Differences in emotional intelligence, professional development needs, job satisfaction and work motivation in relation to gender................25 Table 3. Differences in emotional intelligence, professional development needs, job satisfaction and work motivation in relation to the three educational groups…… …28 Table 7. Differences in emotional intelligence, professional development needs, job satisfaction and work motivation in relation to the three age groups of the students the participants teach….31 Table 10.
Literature Review I
Teacher Motivation
Professional identity and identity in general focus on how people understand who they are in relation to the world (Norton, 1997: 410). Research on learning to teach emphasizes the importance of teachers' personal biographies in their professional growth and flourishing (Kagan, 1992). Similarly, teachers' behaviors, attitudes, and beliefs are motivations carved out of prior experiences, social contexts, and educational environments.
Teacher‘s Personal and Professional Development
This leads to the assumption that each teacher creates his/her personal and autonomous pedagogical model profile. Every initiative that the teacher undertakes, as well as the way he/she instills these initiatives in the students, evokes in his/her students. However, it is not the teacher's responsibility to provide answers to problems as a deus ex machina, but his/her task is to help students achieve a form of critical thinking about the situation (Freire, 1973 as cited in Rugut and Osman, 2013 :24).
Literature Review II
Job Satisfaction
Emotional Intelligence
In the same vein, Gkonou and Mercer (2017) found that there is a relationship between self-efficacy and language (in)security. Based on this finding, it could be hypothesized that conflict resolution strategies in the workplace could be considered as aspects that allow teachers to develop self-efficacy and emotional intelligence. Finally, studies on social-emotional intelligence and self-efficacy in Greek EFL teachers were not found.
Conclusion
However, this study, which was conducted for EFL Greek teachers, found that emotional intelligence is the cornerstone for teachers. To summarize, job satisfaction is a kind of emotional tribute to teachers' professional progress, which confirms their teaching effectiveness and the fulfillment of their goals. We could assume that motivation is the spark to enter the teaching profession and set goals to develop professionally, whereas emotional intelligence is the awareness of our inner self, which stems from relationships with others.
Research Methodology
- The Research Questions
- The Participants
- The Research Instruments
- Description and Rationale of the Questionnaire
- Description and Rationale of the Interviews
- Research procedure
- Conclusion
74% of the participants have a full-time work status and the remaining 26% of the participants have a part-time work status. The backbone of the questionnaire mainly consisted of closed questions N=24 and two open questions. The normality of the data was tested using the Kolmogorov Smirnov and Shapiro Wilks test (see Appendix IV, Table 1).

Presentation of the Research Findings
- Presentation of the Descriptive statistics
- Inferential statistics
- Gender
- Full or Part-time employment
- Work Experience
- Age
- Educational Achievement
- Teaching Context
- Position held
- Age group of students
- Best age group to teach
- Correlation and Multiple regression
- Presentation and Interpretation of the Interview Findings
- Phase 1: Language Teacher Incentives; From the Ideal to the Practical Self
- Phase 2: Drawing upon Teacher Education and Mentoring to study
- Conclusion
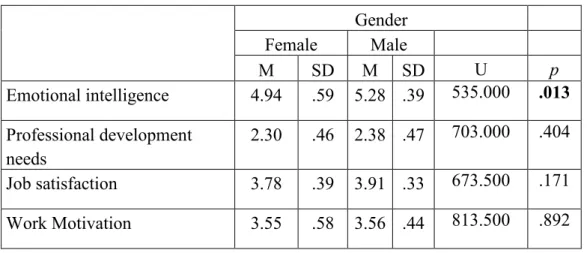
Differences in emotional intelligence, needs for professional development, job satisfaction and work motivation in relation to gender. Differences in emotional intelligence, professional development needs, job satisfaction, and work motivation in relation to full-time and part-time employment. Differences in emotional intelligence, professional development needs, job satisfaction, and work motivation in relation to work experience.
Differences in emotional intelligence, professional development needs, job satisfaction and work in relation to age. Differences in emotional intelligence, professional development needs, job satisfaction and work motivation in relation to the three educational groups. Differences in emotional intelligence, professional development needs, job satisfaction and job motivation in relation to the positions held at work.
According to table 8 and Kruskal Wallis test, it can be seen that there is a statistically significant difference between the four positions of the participants in relation to their emotional intelligence, professional development needs and job satisfaction (p < .05). Differences in emotional intelligence, professional development needs, job satisfaction and work motivation in relation to the three age groups of the student teaching participants. Differences in Emotional Intelligence, Personal Development Needs, Job Satisfaction and Job Motivation in relation to the three age groups of the students that participants prefer to teach.
According to table 10 and the Kruskal Wallis test, it can be seen that there is a statistically significant difference between the three age groups of students that the participants prefer to teach regarding their professional development needs and job satisfaction (p < . 05). .
Discussion of the Results
- Greek EFL teachers‘ motivation
- Greek EFL teachers‘ job satisfaction level
- Greek EFL teachers‘ professional development needs
- Trait emotional intelligence
- Potential predictors of job satisfaction
- Suggestions for Further Research
- Limitations
- Conclusion
Statistically significant predictors of job satisfaction are the type of school or level participants teach most, emotional intelligence, and work motivation. Similarly, the present study found that there is a positive statistically significant relationship between emotional intelligence and job satisfaction (see Table 11). Furthermore, job satisfaction at the workplace (see Appendix II, Table 4.3) appears to be high in terms of the importance of student well-being (3.93) and student support from most teachers (3.76).
However, the low fluctuation of job satisfaction levels is related to teachers' attitudes towards their colleagues. Regression analysis confirmed that emotional intelligence and work motivation are statistically significant predictors of job satisfaction. Overall, work motivation, emotional intelligence, and the type of school or degree most participants teach were found to be significant predictors of job satisfaction.
The aim of the current study was to identify the influencing factors of Greek EFL teachers' motivation, their level of job satisfaction, their professional development needs and their level of emotional intelligence. The results of this study have provided quite a few implications for future research. . These results could be justified if we find that teachers (5.2) demonstrate both a kind of personal strength (see Appendix III, Table 4.2) and a sense of job satisfaction (3.79) because they feel that they make a significant educational difference in the education sector. lives of their students (see Appendix II, Table 4.3). The professional identity of beginning and novice teachers and its relationship to leaving the profession.
Trait emotional intelligence of Greek special education teachers in relation to burnout and job satisfaction.
Template
Which of these categories best describes your current position (or your previous position . in case you are retired or unemployed) in the field of education. In thinking about your professional development needs, please indicate the extent to which you have such needs in each of the areas listed. Please tick one choice on each line. http://www.oecd.org/education/school/TALIS-2008-Teacher-questionnaire.pdf).
In this research, professional development is defined as activities that develop the skills, knowledge, expertise and other qualities of an individual as a teacher. 13a) Have you participated in any of the following types of professional development activities in the last 2 years?. Mark only the activities in which you were involved. a) Courses/workshops (e.g. on the subject or methods and/or other topics related to education).
If you have participated in any professional development activities, briefly explain which ones have had a positive impact on your work life. Based on: http://www.oecd.org/education/school/TALIS-2008-Teacher- questionnaire.pdf).. for yourself as . teacher in this school Fort. Most of the teachers in this school are interested in what the students have to say. In this school, the teachers are good at their jobs.
On the following seven-point scale, please indicate the extent to which each of the following factors is a motivating or non-motivating factor for teachers.

Questionnaire Findings-Tables
71 a) d) Participation in a network of teachers formed .. specifically for the professional development of teachers.. e) Courses on Internet use and applications (word processing, 34% .. f) Course on multimedia (use of digital video, audio equipment , etc.). M a)I usually know how to reach students. 3.97 b)I am successful with the students in my class. 3.91 c)If I try very hard, I can make progress even with the most. difficult and unmotivated students.. 3.86 . e)I feel like I am making a significant educational difference in... the lives of my students. 3.79 . f)Teachers in this local community are highly respected. What's happening at this school? . g)Most of the teachers at this school believe that the well-being of the students is important. 3.93 h)If a student from this school needs extra guidance, the school can . does it offer .. 3.76 i)At this school, teachers and students generally get along well with . each other. 3.71 j) Most teachers at this school are interested in what students do. must say.. 72 k)At this school, teachers have built a positive relationship with . parents. 3.59 . l)At this school, teachers get along well with their colleagues. 3.46 m) At this school, teachers work together with colleagues.

TEIQue-SF Means
Questionnaire Findings-Figures
Interview Questions
Question k: According to your point of view, what is the most important skill of language learning; read, write, listen or speak.
Transcription
Peter grew up in a town in southern Greece and graduated from the same University of Thessaloniki as Anna. Question a: Reflecting on your experience as a beginning teacher, how would you describe your behavior and interaction in the classroom. We tried to solve tasks in the target language and at the end of each lesson we played a game.
So I started to think that abandoning a pre-planned curriculum can lead to grammar gaps, content gaps. I was filled with dread at the possibility of my students failing, but on the other hand, I had many fears about teaching too much grammar and spelling in the usual way. It occurs to me that at the beginning of the lesson she wrote some topics in the middle of the board and gave us the opportunity to choose which topics we wanted to learn.
I think that the teacher should be an intrinsic motivator in the sense that she will even make the tests more interesting than they are. For example, what a teacher should do when certain things, such as specific types of behavior occur in the classroom. Learners are eager to speak when they are interested in the subject and if they have prior knowledge.
It is not easy to use only the English language in the classroom, although this is my reward for being a teacher; to improve my students' communication skills in English and to develop their confidence beyond their speaking skills.