Logistic regression analysis of the proportion of aphids consumed as a function of initial density showed that all larval instars and adults of P. quatuordecimpunctata exhibited a type II functional response when foraging for A. Data fitted with the random equation of Rogers predators. 2nd, 3rd, 4th instars, adult female and male respectively. Coccinellidae) were exposed for 6 hours in plastic containers with different densities of the black bean aphid, A.
Τα αρπακτικά είδη της οικογένειας Coccinellidae
Το είδος Propylea quatuordecimpunctata
Έχουν προταθεί διάφορα μαθηματικά μοντέλα για τη μελέτη διαφόρων οικολογικών διεργασιών, όπως ο ρυθμός ανάπτυξης των αρθροπόδων ως συνάρτηση της θερμοκρασίας (π.χ. Lactin et al. 1995, Briere et al. 1999), ο ρυθμός αύξησης του πληθυσμού ως συνάρτηση της θερμοκρασίας (Roy et al. 2003), η θήραση ως συνάρτηση της πυκνότητας του θηράματος (π.χ. Holling 1959, Jeschke et al. 2002), ενδοειδική επίδραση (π.χ. Beddington 1975, DeAngelis et al. 1975, Crowley and Martin 1989), ή μεταξύ των ειδικών Lóllepezeuilde Sepulcre 2011) διαγωνισμός κατά τη διάρκεια της αρπαγής. . Η επίδραση έξι ειδών αφίδων σε ορισμένες παραμέτρους ζωής της πασχαλίτσας Propylea quatuordecimpunctata (Coleoptera: . Coccinellidae).
Abstract
Introduction
Although coccidophagous ladybird beetles have been more successful biological control agents than aphid species, mainly due to their ability to develop faster than their prey (Dixon 2000), aphid species cause significant mortality on aphid pests in a number of agricultural systems (Obrycki et al. 2009). A common aphid predator that is widespread in the Palearctic region, and which has also been introduced and established in the Nearctic area (Day et al. 1994), is the fourteen-spotted ladybird beetle, Propylea quatuordecimpunctata L. 1975) and Kalushkov and Hodek (2005) claimed that this species is probably a weak aphid predator based on its relatively small effect against the green peach aphid, Myzus persicae (Sulzer), populations, Papanikolaou et al. 2011) reported an inverse density-dependent mortality of its aphid prey.
Materials and Methods 1. Insect culture
The relationship between temperature and developmental rate was described by the non-linear Briere model (Briere et al. 1999). Therefore, it is suitable for estimating the minimum threshold temperature for development (Kontodimas et al. 2004, Dixon et al. 2009). Estimated parameters (± SE) and coefficient of determination (R2) for Briere (a is an empirical constant; T0 the lower and TL . the upper thermal limit; Tm the point of the maximum development rate) and Ikemoto and Takai (K indicates thermal summation and T0 the lower thermal limit) models mounted on P.
The effect of temperature on preimaginal development duration was previously reported by Obrycki et al. 1993), and Honěk and Kocourek (1988) studied the effect of temperature on the development of eggs and pupae.
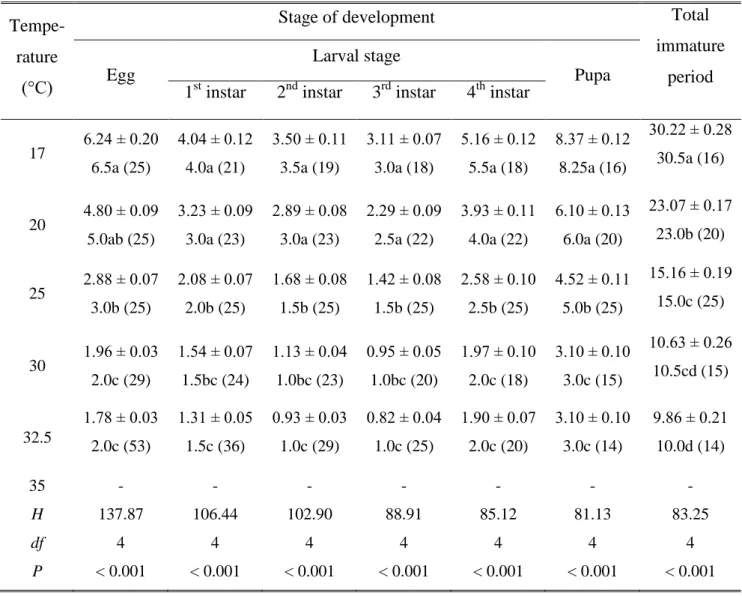
The probability of establishment of a biological control agent increases if the climatic conditions in the release area are similar to those to which the agent is adapted. Moreover, these parameters are useful tools for predicting the phenology of an insect pest and/or its natural enemy, as coexistence of a predator and its prey in field conditions is often desirable. Temperature-dependent development of the two-spotted ladybug, Adalia bipunctata, on the green peach aphid, Myzus persicae, and a virtual food under constant temperatures.
Comparative temperature-dependent development of Nephus includens (Kirsch) and Nephus bisignatus (Boheman) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) preying on Planococcus citri (Risso) (Homoptera: Pseudococcidae): evaluation of linear and different nonlinear models using specific criteria.
Abstract
Introduction
This enables the calculation of several parameters that allow the prediction of insect performance, as well as an investigation of mortality and reproduction patterns. In addition, the ratio of prey to predator generation time is often used as an indicator of prey population regulation (Kindlmann and Dixon 1999, Borges et al. 2012). A Palearctic aphidophagous coccinellid that has also established in the Nearctic region (Wheeler 1990) is the fourteen-spotted ladybird beetle, Propylea quatuordecimpunctata L.
Kalushkov and Hodek (2005) reported up to twenty aphid species as possible food for this predator, including the bean aphid, Aphis fabae Scopoli (Hemiptera: Aphididae). 2013) have detailed information on the effect of temperature on the development, survival, longevity and fecundity of P.
Materials and Methods 1. Insects
Using data on development, survival, fecundity and longevity of P. quatuordecimpinctata from a previous study by Papanikolaou et al. 2013) the following parameters were calculated at 30 ± 1 °C, 65 ± 2% RH and a photoperiod of 16:8 (L:D) h (Kontodimas et al. 2007, Borges et al. 2012): cohort survival to age x; age-related mortality; age-specific fecundity by multiplying the average number of eggs by the ratio ♀/(♀+♂) (observed by sorting 150-200 hatchlings); net reproduction rate; intrinsic rate of increase; final increase rate; mean generation time; doubling time; reproductive value of females; expected remaining life of females. Significant differences between life table parameters at each of the investigated temperatures were tested by superposition of 95% confidence intervals (Wald test) obtained by running in R (R Development Core Team, 2010). The Kaplan-Meier method was used to estimate survival curves for total immature stages and females at each of the temperatures examined.
Kaplan-Meier estimation was used to obtain median survival times and their 95% confidence intervals.
Results
Fitting the Lactin Model to the Observed Values of the Intrinsic Rate of Increase in P. The selection and release of candidate biological control agents are usually based on their comparative values of the intrinsic rate of increase (Gutierrez 1996, Kontodimas et al. 2008 ) . In general, Propylea species exhibit competitive values of intrinsic growth rate compared to other coccinellids (Kontodimas et al. 2008, Pervez and Omkar 2011).
On the other hand, a study of the population parameters of Hippodamia variegata Goeze reared on A. fabae by Forhadi et al. 2011) reported a higher value of intrinsic coccinellid growth rate. 1993) studied three different populations of P.
Life table parameters for the aphid predators Coccinella septempunctata, Ceratomegilla undecimnotata and Propylea quatuordecimpunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Temperature-dependent development, survival, lifespan and fecundity of the aphid ladybird, Propylea quatuordecimpunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Biology and life table studies of the oriental tobacco budworm, Helicoverpa assulta (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), as affected by different larval diets.
Funksionele reaksies van onvolwasse stadiums van Propylea quatuordecimpunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) op Aphis fabae (Homoptera: Aphididae).
Abstract
Introduction
Functional responses of immature stages of Propylea quatuordecimpunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) to Aphis fabae (Homoptera: Aphididae) . 61 and Honĕk 1996). The fourteen-spotted ladybird beetle, Propylea quatuordecimpunctata L., is an aphidophagous coccinellid, widely distributed in the Palearctic region. In Greece it is found in several habitats, such as citrus orchards, tobacco fields, cereals and cotton, preying on different types of aphids (Kavallieratos et al.
Functional response curves are used to understand the fundamental mechanisms driving predator–prey interactions, to elucidate coevolutionary relationships, and to improve practical predictive capabilities for biological control (Houck and Strauss 1985, Martinou et al. 2010).
Materials and Methods 1. Insect culture
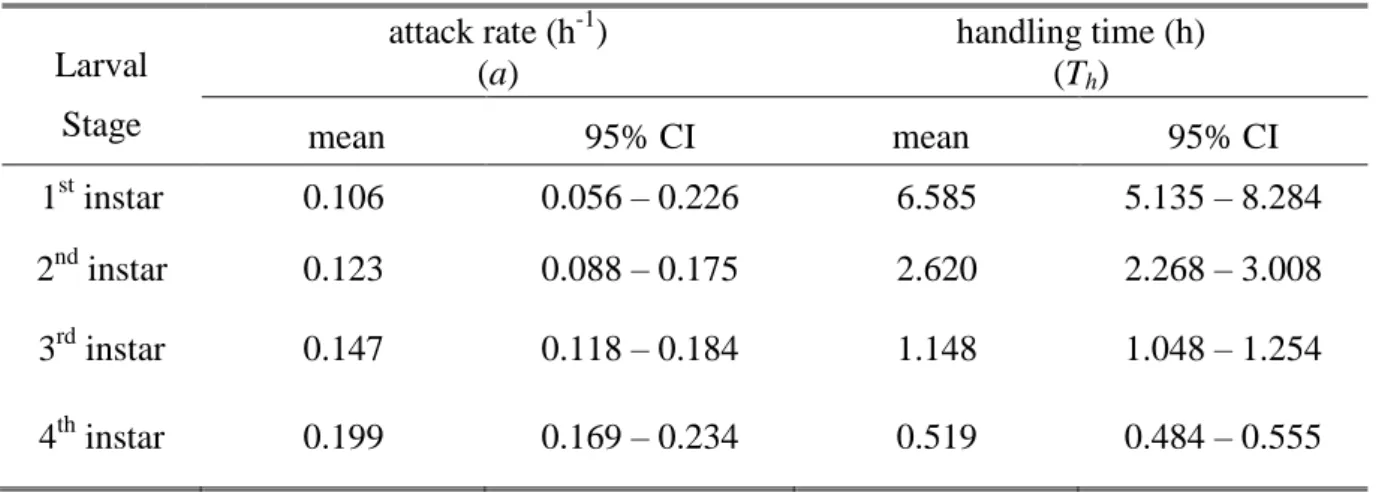
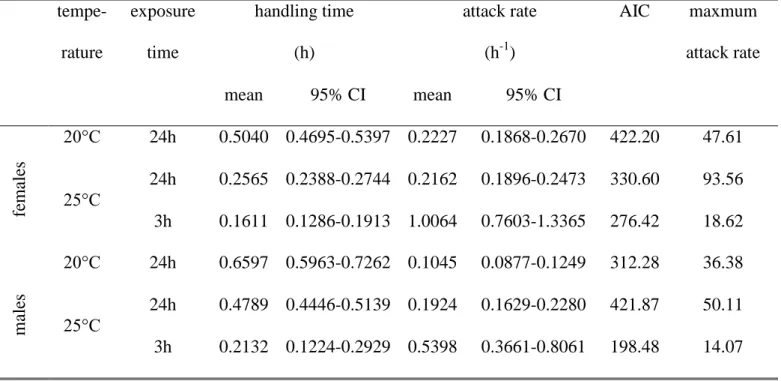
Because the dependent variable is dichotomous (each aphid is either alive or dead at the end of the trial), a logistic regression analysis of the proportion of aphids eaten versus initial aphid density was used to determine the shape of the functional response (Trexler et al .1988). ). The above parameters were estimated using the maximum likelihood method and used to determine the shape of the functional response (Juliano 2001). 63 where a is the attack rate; This is the processing time; T is the total time the predator spent in the experimental arena (24 hours).
Significant differences between functional response model parameters for all larval stages were tested by overlapping 95% confidence interval criterion.
Results and Discussion
The attack rate determines how steeply the functional response curve rises with increasing prey density. The functional response of predators to prey density and its role in mimicry and population regulation. Host plant changes the shape of the functional response of an aphid predator (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae).
Development and functional response of Coleophora inaequalis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) feeding on brown citrus aphid, Toxoptera citricida (Homoptera: Aphididae).
Abstract
Introduction
Subsequently, various modeling approaches for type II functional responses have been pursued with respect to the attack rate (see Jeschke et al. 2002 for a review). Although digestion and handling of prey are discrete phenomena, digestion must be considered as a background process, acting in parallel with the handling of prey, which affects the predator's hunger level and consequently its probability of searching for prey (Jeschke et al. 2002 ). Dissociation between handling time and digestion was suggested by Jeschke et al. 2002), which separates predators into two categories: those whose digestion limits their predation capacity (digestion limited predators) and those whose limitation is the time they handle the prey (handling limited predators).
Ladybird tuqaa kudha afur qabu Propylea quatuordecimpunctata L. gosa Palaearctic beekamaa ta’ee fi raammoo aphid adda addaa kan adamsudha (Kontodimas et al. 2008, Katsarou et al. 2009).
Materials and methods 1. Insects culture
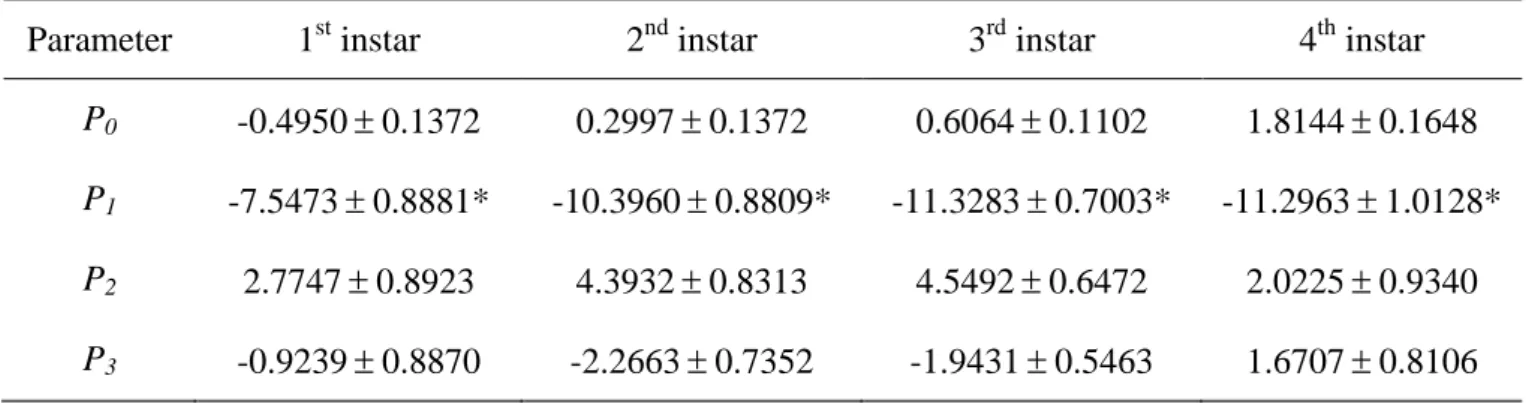
The shape of the functional response was determined by logistic regression analysis of the proportion of aphids eaten versus initial aphid density (Trexler et al., 1988; Juliano. The order of the polynomial function was determined by Akaike's lowest information criterion (AIC). To derive more stable to estimate the calculated parameters, we used Lambert's W function, which provides a numerical solution to the equation W(x)eW(x) x (Coreless, 1996).
We assumed that physiological prey mortality was negligible when compared to predator-induced mortality.
Results
Therefore, prey predation by a generalist predator could conceivably lead to a sigmoid response in the field (Begon et al. 1996). In general, functional response models are characterized by an increase in predation rate to a maximum, where it levels off and reaches a plateau (Hassell 1978, Jeschke et al. 2002). Traditionally, limitation of predation rate at high prey densities has been attributed to handling time or satiation (Mills 1982, Jeschke et al. 2002).
The attack rate can follow a hump-shaped relationship with temperature, as it does for the ladybird Coleomegilla maculata lengi DeGeer (Sentis et al. 2012).
The influence of temperature on the functional response of Anisopteromalus calandrae (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae), a parasitoid of Rhyzopertha domenica (Coleoptera: Bostrichidae). Functional response of the ladybird Harmonia axyridis (Pallas) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) to the aphid Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae). Effect of temperature on the functional response and foraging behavior of the sand shrimp Crangon septemspinosa preying on young winter flounder Pseudopleuronectes americanus.
Towards a realistic predator-prey model: the effect of temperature on the functional response and life history of larvae of the damselfly, Ischnura elegans.
Abstract
Introduction
P the predator; a the attack rate of the predator, i.e. prey mortality per per capita at low prey densities and Th the handling time, which reflects the time a predator spends pursuing, subduing, eating and digesting its prey. Their effectiveness in suppressing aphid populations makes them popular in biological control, especially for short periods (Obrycki et al. 2009). In addition, larvae typically stay within an area during their lifetime, unlike adults, which are characterized by their ability to fly (Dostalkova et al. 2002).
The fourteen-spotted ladybird beetle Propylea quatuordecimpunctata, which is widespread across Europe and established in the Nearctic area (Day et al. 1994), was used as a model organism.
Results
This indicates that the coccinellid feeding rate at low prey densities is modified by a critical predator density. This means that the limitation of predation rates at high prey densities is attributed to satiation. It is expected that at high prey densities, the loss of time during digestion pauses can fully offset the costs of interference (van Gils and Piersma 2004).
Our laboratory study supports that mutual interference does not affect the feeding rate of coccinellid larval stages at high prey densities, whereas at low prey densities it is affected by a critical predator density.
In addition, Agarwala et al. 2003) reported that pregnant females of the aphidophaous coccinellid Menochilus sexmaculatus Fabricious (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) reduced oviposition, but not feeding, when exposed to immobilized species. The components of predation as revealed by a study of small mammal predation of the European pine sawfly. Two common aphid coccinellids that are widespread in the Palearctic region and also established in the Nearctic region are Coccinella septempunctata L. and Propylea quatuordecimpunctata L., which prey on numerous economically important aphid species. septempunctata are invasive in the US, but P. quatuordecimpunctata, although found in many regions of the world, has never been considered an invasive species. 2008) indicate that these two species behave in a very different way to the increasing abundance of aphids; the laboratory studies will allow us to test these observations in controlled conditions.
The modeling component, as the ultimate goal of the project is to incorporate the parameters of the above models into a new model capable of describing and predicting population dynamics in a predator-prey system.