Conventionally, the translational and scale invariant functions of Tchebichef moments can be obtained either by normalizing the image or by expressing it as a linear combination of the corresponding invariants of geometric moments. In this paper, we present a new approach based directly on Tchebichef polynomials to derive the translation and scale invariants of Tchebichef moments. The translation and scale invariants of Zernike and Legendre moments were achieved by using image normalization method [19-20].
An efficient method for constructing translation and scale invariants of Zernike and Legendre moments from their respective orthogonal polynomials was developed by Chong et al. To the best of our knowledge, so far, no report has been published on how to derive the translation and scale invariants of orthogonal discrete moments. Traditionally, this can be done in one of the following two ways: (1) Image normalization; (2) Indirect method, i.e., using the translation and scale invariants of the geometric moments to form the corresponding Tchebichef moment invariants.
In this paper, we propose a new approach to derive the translation and scale invariants of Tchebichef moments, based on the corresponding polynomials. In Section 2, we review the definition of Tchebichef moments, and briefly describe how to derive the translational and scale invariants of Tchebichef moments from the geometric moments. In this section, we first review the theory of Tchebichef moments, and then give a brief description of how to derive the translational and scale invariants of Tchebichef moments from the geometric moments.
To obtain the translation and scale invariants of Tchebichef moments, a common way is to express the Tchebichef moments as a linear combination of geometric moments, and then use translation and scale invariants of geometric moments.
Experimental results
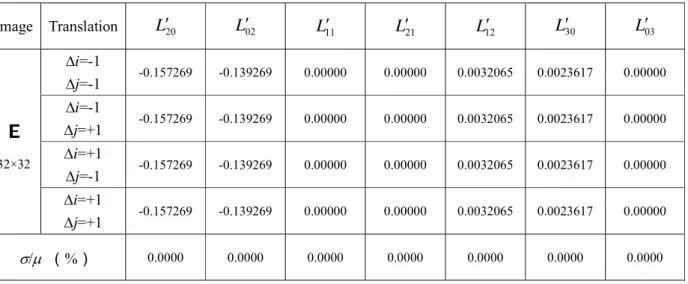
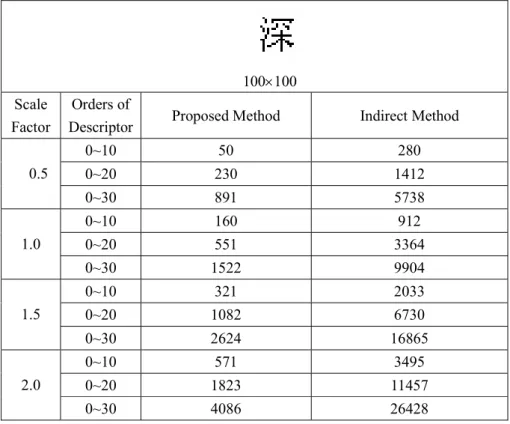
Several experiments have been conducted to validate the effectiveness of the proposed method using a large set of simple to complex samples, with and without symmetries, subjected to different scales or not, corrupted or not by noise. A set of Tchebichef central moments of order up to 3 is calculated for each translation, the results are shown in Table 1. We also use the deviation of the central moments as suggested by Chong et al.
21-22], represented by the percentage dispersion of the corresponding means of central moments σ/µ, to measure the performance of the proposed invariant descriptors. As can be seen from this table, the values of the central moments of Tchebichef remain unchanged for all translations and σ/μ is zero. Moreover, we see that the translation-invariant descriptors take different values for the Chinese character and the Latin character.
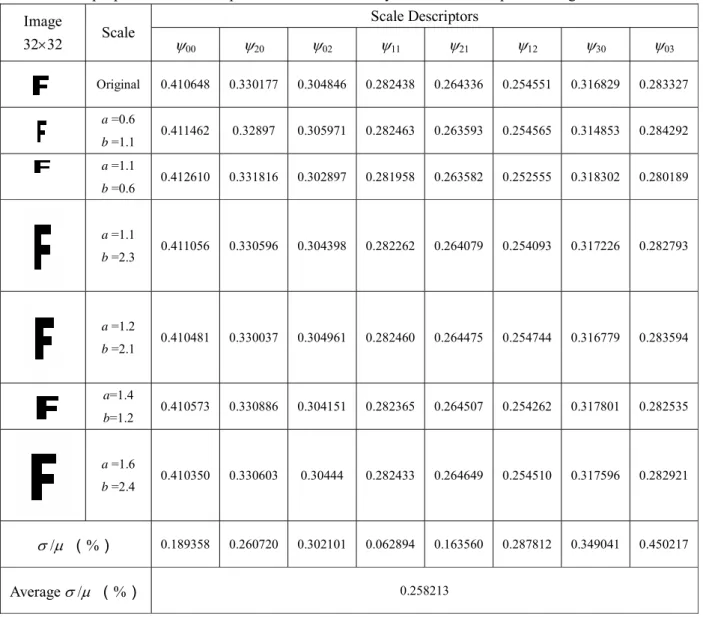
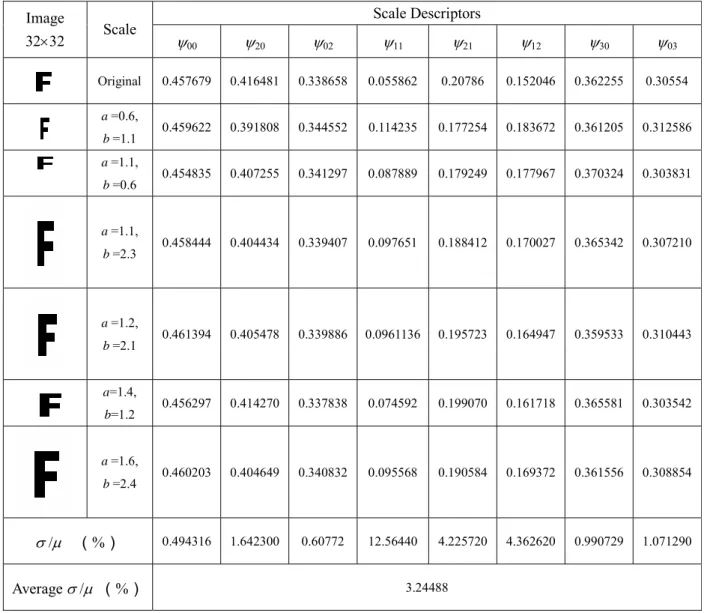
In the third example, we apply both Tchebichef central moments and Legendre central moments to the 32 × 32 pixel English letter 'E', which is symmetric about the x-axis. As can be seen from Table 4, the Legendre central moments L'pq take all zero values for odd order q, while this is not the case for the Tchebichef central moments. From these tables, we can see that the descriptor values remain almost unchanged under different non-uniform scaling transformations and that scale invariants based on Tchebichef moments perform better than those derived from Legendre moments.
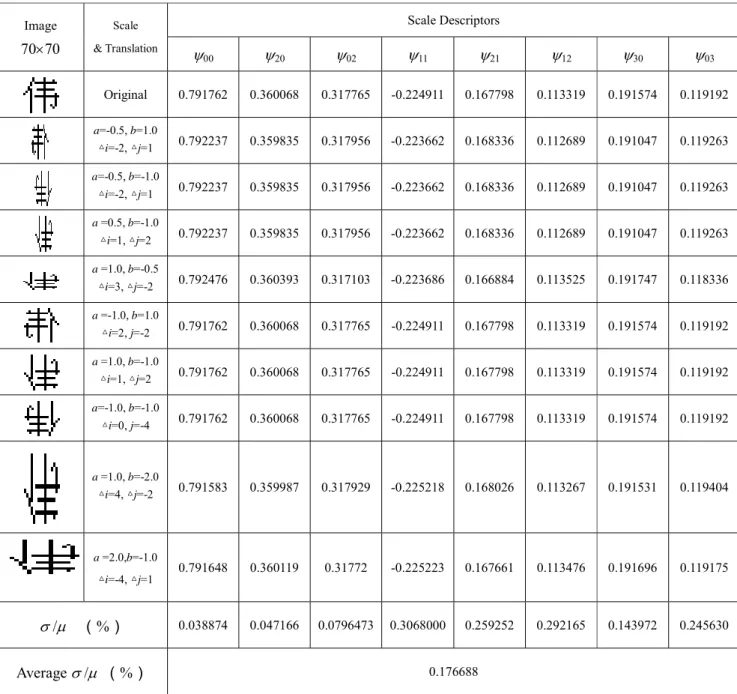
In the third experiment, we test the performance of the proposed descriptors on both translation and scale invariance. We also compare the computational speed of the new approach with that of the indirect method, i.e. the method described in subsection 2.3. During classification, features of the unknown character are compared with the training information assigned to a specific class.
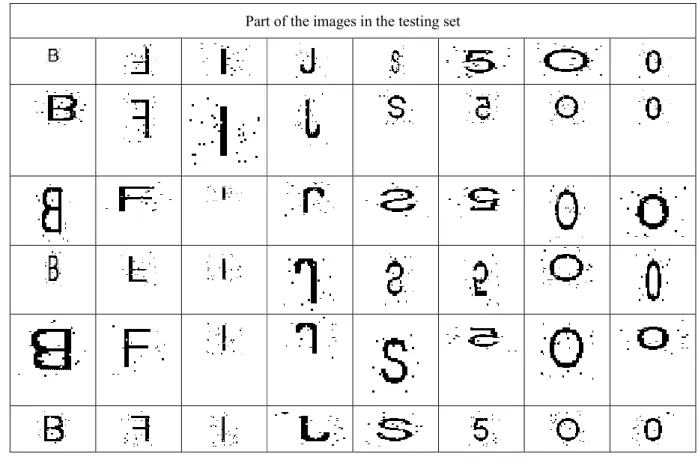
However, the proposed approach outperforms the invariant descriptors based on Legendre moments in terms of the recognition accuracy for . The original images of the second experiment were downloaded from the website [29]. The second test set is generated in the same way as the first test set. The classification results of the image with translation and scaling transformation are depicted in Table 11.
Discussion and conclusion
It was carried out within CRIBs, an international joint laboratory accompanying the University of Southeast, the University of Rennes 1 and INSERM, with a grant provided by the French Consulate in Shanghai. We thank the anonymous referees for their careful review and valuable comments to improve the quality of the paper. Using the change of variable l =k−l′ in the first term of the right-hand side of Eq.
The coefficient of < a >k–i on the right side of the above equation is. Using the change of variable m=m′+k−i in the last term of the above equation, we can easily Eq. Wursig, An affine invariant curve fitting method for photo identification of marine mammals, Pattern Recognition.
Srinath, Combined features of cubic B-spline wavelet moments and Zernike moments for invariant character recognition, In: Proceedings of International Conference on Information Technology. Faez, Signature pattern recognition using pseudo Zernike moments and a fuzzy logic classifier, In: Proceedings of ICIP-96, Switzerland. Mukundan, A new class of rotational invariants using discrete orthogonal moments, In: Proceedings of the 6th IASTED Int.
The proposed translation and scale-invariant descriptors for a translated, non-uniform contracted, expanded, and reflected Chinese character. Classification results of the image with translation and scale transformation Pepper and salt Noise Noise free. Part of the test set images in the experiment. a) Image of Cozume Island.