Teacher training is part of teachers' professional development (Papanaoum, 2008) and can be achieved through various actions, such as the participation of teachers in seminars, sessions, workshops and educational programs (Papanaoum, 2008). In addition, Papadopoulou (2010) emphasizes that the blended (PEAP) program met the teachers' training needs. Moreover, Krikhaar & Lopriore (2011) summarize that one of the most significant components of successful Foreign Language Learning (FLL) is "teachers' in-carrier training".
The purpose of this study is to explore the opinions of Greek teachers who participated in the PEAP program, regarding their training in EFL.
Early EFL Learning
- Introduction
- Importance of English as a Foreign Language – English Language Learning
- Characteristics of very young learners
- Teaching English in the first grades of the Greek state primary school
- Challenges of EFL teachers
- The Curriculum of English Language Learning in the Greek Primary School
- Conclusion
This is summarized in the Critical Period Hypothesis (CPH, Krashen, 1975), according to which there is a period in a person's life after which language learning is imperfect or incomplete (Muñoz, 2010). One of the challenges in the EFL setting concerns teaching English as a second language. Teachers must participate in creating the school culture through their knowledge and skills by acquiring appropriate skills and competencies (Aubusson, Buchanan, Russell & Schuck, 2012).
Following the principles of the Curriculum assigned by the Ministry of Education, the PEAP syllabus is aligned with the CEFR descriptors and achieves "the earlier the better" concept regarding young learners' progress (Zouganelli, 2013 ).
Teachers’ Training on Early EFL Teaching
- Introduction
- Concept of Teacher Training and Training Types
- Factors of Effective Teacher Training
- EFL Teacher Training in the Greek Educational System
- Teacher training concerning ELL in Greece
- Conclusion
More specifically, the training philosophy addresses questions such as the need and purpose of training, based on the existing education system, and the orientation of the school. The second point highlighted by Papanaoum (2008) is the design of the training program based on scientific data. Adapting the program to teachers' educational needs, the lack of uniformity among the teachers and the difficulty of teaching young learners was another challenge for the designers of the PEAP electronic platform (Karavas, 1998; Dendrinou & Stathopoulou, 2013 ; Papadopoulou, 2013).
In addition, they claimed to feel more confident about teaching in the first grades of primary school.
Research Methodology
- Introduction
- Research Questions
- The Research Methods: Rationale
- Methodological Instruments
- The questionnaire
- The interviews
- Demographic profile of the interviewers
- Conclusion
The quantitative methodological instrument chosen for this study is the questionnaire. Teachers' views on their training regarding the PEAP are explored in the third part of the questionnaire. The fifth part of the questionnaire asks for suggestions from teachers for effective training.
The above-mentioned results confirm that the composition of the teaching staff of PEAP is heterogeneous (Papadopoulou, 2013).
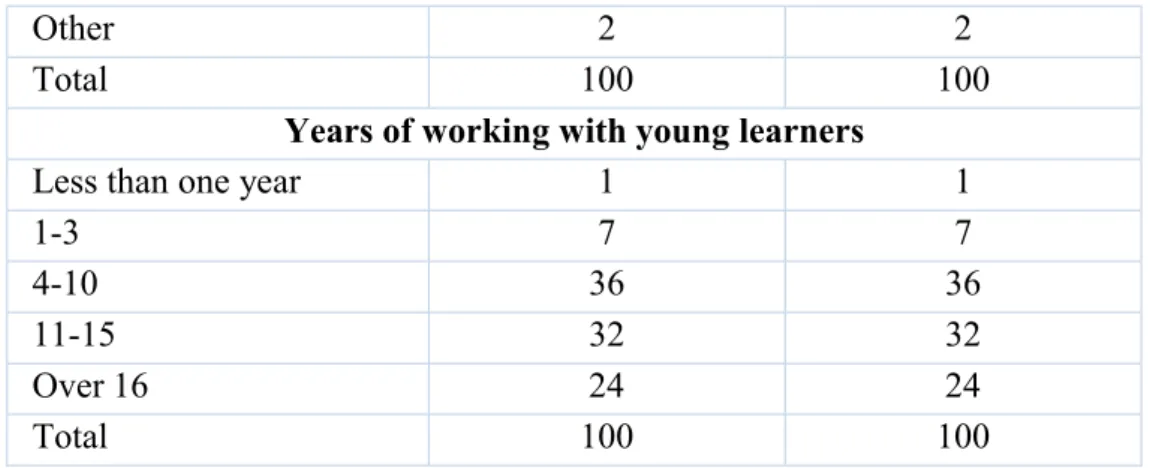
Presentation of the Results
Introduction
The Questionnaire Results
- Teachers’ attitudes towards the PEAP program
- Teachers’ opinions about their training regarding the PEAP program
- Teacher’s training needs and preferences regarding the PEAP program
- Teachers’ suggestions for effective training courses
As can be seen, half of the teachers (57%) claimed that it equally integrated theory and practice. Regarding the PEAP material, however, the PEAP material in Figure 10 (Appendix C, p.93) was characterized as satisfactory, with most of the teachers saying it was satisfactory and 18% saying it was excellent. Despite the above, more than half of the teachers who participated in the research (56%) responded that they feel safe and informed after studying the PEAP program (Figure 11, Appendix C, p.93).
As can be seen, the teaching experience for the PEAP program explicitly influenced their knowledge of teaching young students (61%) and their understanding of the characteristics of young students (57%). ). This section presents the results obtained on the topic of teachers' opinions about their training regarding the PEAP program. In terms of the number of seminars, it can be seen from Figure 13 (Appendix C, p.95) that half of the survey participants (53%) have attended only one seminar in the last four years, followed by those who attended 2-4 (40%) attended.
As can be seen from Figure 15 (Appendix C, p.96), 52% of the teachers who participated in this research claimed that the seminars they have attended on the PEAP program over the past four years has helped them a lot. (46%). As shown in Figure 16 (Appendix C, p.96), a large percentage of the seminars were primarily held by school counselors (86%). As can be seen from Figure 17 (Appendix C, p.97), 69% of the teachers who participated in the survey claimed that they were able to apply some of the ideas presented in the course in their professional practice.
Only 25% used most of the ideas, while 6% said they did not use the ideas presented in the courses. Furthermore, as shown in Figure 22 (Appendix C, p. 100), all survey participants (100%) claimed that they should be asked about the topic of the training course.
Comparative analysis
Finally, the teachers' suggestions were examined in the areas they would like to have a special education regarding YLs. With reference to contrasting teachers' qualifications and their opinion about the PEAP program, significant results were also obtained with a high statistical significance (τ=0.043, p=0.002). Subsequently, the statistical analysis linking the percentage of participants in relation to their work in youth education, for the question of the extent to which the education has helped them with their teaching practice regarding young learners, will be examined (τ=0.082, p <0.0001) .
If we look at Figure 29 (Appendix C, p.104), the researcher can sketch that 62% of the teachers who have worked in secondary education in the past have been helped a lot (55% have been helped a lot and 7% have been helped a lot ). helped a lot). On the other hand, only 26% of teachers who responded negatively to the previous question were helped a lot (22% were helped a lot and 4% were helped a lot). Notable findings emerged from the distribution differentiation of the percentage of participants with regard to their work in secondary education for the item “I was satisfied with the content of these courses” (τ=0.068, p<0.0001).
However, 11% of teachers who have never worked in secondary education were satisfied (7% were satisfied and 4% were very satisfied). In figure 31 (Appendix C, p.105), 63% of teachers who have worked in secondary education were quite interested in meeting other colleagues and sharing ideas and problems with them (21% were quite interested and 42% were very interested). On the other hand, only 11% of teachers who have never worked in secondary education were quite interested.
In addition, the results are also independent of the current job of the participants and their qualifications, except for some special points. However, some significant findings were detected on the subjects of teachers' current working position, their qualifications and their previous experience in secondary education.
The interview results
The types of training participants were exposed to during these courses generally included lectures, group work, and some workshops. As long as we work, we must be trained and we must try to become better and better every year (Teacher B, Appendix E, p.113). The majority of interviewees felt it appropriate to attend such seminars, which were delivered by school counselors, experienced fellow teachers, university lecturers or teacher trainers.
According to the respondents' answers, the seminars should include various topics such as: inclusion of new technology, use of the new material, workshops on drama therapy and theatre. Another issue raised by Teacher A (Appendix E, p.110) as "How to deal with students with learning difficulties and make them love English". Regarding the question of whether they were asked to reflect on their teaching practice during these seminars, most of them responded negatively.
Furthermore, they recommended that they would like to be trained on issues such as intercultural approaches, school psychology, classroom management, drama therapy, and the inclusion of new technology and the use of the new materials, arts and crafts. Likewise, supplementary teachers' suggestions for effective training courses were recorded on the fourth axis of the interview. If asked to suggest the topic of a training course on YLs, they would choose topics related to various issues.
By using the PEAP materials, how we can keep them more focused in our class and how we can make them feel that English is not something to be done only with grammar. The development of writing skills in YLs…….Furthermore, drama techniques and finally ways to develop the sentimental intelligence of Ss.
Conclusion
Introduction
Discussion
- Teachers’ beliefs and attitudes towards the effectiveness of the PEAP
- Teachers’ opinions and the suggestions of EFL teachers about their training
- Teacher’s training needs and preferences regarding the PEAP program
- The problems secondary EFL teachers who work in primary education
- The interviews
More than half of the research participants said they feel safe and informed after studying the PEAP program. More specifically, teaching experience with the PEAP program influenced teachers' knowledge about teaching young learners, as well as their understanding of young learners' characteristics. The positive effect of the PEAP program on primary school teachers has been reported by a number of researchers (Zouganelli & Karava, 2013; Tsianti, 2013).
Through the primary research, it was found that the conducted seminars regarding PEAP have helped more than half of the teachers, but again a high percentage had an opposite point of view. The second research question was partially justified as more practical ideas involving classroom reality are demanded by teachers. It could then be argued that the results of this study are consistent with those of Res & Varsamidou (2006).
A large percentage of teachers who have worked in secondary education were satisfied with the content of these courses, in contrast to the small percentage of teachers who have only worked in primary education. In fact, contrasting teachers' qualifications and their opinion of the PEAP program, only B.A. The question of the differentiated answers between teachers who come from secondary education is often raised in the light of the remarks earlier in section 4.3.
Another interesting point was that most of the teachers interviewed agreed on the necessity of more practical orientation in such seminars. Gyftopoulou (2010) confirms the view that in training courses due to the lack of integration of theory and practice, the courses do not influence the teachers' practices.
Theoretical and practical implications of the study
Introducing new techniques has always been attractive to teachers, but perhaps with more clarification and practical involvement. The view expressed by the teachers in the interviews is consistent with the results of the questionnaire. In this way, the ideas presented in the program can be implemented in educational practice.
The PEAP program could include more training courses on management issues, new trends and approaches in teaching young learners, and specific educational issues about young learners. This was also indicated by Anastasiadou (2016), who emphasized that teachers are interested in training on management issues. Teachers may not be familiar with this type of training and should use the PEAP platform more often.
Limitations of the study and suggestions for further research
Conclusion
Did you take any courses in college on how to teach English to young learners? How many seminars on the PEAP program have you attended in the last four years? . a)1 b) 2-4. Duration of seminars attended by teachers on the PEAP program during the past four years.
Were there any new useful ideas presented during the seminars you attended regarding the PEAP programme?
