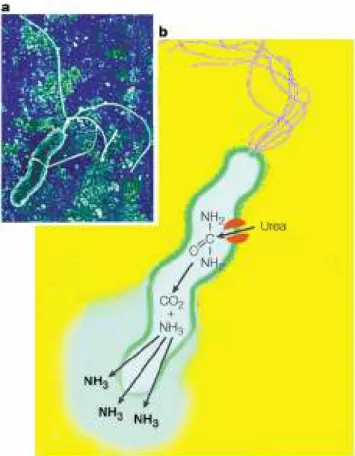
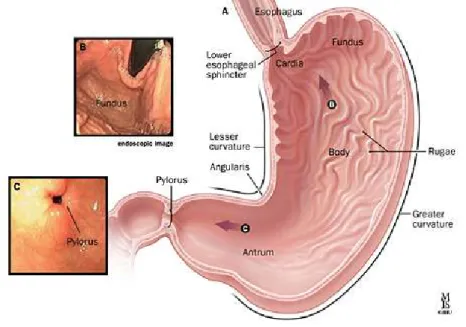
It opens to allow food to pass from the esophagus to the stomach when the food reaches the end of the esophagus. Pylorus: is the lower part of the stomach and contains G cells that secrete gastrin.
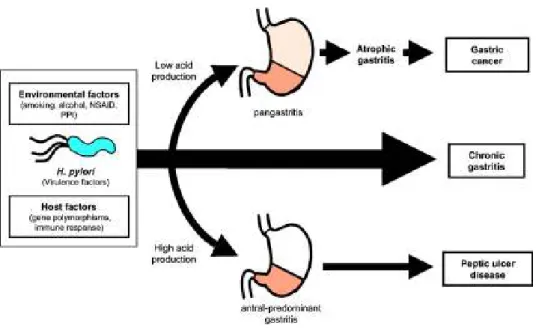
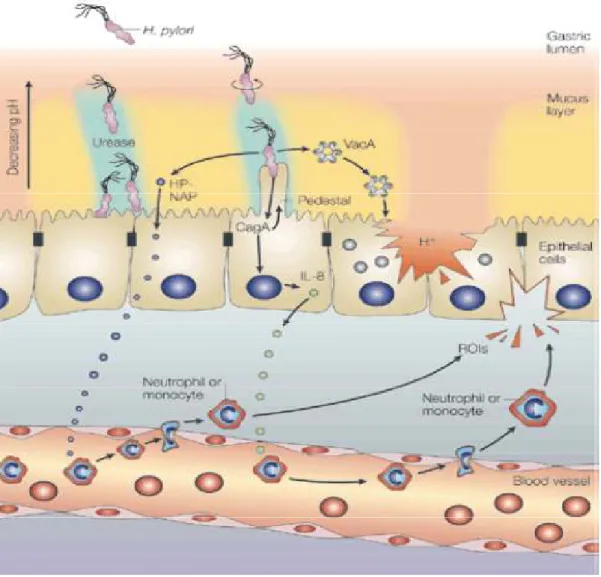
Helicobacter Pylori
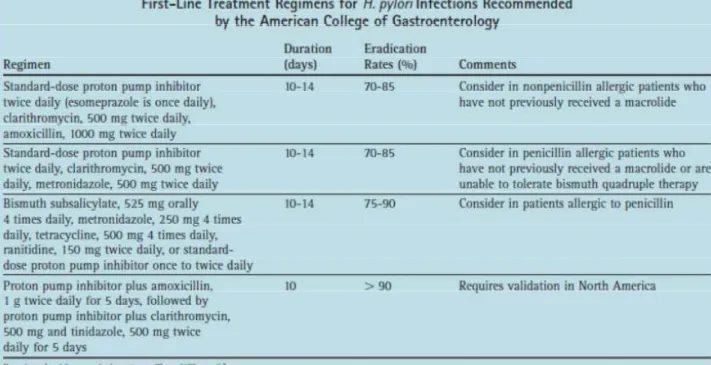
Helicobacter Pylori – Therapeutic Approaches
The most frequent dose of clarithromycin (500 mg three times a day provides even more effective eradication rates between 63% and 81%) (Harris et al., 1995). Resistance to clarithromycin is rapidly increasing at rates of up to 15% due to its widespread use in respiratory tract infections (Tompkins et al., 1997).
Product availability on the market
The outer part of the capsule contains a mixture of 140 mg bismuth subcitrate potassium and 125 mg metronidazole. The use of this capsule formulation does not affect the bioavailability of any of the product components (Table 3).
Helicobacter Pylori – Pharmacology of the treatment
It is a sucrose sulfate-aluminum complex that reaches the mucous membrane and thus creates a physical barrier that impedes the diffusion of hydrochloric acid in the gastrointestinal tract and prevents the breakdown of mucus by acid. Sucralfate is a locally active substance that reacts with hydrochloric acid in the stomach in an acidic environment (pH<4). It binds to the ulcer surface (attaches to exposed proteins) and coats the ulcer, protecting the ulcer surface to some extent from further damage by acid and pepsin.
Directly inhibits pepsin (an enzyme that breaks down proteins) in the presence of stomach acid. The mastic of Chios is produced from the mastic tree, which belongs to the Pistacia lentiscus L. The mastic tree is cultivated or found naturally in the south of the island of Chios, which is the only area that can thrive.
Studies have been conducted to investigate the therapeutic properties of Mastic in the gastrointestinal tract.

Modified release solid oral dosage forms
In this way, it is possible to achieve a constant drug release rate, which reduces drug level fluctuations in the blood and maintains a stable concentration over a longer period. It is thus possible to target drug delivery to its site of absorption or action, reducing unwanted side effects 52 .
Hydrophilic Matrix Systems
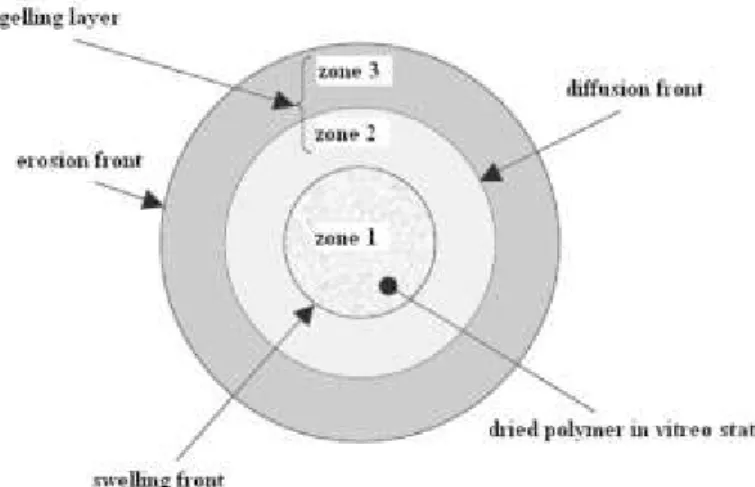
When the content of HPMC in the matrix reaches high percentages (30-40%), the degree of substitution becomes less influential on the release kinetics of the drug. Also, the size of the polymer particles affects the rate of hydration of the polymer itself, altering the release of the drug. The movement of the swelling front depends on the speed at which the water enters the matrix;
Therefore, the undissolved drug is present only in the dry core of the matrix and the diffusion front coincides with the swelling front. In addition, drug solubility also affects the thickness of the diffusion front and its rate of change. Drug release from the matrix is controlled by the interaction between water, polymer and drug 66 .
The properties of the drug that affect the release are the solubility and the particle size.
Release Kinetics
Dome Matrix technology
Female Module
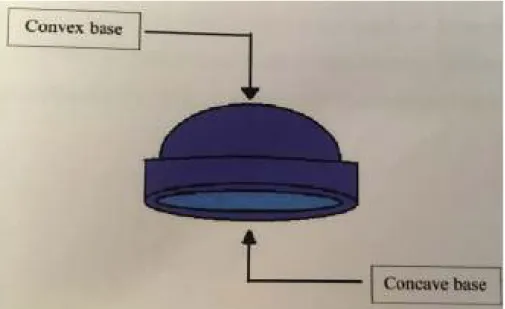
The first, the terminal module, only allows a male or female module to be inserted into its concave base. In contrast, the second type, in addition to being able to receive the module in the base concave, can be folded on its convex base due to the special geometry of its face into the concave base of the second module woman 74 (Fig. 12).
Male Module
Dome Matrix assembling configurations
This configuration is characterized by an internal void that ensures the buoyancy of the assembled system, resulting in delivery systems that can float on the gastric contents and release the drug in the stomach (Figure 16c) 75,76. A configuration of this type may be useful for drugs with an absorption window and a site of action in the stomach. Obviously, with these forms of gastroretentive drugs, gastric emptying must be considered.
By using both configurations, empty and mixed, it is possible to obtain a delivery system in which the modules are assembled in mixed configuration (Figure 17). For example, in the case of chronic diseases, which require the administration of several medicinal products, the Dome Matrix dispensing system can reduce the number of dosage units and adjust therapy, increasing patient compliance. Modules of different drug types, doses and release kinetics can be combined into one single unit.
The targeted therapeutic regimen and drug release kinetics can be tailored to the disease state and healthcare/patient management convenience simply by changing the number and type of modules that make up the system.

Aim of the work
Materials and Methods 1. Materials 1.Materials
Methods
- Development of an HPLC analytical method for Tetracycline HCL and Metronidazole
- Preparation of mastic powder
- Preparation of sucralfate granules
- Manufacture of tablets
- Mechanical characteristics of the tablets
- Measurement of the hardness of the tablets
- Friability Test
- Disintegration time
- In Vitro dissolution test of Metronidazole and Tetracycline HCL (as individual modules and as assembly system) HCL (as individual modules and as assembly system)
- Floating of assembly system
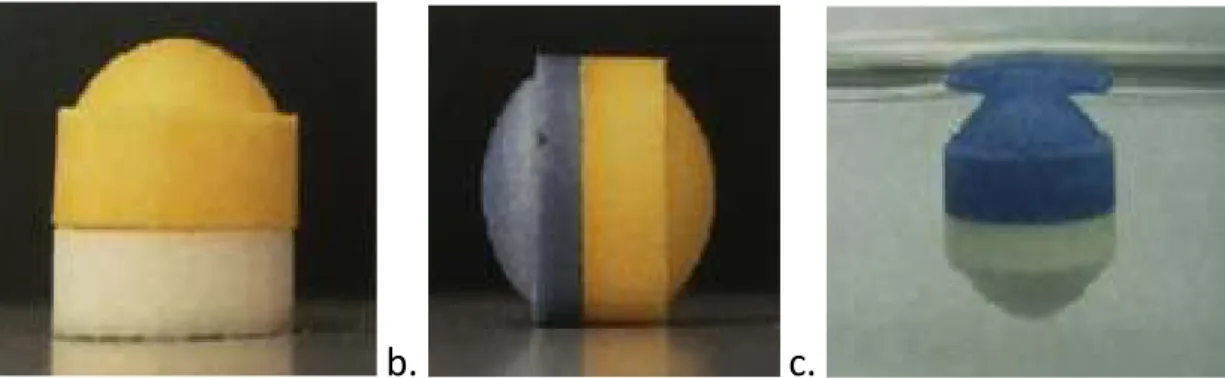
The moist sucralfate gel was manually poured into small pieces and left in the oven for 4 hours at a temperature of 60°C. The assembled systems were obtained by manually 'clicking' the modules in the following way: one female module of Metronidazole (Figure 5a) and one male module of Tetracycline (Figure 5b) were attached concave to concave face. The module is firmly attached to the surface of clamps that are flat and wider than the.
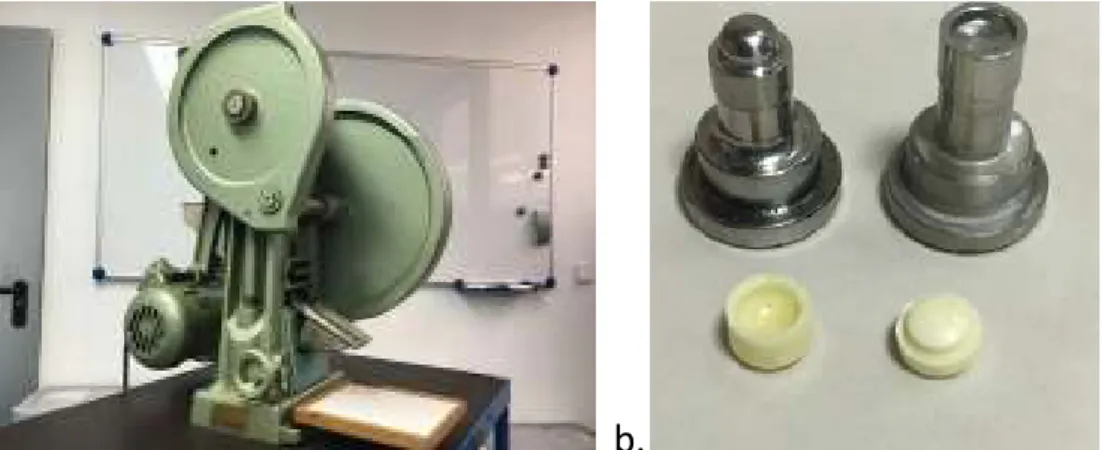
The number of tested modules per batch was twelve (six in one position and six in the other). The tablets were then placed in the drum of the friability testing apparatus (ERWEKA, TA3P, Figure 8) and The modules were tested in two different media; in European Pharmacopoeia pH 1.2 simulated gastric fluid without enzymes and in phosphate buffer pH 3.5 at 37 oC, and 900 ml was used in each container to dissolve individual modules and assembled systems.
The flotation of the assembly system was visually assessed using a type II dissolution tester with 900 mL of dissolution medium.

RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
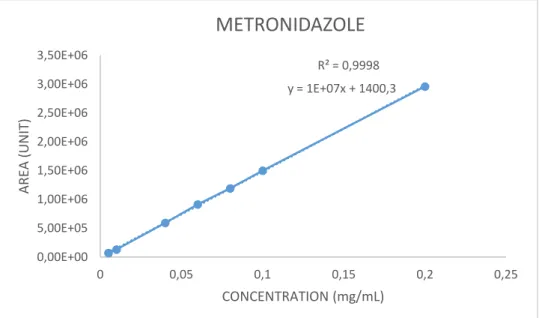
Validation of the HPLC method for the Tetracycline- Metronidazole assay
A complete system of metronidazole-tetracycline HCL was inserted into the container and the flow time was assessed visually. A calibration curve was constructed using 7 concentrations of TTC-MND dissolved in simulated gastric fluid as reported in Figures 1 and 2. Antibiotic stability was analyzed in European Pharmacopeia pH 1.2 simulated gastric fluid without enzymes and in a phosphate buffer pH 3.5 at 37 oC.
Tetracycline HCL and Metronidazole were inserted together into a volumetric flask containing the buffer, placed in a water bath, and HPLC analysis of the samples was performed at frequent time intervals (hours).
Tetracycline HCL pH 1.2
Tetracycline HCL pH 3.5
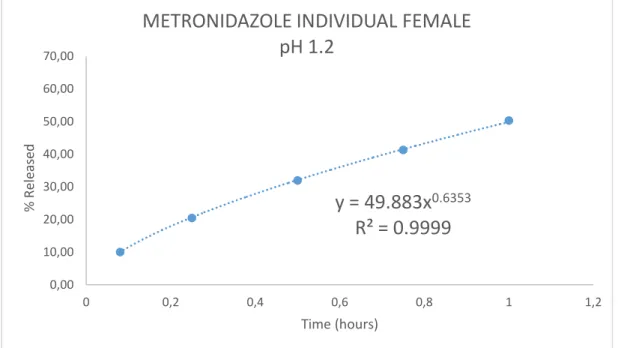
Metronidazole pH 1.2
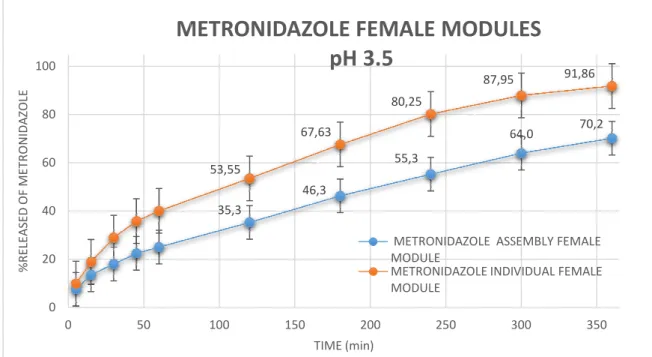
Metronidazole pH 3.5
Formulation of antibiotics
- Manufacturing of Tetracycline HCL controlled release modules
- Manufacturing of Metronidazole controlled release modules
- Manufacturing of Sucralfate immediate release tablets
- Manufacturing of Mastic immediate release tablets
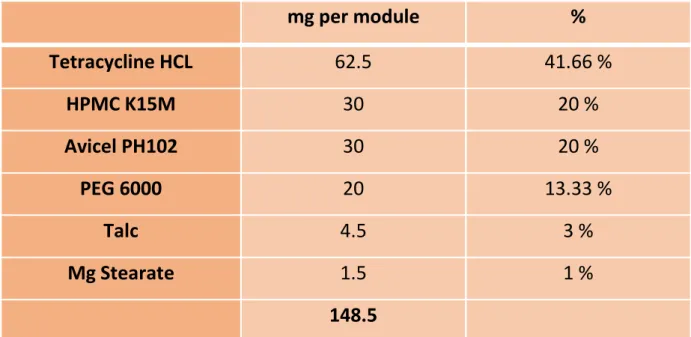
Modules of Tetracycline HCL were manufactured to contain 62.5 mg each and present appropriate mechanical and release properties. Handome Matrix modules of tetracycline were prepared by direct compression according to the procedure described in 3.2.4. Hundome Matrix modules of metronidazole were prepared by direct compression according to the procedure described in 3.2.4.
Sucralfate tablets have been designed to contain the maximum possible amount and have the appropriate mechanical and release properties. The mastic resin was processed according to the procedure described in 3.2.2 to produce the mastic powder. Chios Mastic tablets were made after mixing the powder with appropriate immediate release excipients.
Cylindrical bilayer tablets of Sucralfate-Mastic were produced by direct compression, according to the procedure described in 3.2.4.
Configuration of the final formulation
An advantage of this option is that there is enough space left in each capsule for p. An advantage of this option is that there is enough space left in each capsule for possible expansion of the modules on doctor's prescription. In addition, we can use different colors for identification of their content and better patient.
The patient will therefore take two identical capsules, each consisting of one Dome Matrix assembly system, antibiotics (62.5 mg each module) and one. The advantage of this option is that there is enough space in each capsule for a possible increase in the required modules and that the capsules are identical, which can lead to better patient compliance. suggests using two separate capsules that are identical in composition. Thus, the patient will take two identical capsules, each consisting of one Dome Matrix component system.
So the patient will take two identical capsules, each of which consisted of a Dome Matrix assembly system with a double-layer tablet of Mastic- The advantage of this option is that there is enough space left in each.
Hardness test- Friability test- Disintegration time for sucralfate – Mastic tablets
Dissolution Test for MND
In the case of the two-module gap assembly system, the release rate of both antibiotics was slower and less compared to the cumulative drug released from the male and female modules individually. This is attributed to the fact that, after assembly by "clicking" the male and female modules together, the inner surface was no longer accessible. The dissolution profile of the individual female and female metronidazole module at pH 1.2 in 360 minutes was 99.95%, while that of the assembled system was 90.
In pH 3.5 individual module released at 91.86% after 360 minutes, module void collection system, the release rate of both antibiotics was slower and less compared to the cumulative drug released from male and female modules individually. Tested at pH 3.5, where tetracycline is less soluble ref, the module showed a lower drug release. Specifically, tetracycline as an individual male module released 37.06%, from the middle module released 40.08% at 360 min, and from the overall system the release was 39.8% at 480 min.
Tested at pH 3.5, where tetracycline is less soluble, the module showed a lower drug release module of 37.06 % released, from the medium released module of 40.08 % at 360 minutes and from.
Dissolution Profile of Pylera
Analysis of Dissolution Profiles- Release Kinetics
- Release kinetics -Metronidazole female module pH 1.2
- Release kinetics -Tetracycline male module pH 1.2
- Release kinetics -Metronidazole female module pH 3.5
- Release kinetics -Tetracycline male module pH 3.5
The exponent n value is in all cases higher for the individual modules compared to the assembly, indicating an effect of the module geometry on the release kinetics (see n values in Table 8). In all cases (except the one from the man-middle module) the value n is between 0.45 and 0.89, so abnormal transport takes place. The case of Tetracycline individual man-mean module at pH 3.5 is the only one in which the n value is <0.45.
Conclusion
Mishra, Development and evaluation of a novel floating in situ gelation system of amoxicillin for eradication of Helicobacter Pylori. Linz B, Balloux F, Moodley Y, Manica A, Liu H, Roumagnac P, et al. origin for the intimate association between humans and Helicobacter pylori. Discovery by Jaworski of Helicobacter pylori and its. pathogenetic role in peptic ulcer, gastritis and gastric cancer.
Viala J, Chaput C, Boneca IG, et al. 34;Nod1 responds to peptidoglycan released by the pathogenicity island Helicobacter pylori cag". 34;Role of type IV secretion in the pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori". 34;cagA Status and eradication treatment outcome of anti-Helicobacter pylori triple therapies in patients with dyspepsia without gastric ulcers". Korman MG1, Bolin TD, Engelman JL, Pianko S. Sucralfate as an alternative to bismuth in quadruple therapy for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori” Helicobacter.
In vitro and in vivo activities of Chios mastic gum extracts and components against Helicobacter pylori.