59 Table 4-29: Spearman test results for factors in terms of social media consumption hours per connection. 60 Table 4-30: Spearman test results for factors in terms of frequency of updating profiles social media. 61 Table 4-32: Spearman test results for factors in terms of frequency of using ad blockers on social media.
Literature review
The development of generations
- The Lost Generation
- The Greatest Generation
- The Silent Generation
- Baby Boomers: "The Workaholics!"
- Generation X
- Millennials
- Generation Z
- Gen Alpha
It is a generation that fights against social norms and racism and fights for women's rights and environmental protection. It is a generation that has established the routine of a generation that “lives to work instead of working. It is the first generation to grow up in the digital age, and one of its hallmarks is a relatively high dependence on technology and the Internet.
Definition of generation z
In terms of their working conditions, Gen-Zers prove to be quite skeptical of business incentives and very demanding in terms of drafting their employment contracts. For this reason, satisfactory wages are placed quite high in the hierarchy of their demands, while many of them do not hesitate to reduce or terminate their employment when they disagree with business practices or employer values (Deloitte, 2019). Gen Alpha includes people born after 2010 and is the first generation born entirely in the 21st century.
Consumer Behaviour
- Basic characteristics of Consumer Behaviour
- Types of Consumer Behaviour
- Motivation of Consumer Behaviour
- The activities of Consumer Behaviour
- Consumer Roles and Behaviour
- Exogenous factors and Consumer Behaviour
- Differentiation of Consumer Behaviour based on the different personality of the
- Consumer Socialization Procedure in Social Media
- Consumers and Social Media
More specifically, the motivations of consumer behavior are the following: physiological needs, the need for This external influence affects the decision-making process of consumers or Consumer socialization is strongly related to the social media network (Kohler et al., 2011).
Consumer behaviour of generation z
- Consumer behaviour from Millennials to Gen-Z
- Consumer Behaviour from Millennials to the Gen-Zs - The Case of Greece
- Sustainability and quality
Sustainability and targeted goals develop the commitment of the Millennials and Gen-Zs generations, especially in emerging or rapidly emerging markets (China, India, Mexico, Thailand and South Africa), where between 40% and 60% of respondents ( in a sample of approximately 45,000 of these generations) said that they would remain loyal to a company committed to environmental sustainability (Kpmg, 2019). As people with special skills in the use of technology, Gen-Zs consumers have created a new kind of data about consumption, which emphasizes the power of digital channels as a means for survival in the market. Since the representatives of the generation of the Gen-Zs grew up with the mentality that the answer to any question is just a click away, they focused on the speed and they are fast in managing technology.
Consumer behaviour during the Covid-19 pandemic
- Impact of the pandemic on consumer behaviour
Pressure points: Around the world, stress levels are very high - caused by fears of the COVID-19 infection and concerns about the impact of the pandemic on work, education, communities and other areas. 63% of adults worldwide say they are more stressed than a year ago, while 80% say they need to take care of their emotional and mental balance. To combat the monotony of congestion and the restrictions of the home, people are looking for new ways to get away.
Loneliness is widespread across the world - one in two say they often feel lonely. 76% of adults worldwide expect brands to take a stand on social issues - and 75% believe brands today are trying to do the right thing. Market experience: In the midst of the pandemic, the way products are bought and searched for has changed.
75% of adults say they are satisfied with how companies have improved their shopping experience since the pandemic began, while 41% do not want to return to the conventional product purchasing process before COVID-19. The 67% of adults around the world are optimistic about the future of autonomous vehicles, while at the same time 68% of parents would rather see their children ride in an autonomous vehicle than ride next to an unknown driver. Maintaining sustainability: At the beginning of the pandemic, air quality seemed to be the positive side of the global lockdown, but this perception did not last long as people turned to plastic and other consumables, which were no longer sustainable.
Young people in particular seem really worried: 46% of Generation Z worldwide declare that the pandemic has produced even more waste on the planet, and 47% believe that the pandemic will have had a negative impact on the environment in the long run.
Millennials & Gen Z in the post-COVID Era
The pandemic increased the degree of empathy at the individual level, while ¾ of those questioned declared that they were more interested than ever in their fellow human beings, but also in acts of social contribution. Both millennials and Gen-Zers were chosen to financially support smaller and local businesses amid the pandemic. However, they expressed the view that they would not hesitate to reject a company that opposes their own values.
The majority of those interviewed positively assessed the way in which governments and companies dealt with the crisis, but did not express complete confidence. More than 50% of millennials and almost half of Generation Z saved, because they were very concerned about the development of the economy and the economic impact of the health crisis. Finally, young people chose to work in companies with a meaningful vision that cared about their people and advocated the values of diversity and inclusion, sustainability and skills development.
It is surprising that for the first time in the last four years of research, the percentage of millennials who want to invest in a company and stay there for a long time has increased from 21% to 35%, for example for a period of 5 years. It is very likely that the world in the post-COVID era will be shaped in a way that will be in line with the values and trends of millennials and Gen-Zs. The post-COVID society has improved the specifications to recover, something that young people want to achieve (Widjaja, 2020).
Methodology
- Aim-research questions
- Research strategy
- Sample
- Questionnaire
- Data analysis
- Reliability analysis
A total of 165 people participated in the research, the majority of whom were women, of Greek nationality and university/higher education level. The first section refers to demographic characteristics with 5 closed questions regarding gender, nationality, education level, employment status and monthly income. The second section refers to the use of social media with 9 questions (6 closed types, 2 Likert, 1 multiple response) regarding the use of social media marketing communication, means of access, time and frequency that users use the social media, how often they log, the number of hours spent on social media per log in, the frequency of updating the social media profile, the exposure to social media content that includes marketing communications, the frequency of using ad blockers when using social media, as well as the type of social media platform they use.
The third section comprises 54 questions that refer to variables of cognitive attitude which are the awareness (9 questions) and knowledge (9 questions), to variables of emotional attitude which are the taste (9 questions) and preference (9 questions) and to the variables of behavioral attitude which are the intention to buy (9 questions) and purchase (9 questions). Scale and Likert variables were presented in the first research question by means of means and standard deviations, while nominal variables with frequencies and percentages were also presented. In the second research question, the statistics performed were parametric independent samples t-test, ΑΝΟVA, non-parametric.
In the third research question, multiple linear regression models were used, with dependent variables behavioral attitude factors and independent variables cognitive and emotional attitude factors (Field, 2017).

Results
Descriptive statistics
- Demographics
- Use of social media
- Cognitive attitude
- Emotional attitude
- Behavioural attitude
Inferential Statistics
- Reliability analysis
Thesis 55 Table 4-20: Results of ANOVA and Kruskal Wallis test for factors with employment status. Thesis 59 Table 4-27: Spearman control results for factors in relation to time spent on social media.
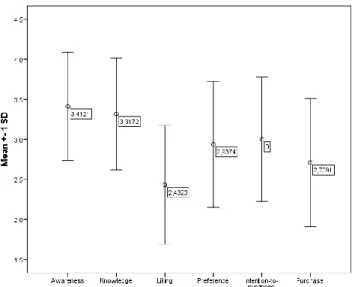
Conclusions
Theoretical Implications
In this regard, the implications that the research of this thesis revealed were similar to the hypotheses, but also to the theoretical background of the thesis. The channels and frequency of social media use influence consumers' purchasing choices. Nevertheless, frequent social media users are more likely to identify and consciously engage with marketing campaigns.
It is not proven that advertising a product/brand on social media in itself influences purchase intention or the purchase itself; unless a number of other conditions are met. Generation Z representatives were born into a world of the internet and mobile telephony and are familiar with social media from a very young age.
Practical Implications
Contribution & Originality
Limitations & Future Research
Future Research
The African Journal of Information Systems Influence of social media marketing communication on young consumers. Available at https://www.rga.com/futurevision/pov/gen-z-social-media-and-what-makes-these-digital-natives-tick. Thank you for volunteering to participate in this study on social media use and marketing communications.
Social media marketing communication improves the image of companies I see products advertised on social media. Social media marketing communication is relevant to me and my interests Marketing communication on social media is effective in stimulating my preference in brands. Marketing communication on social media increases the purchase intention of well-known brands Marketing communication on social media has a favorable impact on my purchase decisions.
I would buy the brands that are promoted on social media if I had the money that I intend to buy products that are featured on social media. Social media marketing communications make me more loyal to the brands I buy products from that are placed on social media. I use a lot of the products that are promoted on social media, I buy brands that are featured on social media.
Marketing communication on social networks has a positive effect on my purchasing activities. I buy products that are promoted on social networks.