médecins généralistes. Le chapitre 2 examine l'effet du secteur des covenants sur l'activité des médecins généralistes et spécialistes. Le chapitre 2 montre les effets à long terme du secteur des conventions sur l'activité des médecins.