Advances in chemistry are beginning to unlock the muscles of the brain: discoveries may help cure alcoholism and insomnia, explain mental illness. However, the text attributed to him does not mention the term diabetes.
Diabetes Mellitus in ancient Greek medical writings Aretaeus of Cappadocia, “On the Causes and Symptoms of Acute
The first evidence of the disease diabetes mellitus, but not the exact term diabetes, is believed to be traced to one of the oldest extant papyri, namely, the 'Ebers Papyrus', dating from around 1550 BC and discovered in 1872 .in Luxor by Georg Ebers. This medical document includes a discussion of a "disease involving polyuria, without physical pain, but melting of the flesh," also reports that this disease is accompanied by a general physical fatigue, and records prescription drugs for the treatment of polyuria.
Aimilios Dim. Mavroudis
The next occurrence of the term diabetes is in the work of the physician Aretaeus of Cappadocia, who probably flourished in Rome (mid. This view is confirmed by the passage quoted above, which attributes the coining of the term for the disease to Demetrius of Apameus.
Antihypertensive drugs and their combination in Diabetes Mellitus
Data from many clinical trials revealed the benefit of excellent blood pressure (BP) regulation in individuals with DM. According to recent studies in individuals with DM, target blood pressure is achieved using an average of 2 to 3 antihypertensive drugs.
Eleni Karlafti
According to the results of recent studies, the goal of BP remains a difficult goal, since the percentage of the successful regulation of BP is very low. In addition, the drug combination, due to the synergy of the active substances by different mechanisms of action, reduces the negative effects of.
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Zisis Kontoninas
DKA is usually diagnosed when testing reveals high blood sugar, low blood pH, and ketoacids in the blood or urine. In addition, markers of infection (complete blood count, C-reactive protein) and acute pancreatitis (amylase and lipase) may be measured.
New predictive Biomarkers and novel therapeutic target in Diabetic Nephropathy
The coexistence of glomerular basement membrane (GBM) enlargement and podocyte damage caused by hyperglycemia and enhanced apoptosis leads to a marked increase in membrane permeability, thus predisposing to the development of diabetic albuminuria. However, MA is not an adequate predictor of DN in the young or in patients without albuminuria, and additional biomarkers of glomerular and tubular damage have been proposed to unmask structural lesions of early renal dysfunction before the presence of MA.
Grigorios G. Dimas
Both MMP-2 and -9 are the main enzymes that degrade col-IV, the major collagen component of the ECM and the architectural structure of BM and GBM. New predictive biomarkers that uncover the initial stages of DN, even before MA occurs, will provide an opportunity for preventive and therapeutic interventions that prevent or delay the onset of irreversible long-term complications and improve outcomes, leading to a reduction of the severe cardio-renal morbidity and mortality progression in diabetic kidney disease patients.
Urinary matrix metalloproteinase and their regulators (TRY-1, TRY-2, TATI) in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Urinary fatty acid binding protein of the liver type and progression of diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetes.
Anemia and Diabetes Mellitus
The risk in diabetics of developing anemia is estimated to be 2-3 times higher than in the general population, when comparing patients with similar glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and iron levels. The etiology of anemia in diabetics is a complex, multifactorial and often unrecognized problem (table)3,4.
Georgia Kaiafa
It should be strongly emphasized that HbA1C should only be used to assess glycemia in the absence of anemia. Report of the International Expert Committee on the role of the A1C assay in the diagnosis of diabetes.
Glycemic control in hospitalized patients
In the hospital setting, hyperglycemia is considered any blood glucose (BG) above 140 mg/dl. In the hospital setting, both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia are associated with adverse outcomes, including death.
Ioanna Zografou
Insulin is the best way to control hyperglycemia in the hospital setting, especially in critically ill patients. Exclusive use of sliding scale insulin in the hospital setting is strongly discouraged.
Nutrition before and during gestation in pre-existing diabetes and in gestational diabetes
In addition, gestational diabetes may increase the risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes in offspring later in life. Finally, nutritional counseling before conception is equally important and provides an opportunity to inform patients about the risk of diabetes in pregnancy and to take advantage of the time when the patient is most motivated to make a lifestyle change that will improve the outcome of the pregnancy and the patient's long-term health status. .
Parthena Giannoulaki
This brain area is the center of the homeostatic control of the rest of the body and contributes to the modulation of peripheral insulin sensitivity as well as glucose flux throughout the body. The modulation of peripheral insulin sensitivity by brain insulin action appears to be strongly dependent on the prandial state.
How the brain controls peripheral metabolism in humans
Research from our department and others has shown that the action of brain insulin improves peripheral insulin sensitivity in humans. Using hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamps, we recently demonstrated that insulin delivery to the human brain improves peripheral insulin sensitivity by suppressing endogenous glucose production and stimulating tissue glucose uptake.
Martin Heni
About 34%-40% of patients with DM have chronic kidney disease (albuminuria or impaired renal function). In contrast, triglyceride levels do not appear to predict the progression of retinopathy in patients with type 1 DM.
The role of triglycerides in the pathogenesis of microvascular complications of diabetes mellitus
Several observational studies in patients with both type 1 and type 2 DM have suggested that elevated triglyceride levels are associated with increased risk for the development of albuminuria and for decline in renal function. In addition, several observational studies in both type 1 and type 2 DM patients have suggested that elevated triglyceride levels are associated with increased risk for the development of peripheral and autonomic neuropathy.
Konstantinos Tziomalos
Emerging data suggest that elevated triglycerides are involved in the pathogenesis of microvascular complications of DM. These actions may also play a role in the prevention and treatment of microvascular complications of DM.
HbA1c for screening and diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus – applications and future perspectives
The rate of unknown diabetes was 3.7%, the number needed to screen was 17 in patients older than 50 years. The high prevalence and negative consequences of diabetes require screening and intensified specialized diabetes treatment in hospitals.
Andreas Peter
After one year, the elevated values could be explained by a reexamined history of the patient indicating a shortened erythrocyte lifespan due to accidental splenectomy. If there are discrepancies between glucose and HbA1c values, there may be analytical measurement interference, including pre-analytical influences, or HbA1c may be influenced by the individual itself.
Discrepancies of blood glucose and HbA1c in diabetic patients – How to proceed in individual cases
Apart from clinical symptoms that may be non-specific, especially in type 2 diabetes, both blood glucose and HbA1c levels are used to confirm the diagnosis. Discrepancies between blood glucose and HbA1c in diabetes patients – How to proceed in individual cases.
Erwin Schleicher
In case of pathological hemoglobins or other interfering factors, the determination of fructosamine can help to evaluate the patient's glycemia. The most important factors are inadequate handling of the glucose sample (special tubes are needed to prevent glycolysis) and food.
A novel combination of basal insulin and GLP-1 analog
GLP-1RAs increase insulin secretion by β-cells and decrease glucagon secretion by α-cells, both in a glucose-dependent manner. However, GLP-1RAs- may not lead to sufficient insulin secretion from β-cells to achieve Hellenic Diabetological Chronicles.
Triantafyllos Didangelos
GLP-1RAs also reduce satiety, delay gastric emptying, may reduce body weight, and are associated with a low risk of hypoglycemia. When titrated according to clinical trials and guidelines, IDegLira offers a treatment that is likely to be less complex than adding multiple prandial insulin injections to basal insulin plus OADs, perhaps making adherence to therapy less difficult for patients. trial HbA1c was particularly impressive in the IDegLira arms of DUAL I–V, with a large number of patients reaching the glycemic target after 26 weeks of treatment, and many patients not requiring the maximum dose to do so.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Angiopathy in Diabetes
However, peripheral artery disease may also place subjects with diabetes in a risk category similar to those with established CVD. Any patients with diabetes already have peripheral artery disease, before the manifestation of CVD.
Angela Lehn-Stefan
If so, peripheral artery disease may already represent a condition of secondary prevention of CVD and CVD mortality. Furthermore, plaques in the carotid arteries or carotid artery stenosis also put people with diabetes at a high risk of stroke.
Crosstalk between fatty liver and pancreatic adiopocytes accentuates local inflammation and impairs insulin secretion
This study aims to characterize the pancreatic fat compartment and its role in islet function. To investigate pancreatic fat cells in more detail, primary preadipocytes were isolated and differentiated into adipocytes in vitro.
Susanne Ullrich 1,2,3
Because of this inconsistency, there is a high degree of variability in the reported prevalence of the MHO and MUNW phenotypes. However, most studies suggest that about 1 in 4 obese and about 1 in 10 normal-weight individuals at any given time show the MHO and MUNW phenotypes, respectively 4–6 .
Metabolically Healthy Obese and Metabolically Obese-Normal Weight individuals
Although the existence (and the relatively high prevalence) of MHO and MUNW individuals in cross-sectional studies is not questioned, there is an ongoing discussion as to whether these individuals maintain their status in the long term, i.e. MHO and MUNW status appears to confer a similar risk of developing diabetes in the future, which is higher than the respective risk of MHNW but clearly lower than the risk of MUO10,11.
Konstantinos Kantartzis
Genetics certainly play a role in the pathogenesis of the MHO and MUNW phenotypes, but their relative importance remains elusive. Dynamic status of metabolically healthy overweight/obesity and metabolically unhealthy and normal weight and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cohort study of a rural Chinese adult population.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver disease
Finally, even such large weight loss does not appear to significantly improve liver fibrosis in most patients with NAFLD. Thus, in addition to the lifestyle intervention, pharmacological intervention becomes necessary in many patients with advanced stages of NAFLD.
Who and how to treat to reduce Cardiometabolic Risk
NAFLD is also a very heterogeneous disease, which can be histologically categorized into nonalcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and which has a somewhat different risk of progression to advanced stages of liver disease. Therefore, a tailored therapeutic approach based on precise phenotyping of hepatic and cardiometabolic risk is necessary to provide personalized treatment to our patients with NAFLD.
Norbert Stefan
Inhibitors of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 reduce the rate of hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes by reducing renal glucose absorption, thereby increasing urinary glucose excretion10. The EMPA-REG OUTCOME study examined the effects of empa-gliflozin, compared with placebo, on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes at high risk of cardiovascular events receiving standard care.
Focus on empagliflozin’s efficacy and EMPAREG-OUTCOME study’s data
The EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to evaluate the effect of empagliflozin once daily (at a dose of 10 mg or 25 mg) versus placebo on cardiovascular events in adults with type 2 diabetes at high cardiovascular risk versus a background standard of care. Eligible patients with type 2 diabetes were adults with a body mass index of 45 or less and an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of at least 30 ml per minute per 1.73 m2 of body surface area, Hellenic Diabetological Chronicles.
Spyridon Bakatselos
However, the proportion of patients with acute renal failure was lower in the emagliflozin groups than in the placebo group, and. The United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) considered the relationship between systolic blood pressure over time and the risk of macrovascular or microvascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Arterial Hypertension in Diabetes Mellitus
Hypertension is very common in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM), with a prevalence approximately twice that of the non-diabetic population, and may precede the onset of diabetes1,2. The prevalence of hypertension is further increased in patients with type 2 diabetes and renal disease, as evidenced by increased urinary albumin excretion, compared with patients with type 2 diabetes and no evidence of renal involvement (80% of patients, ranging from 71% of patients with normal urinary albumin excretion - UAE, £30 mg/day - to 93% in patients with macroalbuminuria - UAE³ 300 mg/day)3.
Christos Savopoulos
So the generalizability of the results of SPRINT to patients with DM, stroke and to the frail elderly is problematic17. Proteinuria can be considered a powerful biomarker that predicts both morbidity and mortality in diabetic patients with hypertension and nephropathy.
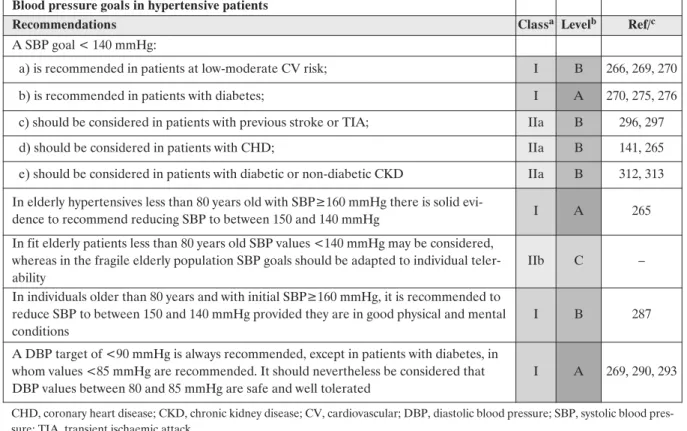
Diabetes Mellitus, hypertension and nephropathy – A vicious triangle
Diabetes mellitus is associated with hypertension and nephropathy, which have a major clinical impact on the course of the disease and its outcome. In this constellation, diabetes, hypertension, and nephropathy appear as a vicious triangle associated with increased morbidity and mortality, primarily due to increased cardiovascular events and death.
Ferruh Artunc 1-3
From a clinical perspective, many patients with diabetes mellitus quite often present in daily clinical practice at the emergency department with symptoms of heart failure and/or pulmonary oedema. Early assessment, diagnosis and management of cardiac dysfunction in the course of diabetes is likely to contribute to the greatest reduction of cardiovascular events due to ventricular dysfunction and heart failure.
Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiac Function
In the present review, we summarize data on the two etiopathogenetic mechanisms leading to LVDD as an initial manifestation and later to heart failure with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction. Heart failure and its treatment are the most important and seriously growing medical and health problem for the entire population.
In this context, the clinical course of cardiac diastolic dysfunction in diabetes mellitus progresses from subclinical cardiac abnormalities to severe diastolic heart failure with normal ejection fraction and finally to systolic dysfunction and finally to heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Diabetic cardiomyopathy is initially characterized by myocardial fibrosis, dysfunctional remodeling and associated diastolic dysfunction, later by systolic dysfunction, and ultimately by clinical heart failure.
Incretin based therapies – novelties to learn 2018
In patients with metformin intolerance or metformin contraindications (e.g. renal failure) they are also often used as monotherapy. GLP-1RA also has a very low risk of hypoglycemia. GLP-1RA also has beneficial potential when using combination therapy with insulin treatment.
Baptist Gallwitz
A GLP-1RA has also received approval for the treatment of obesity independent of type 2 diabetes. Two long-acting GLP-1RAs have shown superiority in cardiovascular outcomes compared to standard antidiabetic therapy.
Introduction
Prediction of Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia: Mechanisms and possibilities of prevention
Asimina Mitrakou
DCCT trial the incidence of severe hypoglycaemia was three times higher in the intensive treatment group than in the conventional2. Just as in studies with type 2 diabetes such as ACCORD, VADT6,7, the rate of hypoglycaemia requiring medical attention was three times higher in the intensive therapy group compared to the standard therapy.
Consequencies of Hypoglycemia 1. Cardiovascular disease and mortality
Furthermore, in the ACCORD study, severe hypoglycemia was associated with sex, race, serum creatinine, age, duration of diabetes, body mass index, albuminuria, education level, insulin use, and higher HbA1c9. Recent analyzes of AC-CORD indicated that c-peptide or GAD antibodies can predict severe hypoglycemia and mortality in type 2 diabetes10.
Physiology and Pathophysiology
In patients with type 2 diabetes, hypoglycemia is associated with several risk factors, including older age, duration of diabetes, comorbidities, more intensive treatment, current insulin treatment, and duration of insulin treatment. This situation is called hypoglycemia unawareness and is associated with a sixfold increase in the risk of iatrogenic hypoglycemia19.
Prevention of Hypoglycemia
Poor cognitive function and risk of severe hypoglycaemia in type 2 diabetes Post hoc epidemiological analysis of the ACCORD trial. Paty BW, Lanz K, Kendall DM, et al. Restored hypoglycemic counterregulation is stable in successful pancreas transplant recipients for up to 19 years after transplantation.
Impact of circadian disruption on energy balance and diabetes risk
Further understanding of the underlying pathophysiology is an urgent need for the development of new preventive and therapeutic strategies. Chronobiology was thrust into the spotlight with the 2017 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine awarded to Jeffrey Hall, Michael Rosbash and Michael Young for their discoveries over the past 15 years of the genetic and molecular mechanisms of circadian rhythms and their fundamental role in regulating cellular metabolism.
Marianthi Archaniotaki
We are excited but passive observers of the "metabolic big bang" that has produced a twin explosion of obesity and type 2 diabetes in the developed world and even in the developing world. The positive part of the loop contains the CLOCK:BMAL1 heterodimeric complex, which binds to E-box motifs and regulates the transcription of circadian genes, including those of the cryptochrome family (Cry1 and Cry2) and the period family (Per1). , Per2 and Per3).
Future Meetings of Hellenic Association for the Study and Education of
Diabetes Mellitus
Scientific Meeting “Diabetes Mellitus. A modern health problem”
2 nd Joint International Scientific Meeting “Diabetes Mellitus. Meet the Expert”
Diabetes Mellitus. Meet the Expert”