His special interest and knowledge of issues related to privacy and new technologies allowed him to guide and motivate me. Finally, I would also like to thank my family, who have always supported me in my education, because without them none of this would have been possible. The thesis deals with the need for privacy, which has arisen due to the rapid development and use of new technologies in all areas of our lives, especially in their use in smart cities, which are rapidly developing.
However, many smart cities have not fully embraced the methods that define a city as "smart", as they lack the necessary means such as proper design, networks. For this reason, as in many other technological areas, in smart cities there are frequent violations, which aim either to steal data and damage the proper functioning of these systems or to cause moral or economic damage.
Privacy on Smart Cities
In the first chapter, we describe the topic of the thesis identifying the research area in which it is involved and at the same time the contribution to the reader and subsequent researchers and in general in the field of IoT and cyber security. In the second chapter we analyze the architecture, categories and characteristics of smart cities as well as the applications of smart cities, giving examples in order to give the reader the opportunity. In the third chapter, we inspect privacy and analyze the basics of privacy, the importance of privacy by design, and privacy issues.
The fourth chapter is about the challenges that come after changes, such as smart cities. In the fifth chapter, we refer to solutions, such as understanding privacy, educating individuals about privacy issues and risks, and list smart city security requirements and potential improvement.
Smart Cities
The sensing layer is the lowest layer of the architecture and is mainly used for data collected by devices such as sensors, cameras, etc. However, cloud computing usually has some disadvantages due to the transfer of large amounts of data. This can improve the efficiency of the applications as a decision can be made quickly based on the data received, which is important in critical decision-making situations.
Looking back at the timeline of smart cities, we can note that the first smart city was in Los Angeles. The State of the City: A Cluster Analysis of Los Angeles project was established in 1974 and has been characterized as the first major urban project in the history of smart cities. There are many types of smart energy, but two of the most popular are solar energy and natural gas.
The result of a failure on the producer's and consumer's side is an outage or breakdown of the network. One of the most famous examples is the National Grid, where they use technology in As we will discuss in the sections below, to understand the importance of privacy in smart cities, we can imagine an attack in one of the main systems of a smart building, viz. in the access control system.
Mobile learning emphasizes the use of mobile devices and focuses on the mobility of the. Another reason why this category tops the list is that there are several solutions with selected projects that support IoT platforms. Below we see a graph showing the top ten application areas of the previous yes.
In the next position, which is the seventh position in the top ten, we can find the area of the supply chain. In the last position of this list, we can find random IoT applications, which occupy 3% of the smart cities project.

Privacy
Organizational usually does not refer to individuals, but to a group of people, for example government agencies, companies, groups/associations and others. All of the above aspects have been established in the field of personal data and privacy for almost a century and are taken seriously when personal information is compromised, published, processed or exploited without the consent of the person to whom it belongs. In 2010, the International Assembly of Privacy Commissioners and Data Protection Authorities recognized the concept of privacy by design as an essential part of fundamental rights and is a core part of the European Union's GDPR.
First of all, it is necessary to define the purpose of the specification, which means that it must be registered which personal data is collected, used, stored and. Additionally, any information they collect should be minimal, and most of the time the collection of personal information must be fair, lawful and limited to what is necessary for the stated purposes. Privacy by design can be a solution to many threats because it can allow engineers to design correctly from the ground up and most of the time to predict as many privacy issues as possible.
Human behavior is one of the biggest paradoxes in the field of privacy and a lot of interesting research has been done. This type of attack is called a cyber attack and the attacker's target is computer information systems. Typically, an attacker can be an individual or group of people trying to access data in restricted areas without permission, possibly with malicious intent.
The default configuration in IoT devices and systems is one of the biggest mistakes made and when an attacker notices this kind of weakness, he can easily gain access due to the weak, without complexity, password and network settings. In the first case, an active attack attempts to modify resources or damage the operation of the systems. Typically, the targets are devices such as IP cameras or home routers, IoT devices that are often designed with poor security or even no security at all.
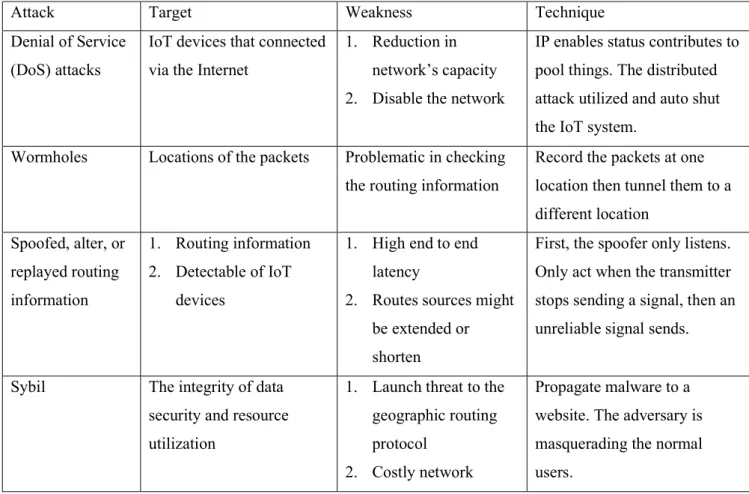
Challenges
They are also one of the core components of IoT infrastructure in a smart city, as they provide access to various services and applications. Furthermore, the way to control objects in a smart city through a smartphone is called Machine to Machine (M2M) communication. All of these types of attacks and many more can provide access to unauthorized individuals who wish to harm a smart city.
In other words, smart city applications must always be up and running, regardless of the type of vulnerabilities or security efforts. Data is the source of IoT, and smart city systems perform the daily tasks of producing, collecting, transmitting, and mining it. Therefore, it is unclear whether privacy would be compromised if smart city organizations monetized the personal data they collect.
Therefore, the monetization of personal data should be thoroughly examined if a core organization in a smart city is to undertake it. Although this practice already occurs every day in the Internet market, if it happened in a smart city, it would be an inevitable part of life that could artificially create different experiences inside. In the near future, social media will most likely be used to facilitate social interactions in a smart city.
In short, securing a smart city with such effective means will be unattainable without proper implementation. Another big challenge is maintaining the trust of citizens, which is so important for maintaining a smart city. This is a kind of motivation for organizations to respect the laws of the smart city.
Solutions
One of the reasons is the way the sensors are made, most of the time they are resource limited, so it is necessary to develop a lightweight method for intrusion detection. One of the most fundamental requirements is authentication, it is used in all different layers of a smart system and is needed to prove identities and ensure that only authorized people can access services across the system. The challenge is to develop advanced technologies that guarantee real-time authentication independently of the growing data from smart cities.
In other words, four different security requirements should exist in every smart city and even in smart devices to protect users' privacy. However, some of them are difficult to install due to the complex design of the devices. Security techniques are another method that includes the triad of a protected system, that is, confidentiality, integrity, and availability, and the techniques can be public key encryption, symmetric encryption, and hashing.
Technologies that use encryption techniques can protect all data up to the strength of the encryption algorithm. In addition to the above, which is the backbone of the security of a smart city, there are also several technologies that we can implement, with the main objective on the one hand that smart cities work correctly and on the other hand the protection. of personal data and sensitive information about citizens. Therefore, the substitution method is an anonymization method that protects the end user's data.
In simple terms, encryption is the method of hiding information in a way equal to the strength of the algorithm and cryptographic key used. During the transmission of messages, information is revealed in the form of confirmation of the occurrence of that communication between parties. This method can be used in a health organization database, where the source or the destination of communication is preferred to be hidden or in many other applications because mixed networks can protect both categorical and numerical information in the network layer and also the identity of the participants. in a way that the path cannot be traced back to the source.
Conclusion
We need to understand that the knowledge we have about new technologies and privacy, if combined in the right way, can improve our way of life.
34; Smart mobility: opportunity or threat to innovate places and cities." 20th International Conference on Urban Planning and Regional Development in the Information Society (REAL CORP 2015).