More specifically, Chapter 1 presents the concept of quality and its dimensions, and then refers to the quality 'gurus'. A prerequisite for the successful implementation of Total Quality Management is the effort by an organization's leadership to convey the message to all employees that the effort for continuous improvement must be collective.
Definitions of Quality and the 8 Quality Dimensions
Feigenbaum states in his book 'Total Quality Control' that the quality of products and services can be defined as the composition of characteristics of products and services related to marketing, engineering, production and maintenance, which make the product and service that will be used will meet customer needs (Feigenbaum, 1991). Perceived: Quality based on image, brand or advertising, despite product characteristics, and of course quality is assessed non-objectively.
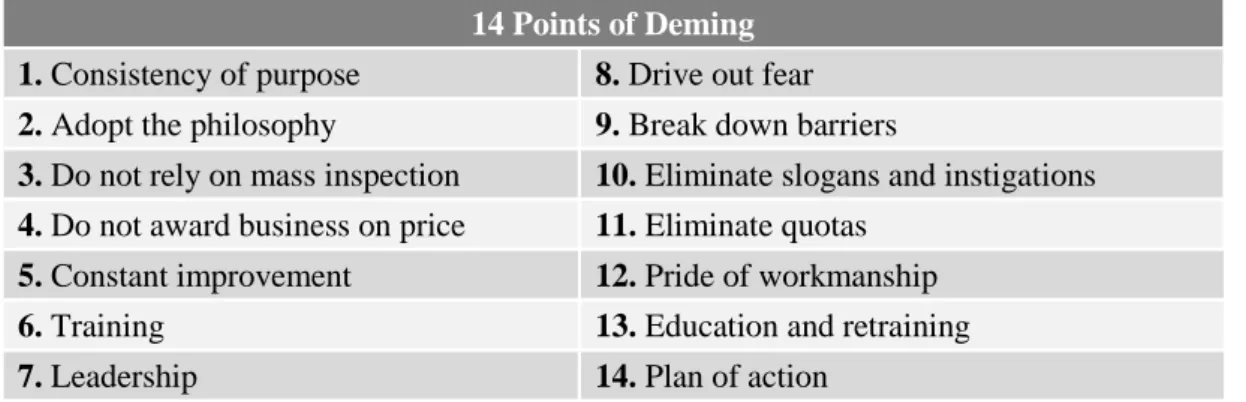
The Quality “gurus”
In 1951, he published the first edition of the "Quality Control Handbook" and it remains the standard reference work for quality managers. In his book Total Quality Control (1983) he develops his ideas for Total Quality Management, regarding aspects such as management of quality, management strategies and quality, engineering technology and quality, statistical technology and control of quality at all stages of the business organization (Volker Krüger, 2001) .
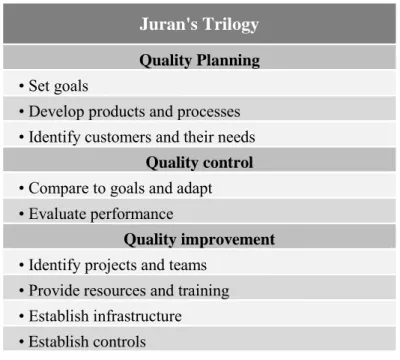
Total Quality Management and its definitions
Despite the fact that the term Total Quality Management is not generally accepted and that there is no generally accepted definition of TQM, several definitions have been formulated, which are discussed below. Pfau undoubtedly gives the most general definition of Total Quality Management, as he defines it as "an approach for the continuous improvement of the quality of goods and services delivered through the participation of all levels and functions of the organization." (Pfau, 1989).
The critical factors of TQM
According to Kanji, TQM is "the way of life of an organization committed to customer satisfaction through continuous improvement. Several authors have proposed through their studies which develop a reliable quality measurement instrument, their critical factors of TQM. The Foundation for Quality Management (EFQM) model in Europe and the Deming Application Award model in Japan (Fonseca, 2014).
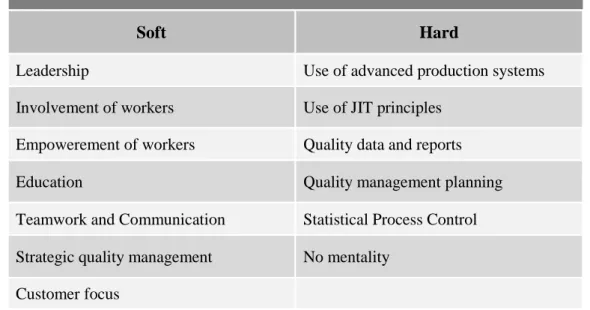
According to Evans and Lindsay (1996), the improvement cycle is also a general methodology for improving the business and consists of four phases: Plan, Do, Study and Act (PDSA). Given the above, the core concepts of TQM can be divided into two broad categories according to the business literature; the social or soft TQM elements and the technical or hard TQM elements (Prajogo and Sohal, 2004). Finally, as we note, the two categories of the core concepts of TQM reflect all the issues a manager must be aware of to fully implement TQM.
Consequently, the implementation of TQM cannot succeed without the use of at least some of the quality management methods.
The Historical Evolution of Total Quality Management
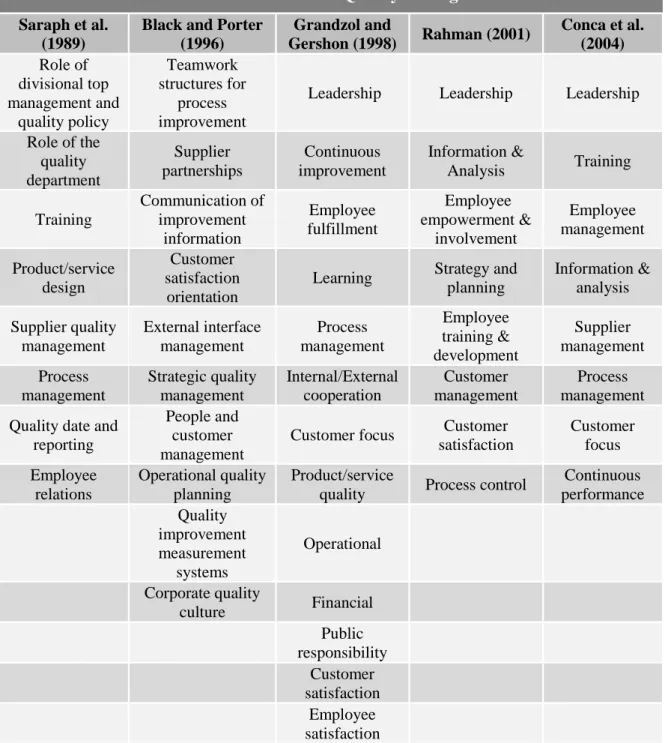
In his 2004 article Rahman, in which he summarizes the research of Saraph et al. Consequently, the Japanese made remarkable progress in quality, resulting in the introduction of Japanese products to the American market (Talha, 2004) . For this reason, the US began using TQM concepts as “weapons” to compete with Japan in the early 1980s.
TQM evolved in four stages to be "designed" as it is now (Dahlgaard et al., 2002). The first stage of TQM development can be seen in the 1910s, when Ford Motor Company rolled one of its models off the production line. The fourth level, TQM, involves understanding and implementing the principles and concepts of quality management in all aspects of business activities.
Implementing TQM is not an easy task as it requires a complete change in organizational culture, a shift of responsibility to management and continuous involvement of everyone in the quality improvement process and procedures.
Human Resource Management
- Personnel Management
- Human Resource Management
- Similarities and Differences between PM and HRM
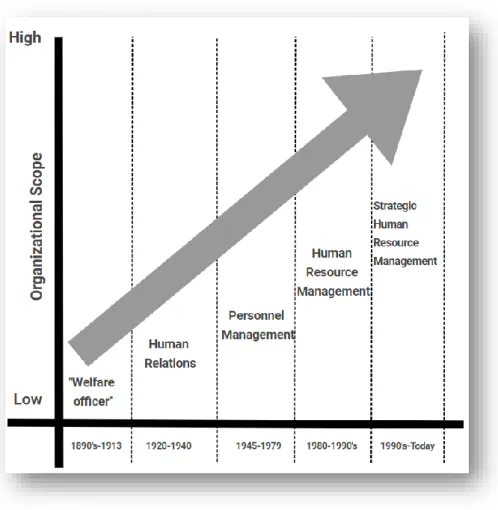
- The historical evolution of HRM
Therefore, Human Resource Management is one of the leading factors in business. According to Hitt, Ireland and Hoskisson, human capital refers to the knowledge and skills of the entire human potential of a company. Finally, according to Armstrong, HRM is defined as "strategic and coherent approach to the management of the organization's most valued assets - the people who individually and collectively contribute to the achievement of organizations' goals" (Armstrong, 2016).
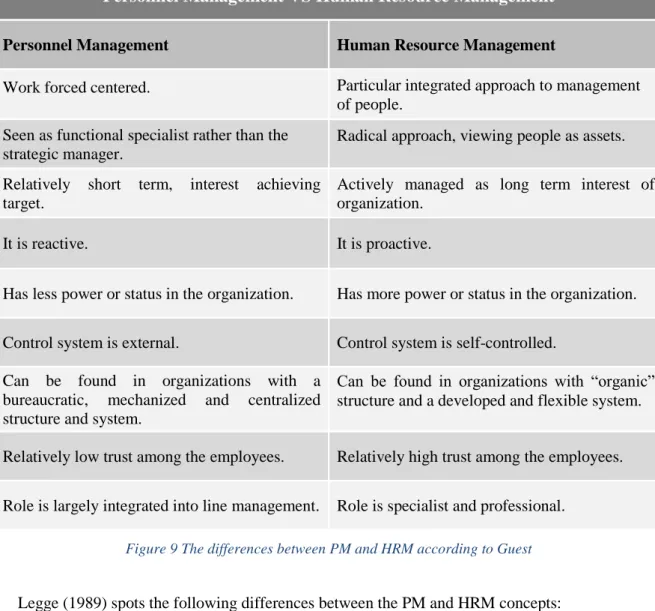
Now that we have presented some of the most significant similarities between PM and HRM recorded in the modern literature, we must also show the differences between these concepts respectively. While Personnel Management is presented as an administrative process aimed at subordinates, Human Resource Management emphasizes the importance of developing employees and managers. Along with the development of theories of human behavior in organizations, the need to manage people to contribute more effectively to organizational success was also emphasized.
In addition, during the same period, William F Taylor's scientific management theory made a huge impact on the foundation of the modern Human Resource theories.
TQM implementation in organizations
Total Quality Management and Human Resource Management
Implementation of TQM in the organization requires support from top management and all staff members. The role of the HR manager in improving quality can be important as it is a primary internal change. HRM and TQM, including supplier and customer association to improve products and processes, are two of the bulwarks of improved competitiveness (Huerta Arribas et al., 2005; Aragon-Sanchez and Esteban-Lloret, 2010).
Therefore, the role of the HR department is crucial to the success of TQM practices (Abu-Doleh, 2012). The formation of the strategy of the quality initiative and the development of quality facilities that take sufficient account of people management. In the next section, we will discuss the impact of HR practices on the implementation of TQM according to the business literature and research.
We will also mention the results of TQM implementation on employees and on company performance.
Impact of HR practices in TQM implementation according to previous studies
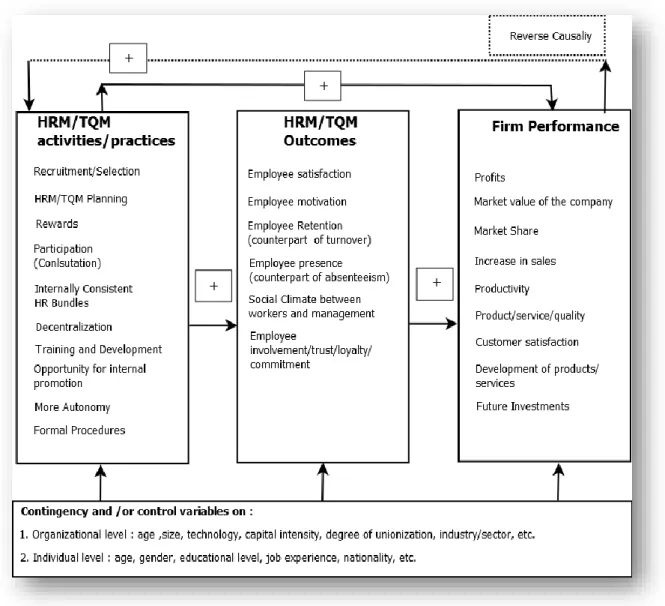
There have been several studies in the business literature that examine the effect of different HRM practices on TQM implementation. Other results of HRM/TQM are: employee motivation, employee retention, employee attendance and social climate between workers and the organization. Figure 16 shows the HRM/TQM activities that are related to HRM/TQM outcomes and firm performance and is an adapted version of J.
Paauwe and Richardson (1997) summarized relevant research on the relationship between HRM/TQM practices and performance, and made a clear distinction between their outcomes, which we mentioned above, and business performance indicators such as profit, market value of the organization, market value and performance indicators. share increase in turnover, productivity, product/service quality, customer satisfaction, product/service development and future investments. It would be appropriate to mention that in some circumstances there will be reverse causality between HRM/TQM practices and business performance. For example, an increase in turnover, which also means an increase in profit, can result in a greater willingness to invest in HRM/TQM practices, such as recruitment and selection and training and development.
Finally, Paauwe and Richardson support that some other contingencies, such as the size of the company or the level of technology it uses, have an impact on the organizational level, and as age, gender or level of education for each level. effect on HRM/TQM practices and.
Recruitment and Selection, Training and Development and Incentive Compensations 30
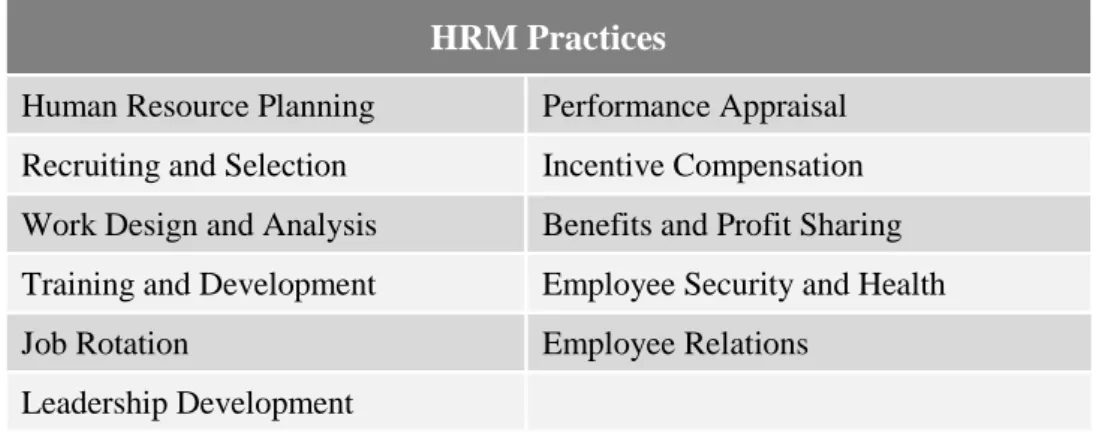
- Training and Development
- Incentive Compensations
Durai (2010) stated that the effectiveness of recruitment and selection can be measured by the quantity and quality of the candidate pool. What may differ from common practices is the emphasis on a quality-oriented organizational culture as the desired outcome of the selection process. In addition, the effectiveness of the training can also be determined by specifically mentioning the qualities of the trainers.
Organizations must realize the necessity and importance of the business training and development process because the main purpose of training and development is to ensure the availability of skilled and willing labor in an organization (Patro, 2013). Moreover, the HR department should focus on analyzing the training needs and preparing the budget for each department. Due to the increasing complexity of the tasks and skills required in the modern business environment, the development of effective training programs is of paramount importance (Lee et al., 2012).
It is therefore essential to establish the compensation system in a way that will act as an incentive factor and contribute to the implementation of the TQM philosophy to an organization that, as we know, is the firmness of competitiveness.
Conclusion
1992), “Total quality-oriented personnel management”, Organizational Dynamics, Vol. 1999), "Human Resource Management: Theory and Practice". 2002), “Focusing on key elements of TQM – evaluation for sustainability”, The TQM Magazine, Vol. 1999), "Managing Quality", Blackwell Publishers, Oxford. 1994), "Total quality and human resource professional", The TQM Magazine, Vol. 2004), "Strategic Management: An Integrated Approach" (5th ed.), Houghton Mifflin, Boston, MA.
2017), "Impact of total quality management implementation on the effectiveness of human resource management in the Jordanian banking sector from the perspective of employees.", Academy of Strategic Management Journal, Vol. 1992), "New Developments in Employee Involvement", Department of Employment Research Paper. Total Quality Management: Text with Cases”, 4th ed. association with job involvement'', Personnel Review, Vol. 2009), “HRM and performance: achievements, methodological issues and prospects”. The International Journal of Human Resource Management How HR professionals drive TQM: a case study in an Indian organization”, The TQM Magazine, Vol. 2013), “The Role of Human Resource Management in Implementation of TQM.”, International Journal of Computer Science and Management Research Total Quality Management gives companies a way to strengthen their position in the global market”, Industrial Engineering, April.
1990), "Editorial: HRM in an international perspective", International Journal of Human Resource Management, vol. 2004), “The sustainability and evolution of quality improvement programs: an Australian case study”, Total Quality Management A comparative study of TQM practice and organizational performance of SMEs with and without ISO 9000 certification, International Journal of Quality & Reliability Journal, Vol . . 1996), "The relationship between the amount and helpfulness of entry training and job outcomes", Human Relations, Vol. 1989), “An instrument for measuring the critical factors of quality management”, Decision Sciences, Vol. 2015), "History, Evolution and Development of Human Resource Management: A Contemporary Perspective", European Journal of Business and Management, Vol.7, No.9.