Before the Covid-19 pandemic, telework may have been the exception, but in the future, employees want to work from home at least a few days a week. This study is concerned with the relationship between the outcomes of telework among teleworkers in the telecommunications sector in Greece during the Covid-19 pandemic. More specifically, the study examines the relationship between work flexibility, job satisfaction, organizational commitment, work-life balance and productivity.
The research finding showed that there are positive relationships between the above telework outcomes. This study aims to support existing knowledge about the concept of telework and motivate organizations to reconsider telework policies and practices by creating and implementing effective telework programs for the future.
Research Purposes- Method Analysis
This study aims to conduct and present a survey on the relationship between work flexibility, job satisfaction, organizational commitment, productivity and work-life balance among teleworkers in the telecommunications sector in Greece.
Dissertation’s Framework
Relevant ideas and theories on telecommuting, productivity, work-life balance, work flexibility, work and theories on telecommuting, productivity, work-life balance, work flexibility, job satisfaction, and organizational commitment will be thoroughly analyzed. It presents all the research questions to be addressed and provides all the necessary theoretical support.
Chapter 3: Theoretical Framework and Hypotheses. It presents all the research questions which will be addressed providing all the necessary theoretical support
Research Results. It presents the main finding deriving from the analysis of the questionnaires after utilizing the appropriate statistical analysis
Chapter 6: Discussion and Conclusion. It links data analysis with fundamental ideas presented in the literature review analysis chapter by providing evidence from
Literature Review Analysis
- Preface
- Teleworking
- Theories related to teleworking
- Teleworking outcomes
- Teleworking and Covid-19
- Productivity
- Work-life balance
- Theories related to work-life balance
- Work-life balance antecedents
- Work-life balance outcomes
- Organizational Commitment
- Organizational Commitment components
- Organizational commitment antecedents
- Organizational commitment outcomes
- Job Satisfaction
- Job Satisfaction outcomes
- Work Flexibility
- Work Flexibility outcomes
Regarding output, components such as quantity, quality and customer satisfaction can be met (Laihonen et. al., 2012). Organizational support is also related to WLB because it can facilitate employees to successfully handle work and non-work tasks (McCarthy et. al., 2013). Several researches have shown that the use of e-mails and tablets negatively affects work-life balance (Stephens et. al., 2007; Waller & Ragsdell, 2012).
In addition, job demands (Chiang et. al., 2010) and work overload (Virick et. al., 2007) are negatively related to work-life balance. According to a study by Macky and Boxall (2008), overwork reduces the performance of employees. - life balance. In addition, organizations that deal with which charities make sure that employees are satisfied with them (Colquit et. al., 2010). In addition, studies have shown that job flexibility makes it easier for employees to reduce stress and thus increase their job satisfaction (Lu et. al., 2008).
Theoretical Framework and hypotheses
- Preface
- Theoretical Framework
- Research’s Model and hypotheses
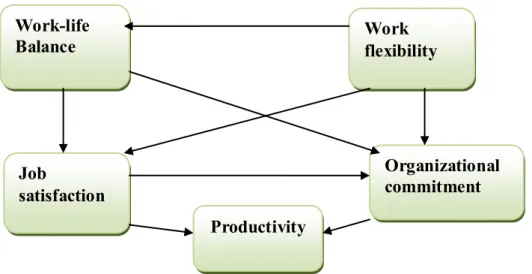
The research's model consists of five factors namely work flexibility, work-life balance, job satisfaction, organizational commitment and productivity. Furthermore, Istrate and Caragea (2008) revealed that work flexibility increases employees' productivity, their commitment and improves their work-life balance. Current research has concluded that work flexibility has a positive effect on employees' work attitudes that increase their job satisfaction (Carslon & Grzywacz, 2010).
In line with this, researchers have found that work flexibility is a motive that can improve job satisfaction (Michel & Michel, 2015). Greater autonomy is related to job satisfaction, which can increase organizational commitment (Hackman & Vedman, 1980). According to Schermehorn (2013), work-life balance refers to a person's ability to achieve harmony between the obligations of work and private life. Empirical research has shown that work-life balance is linked to job and life satisfaction, and organizational commitment (Allen et al. al., 2010).
A study by Adikaram and Jayatilake (2016) concluded that there is an important relationship between work-life balance and job satisfaction. Furthermore, Nurendra and Saraswati (2016) reported that work-life balance can improve job satisfaction, while work-life imbalance can decrease it because it can increase work stress. The relationship between work-life balance and organizational commitment is explained by social exchange theory.
This theory states that work-life practices increase employees' involvement in an organization to the extent that. Furthermore, Noor (2011) found that work-life balance was positively correlated with job satisfaction and organizational commitment, while it was negatively correlated with turnover rate. Furthermore, a study by Azeez and Akutar (2014) concluded that there is a strong and important relationship between work-life balance, job satisfaction and organizational commitment.
More detailed findings of their research showed that with an increase in work-life balance and job satisfaction, the impact on organizational commitment was 37%.
Research Analysis
- Preface
- Research Approaches
- Questionnaire structure
- Sample
- Survey Procedure Analysis
Finally, it does not need to take long to complete and anonymity allows participants to respond honestly (Karagiorgos, 2002). The questionnaire is accompanied by an introductory letter explaining the objectives of the study to the participants. The majority of the questions are measured using the Linkert five-point scale in a range from (1) to (5).
In addition, the research complies with the ethical codes necessary to conduct the research. According to the latest data from the Greek Telecommunications and Posts Commission, the turnover of the sector increased to 5.0 billion euros, while its contribution to the Greek Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in 2019 was 2.7%. Specifically, in 1859, the first telegraphy system was established and the first submarine cable was sunk, connecting Athens to the island of Syros, while telephone service was provided later.
Until 1941, several steps were carried out at the management and technological level and the connection with neighboring countries was kept. In 1949, the Hellenic Telecommunications Organization was founded from the merger of the Directorate of Post, Telegraph and Telephony, the Greek Telephone Company Limited and the Rhodes Electric Company Limited which undertook the monopolistic provision of all telecommunications services. During the decades 1960-1970, the Hellenic Telecommunications Organization delivered important achievements such as the high growth rate, the high quality of telephone and the low telecommunication costs.
In the 1990s, the level of investment tripled, net digitalization accelerated significantly and the quality of communication improved noticeably. The questionnaire was prepared in the Greek language and was accompanied by a short introduction presenting the study and its objective. Online questionnaires can be sent to many recipients simultaneously and allow the clarification of results.
In probability sampling, the sample is selected randomly and all individuals have an equal chance of being selected.
Research Findings
- Preface
- Demographic Data
- Descriptive Statistics
- Work –life Balance
- Productivity
- Work Flexibility
- Job Satisfaction
- Organizational Commitment
- Factor Analysis
- Correlation Analysis and ANOVA Analysis
- Structural Equation Modeling
The distribution of the sample according to the number of children is shown in table 5.5. According to Table 5.6, respondents believe that "working in this institution affects my family life" (mean = 2.45). From the above, we can assume that the respondents' satisfaction with regard to the factors of balancing professional and private life is not very satisfied on average, as all averages are around and below 2.5, which is the average rating of the scale.
According to the results in table 5.7, the respondents believe that they can complete a large number of tasks daily while working remotely (mean=2.23). In this group of questions, we can realize that the majority of respondents are satisfied with their productivity in their work environment, since the score is close to 4, nor can they be productive in the context of remote work, since the score is around the neutral 2.5. According to the results in table 5.8, the respondents state that their company allows them to organize their own working hours (mean= 2.68).
In addition, the results for the questions "I feel like "part of the family" in my company" and "This company is like my second home" are somewhat neutral (mean = 2.80 and 2.93, respectively). Total variance explained (TVE) refers to the importance of factors and measures the extent to which a factor can explain the variance in the set of items studied. Regarding the demographic data and the main factors of the research model, a strong negative relationship was found between organizational commitment and age.
The following table (5.13) presents one-way ANOVAs between some work balance factors and the dependent variables of the respondents. As we can see, in terms of gender, the significance value is 0.050 (ie, p = .050), which is equal to 0.05 and therefore, there is a statistically significant difference in job satisfaction between men and women . In other ANOVA tests we can assume that there are no statistically significant differences between groups.
Based on figure 5.1b, it can be seen that some demographic factors, which were not included in the initial research model, influence the main factor of the model.
Summary and Conclusions
- Brief Summary of the Followed Steps
- Discussion
- Managerial Implications
- Research Restrictions
- Recommendation for Future Research
Subsequently, ANOVA analysis showed that there was a significant difference in job satisfaction between men and women. Furthermore, ANOVA analysis showed a statistically significant difference in organizational commitment between the different age groups. The first hypothesis H1 proposed that work flexibility is positively related to work-life balance, which was accepted.
The fourth H4 and fifth H5 hypotheses suggested that work-life balance has a direct impact on job satisfaction and work-life balance has a direct impact on organizational commitment were rejected because no evidence was found to support them. In addition, the sixth hypothesis H6 proposed that job satisfaction has a direct effect on organizational commitment, which was accepted. The seventh hypothesis H7 proposed that job satisfaction has a direct effect on productivity, which was also rejected.
Marital status is positively related to work-life balance, while age is positively related to organizational commitment. On the other hand, gender and number of children are negatively related to job satisfaction. First, the study concluded that there are differences between organizational commitment and age groups, as well as between job satisfaction and gender.
This is a common occurrence due to the conditions in the labor market and the position of employed women in the market. As already mentioned, many researchers have found that telecommuting increases work flexibility, employee productivity, job satisfaction, organizational commitment, and improves work-life balance. The results of the study showed that work flexibility has a significant positive impact on work-life balance, job satisfaction and organizational commitment.
By improving work flexibility through appropriate telecommuting programs, organizations will increase their employees' job satisfaction and organizational commitment and improve their work-life balance.
Demographic data and occupational position 1.What is your gender?
Productivity
Job satisfaction