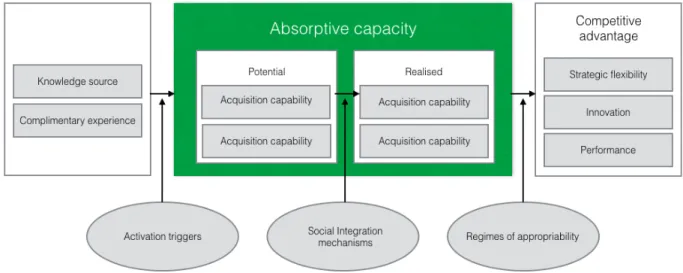
The conceptual model of relationship between absorptive capacity and the determinants of the knowledge culture. It is unclear which dimensions of the knowledge culture influence the various capacities of SMEs' absorptive capacity.
Absorptive Capacity Model
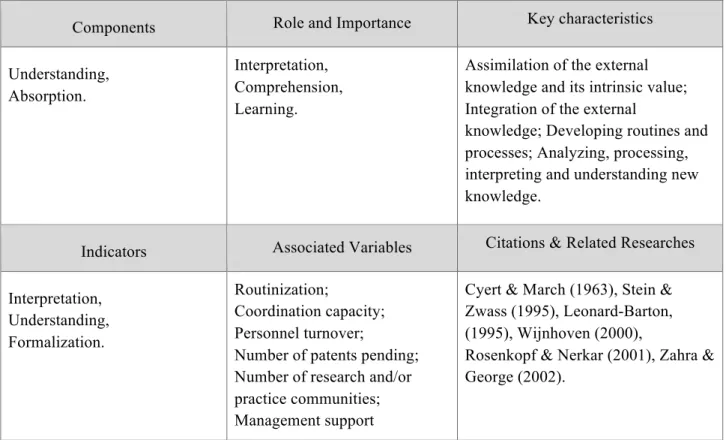
- The Acquisition Capability
- The Assimilation Capability
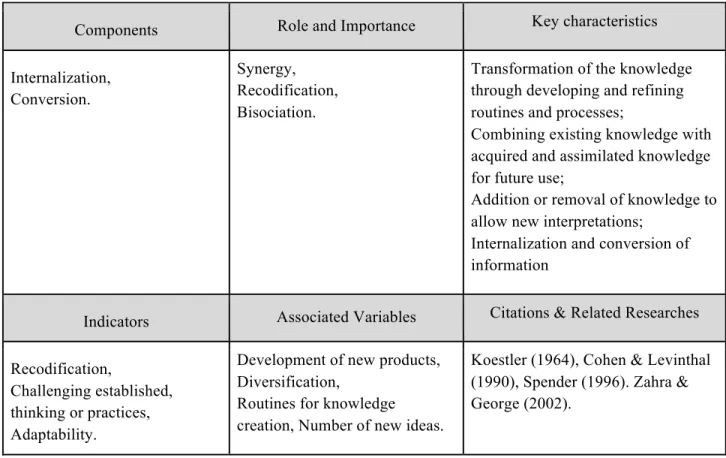
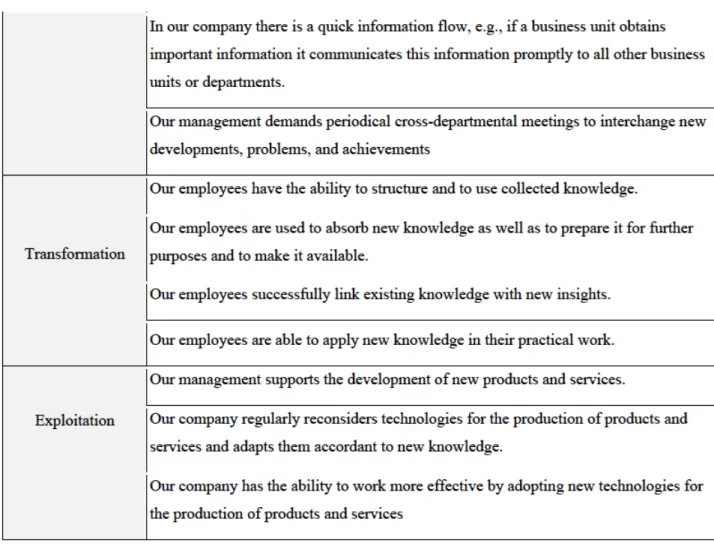
- The Transformation Capability
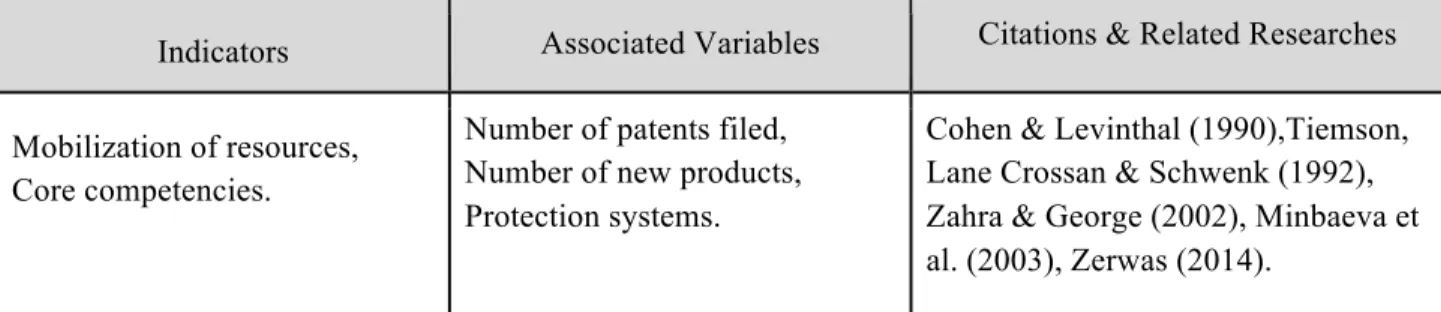
- The Exploitation Capability
Dimensions of transformational capability (based on Zahra & George (2002) & Jean-Pierre Noblet et al (2014)). Dimensions of exploitation capacity (based on Zahra & George (2002) & Jean-Pierre Noblet et al (2014)).
Organizational Culture
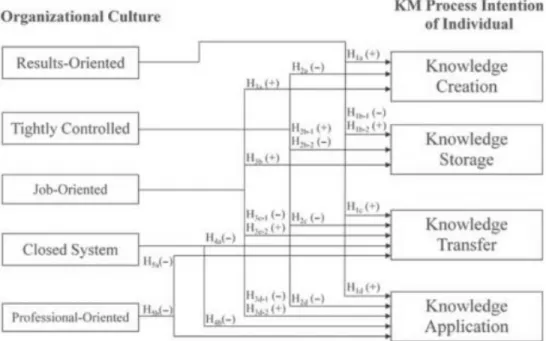
Organizational culture and knowledge management
Nevertheless, knowledge management requires a critical shift in organizational culture and the strongest commitment from all management levels to make it work (Ajmal and Koskinen, 2008). Furthermore, organizational culture is vital to enable not only knowledge creation, but also storage, transfer and application (Ajmal and Koskinen, 2008).
Organizational culture and absorptive capacity empirical studies
The result of the study has shown that adhocracy culture is positively related to both potential and realized absorptive capacity, while market and hierarchical culture hinder both potential and realized absorptive capacity. All three studies are designed as a model of one of the commonly used organizational culture concepts (Hofstede 1980, Hofstede et al. 1990, Quinn 1988) and dimensions of absorptive capacity/knowledge management.
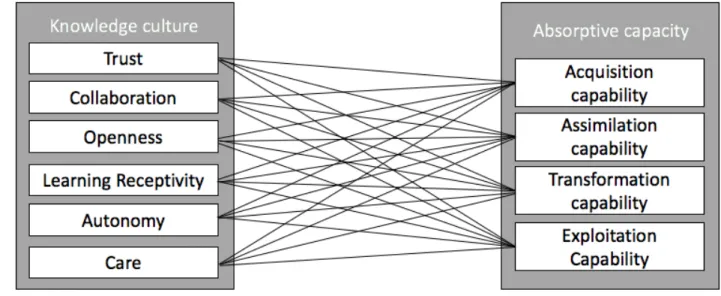
Absorptive capacity and Knowledge culture
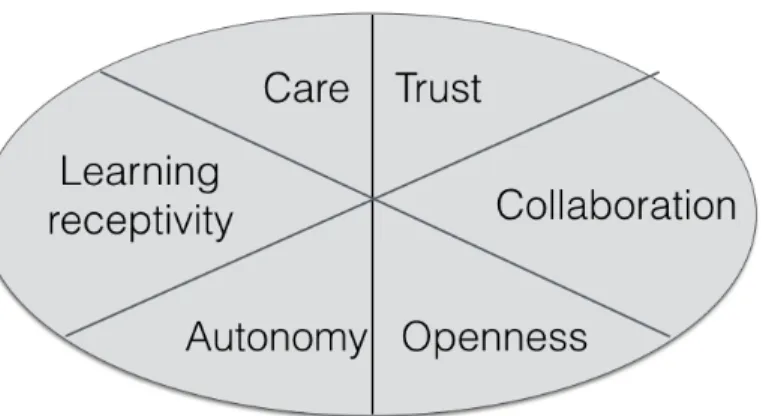
- Trust
- Collaboration
- Openness
- Learning receptivity
- Autonomy
- Care
Trust is “a willingness to accept vulnerability based on positive expectations about the intentions or behavior of another” (McEvily et al. 2003, p. 92). Therefore, trust fosters a climate that is beneficial for knowledge exploitation by alleviating the fear of risk and ambiguity (Choi, 2002). Open innovation is "the use of dedicated inflows and outflows of knowledge to accelerate internal innovation or to expand markets for the external use of innovation".
Malhotra, Gosain & El Sawy (2005) also emphasized the importance of collaboration for the exploitation of knowledge. Furthermore, the exploitation of knowledge requires the sharing of relevant knowledge between members of a company to promote mutual understanding (Zahra & George, 2002). If the company wants to adopt a new way of doing things, it must "unlearn" the old ways.
Research Gap and Research Questions
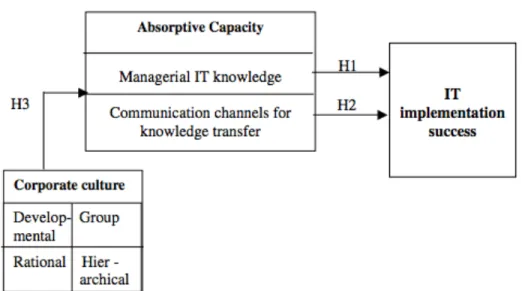
Research objective is to identify whether knowledge-oriented organizational culture dimensions have a positive impact on the level of organizational absorptive capacity, namely acquisition, assimilation, transformation and exploitation capabilities. The overall objective of this thesis is to develop and validate a model that allows an analysis of the relationship between organizational culture and the absorptive capacity capabilities at the organizational level of Russian SMEs and. In this chapter, the research model will be created and analyzed through an explanatory approach that establishes causal relationships between variables, and deductive approach will be used to develop a conceptual framework, test it empirically, draw particular conclusions from the general ones.
The method of the thesis is quantitative (survey) and would be collected via an online questionnaire. Data analysis methods are reliability analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, Pearson correlation and four regression models for each of the absorptive capacity dimensions. The following paragraphs include the research model, operationalization of absorptive capacity and knowledge culture models, questionnaire, descriptive analysis, reliability analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, Pearson correlation and four regression analyses.
Research model
The proposed problems regarding SMEs' external knowledge absorption represent insufficiently studied issues.
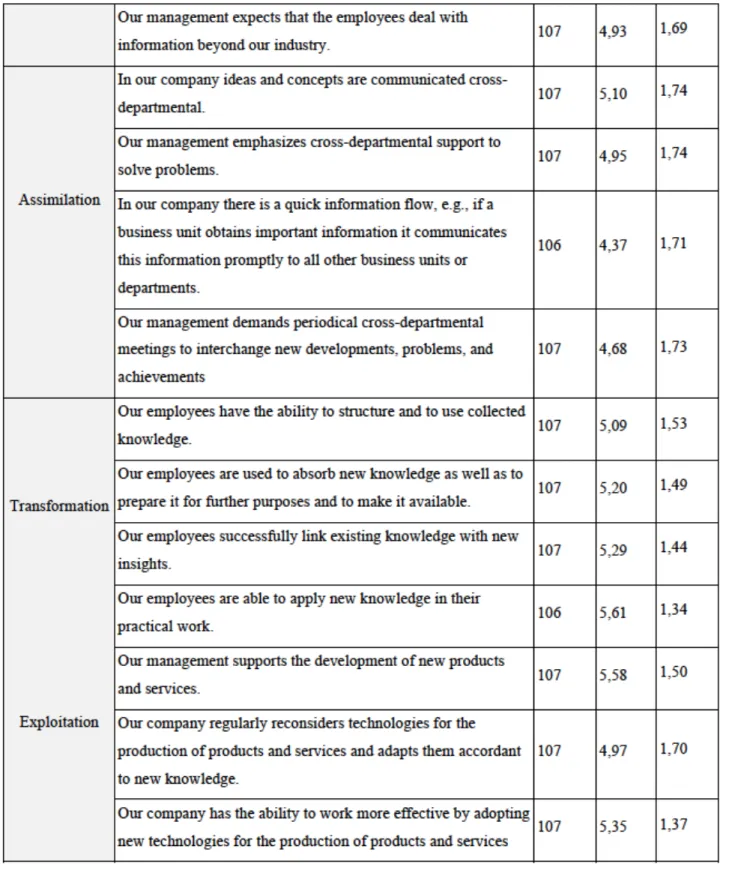
Operationalization of the model
The operationalization of the conceptual variables was made based on the Flatten et al. 2011), who developed and validated a multidimensional measure of absorptive capacity. Flatten et al. 2011, p. 110), consisted of three questions on acquisition capability specifying the extent to which the company uses external resources to acquire information (eg personal networks, consultants, seminars, internet, etc.); four questions about assimilation capacity, which determine to what extent the statements fit the communication structure in the company; four questions about transformational ability that specify to what extent the statements fit the knowledge processing in the respondent's company; and three questions about exploitation capability that identify to what extent the statements fit the commercial exploitation of new knowledge in the respondent's company departments such as R&D, production, marketing, and accounting etc. Operationalization of the Absorption Capacity” and was measured in the questionnaire by Likert scale where 1 – absolutely disagree with a statement and 7 absolutely agree with a statement.
Absorptive capacity is divided into two types: potential (1) and realized (2), which are divided into acquisition capacity, assimilation capacity and transformation or exploitation capacity, which are determined by Flatten sentences measured by a Likert scale. In terms of factor analysis, Sollberger eliminated those items that could not be attributed to a factor or where it could not be assigned clearly enough. The company and respondent background section of the questionnaire consists of 5 questions, including company name, company industry sector, company size, respondent's department, and job title.
Questionnaire
Description of the the Sample
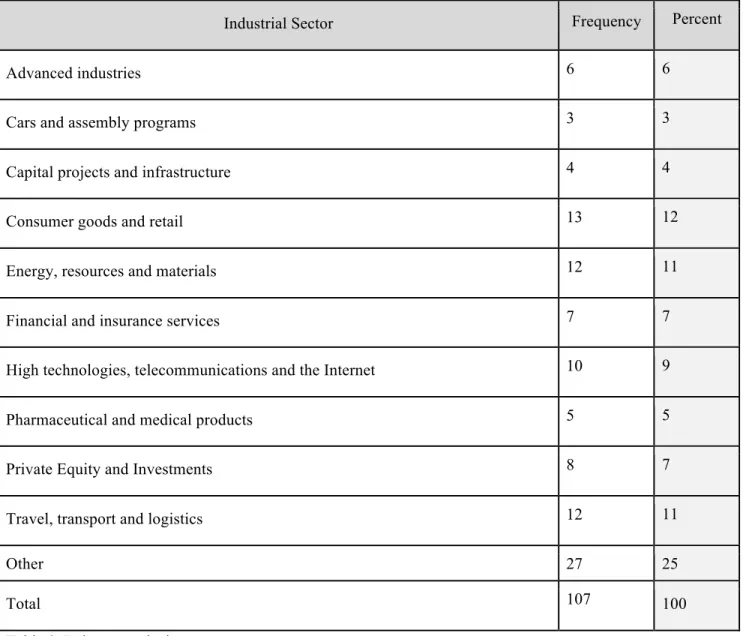
All the other industries are distributed with a percentage from 9 to 3% and together represent 41% of the analyzed sample. According to research purposes, the elimination of the representations, subsidiaries and foreign companies without any kind of Russian registration was done with a Spark-Interfax. After the elimination, two groups of companies have left: Russian companies and one and a group of foreign companies working under LLC, JSC, CJSC registration.
The analyzed data divided into three categories of small and medium-sized companies as follows, the majority of companies represent medium-sized companies that have from 251 to 500 employees, (48%), then companies with 101-250 employees (32%) , and small companies with 1-100 employees (20%). In the analyzing sample, a quarter of the respondents belong to "Other", a fifth work in the "Marketing and Sales" department, and the rest of the respondents are heterogeneously spread between Purchasing, EDP and IT, Finance and Control, R&D, Customer Service and Logistics departments with 54% of the total sample. By generalizing the sample, it can be said that 6% of the sample are department managers, 36% of the sample marked themselves as management, 30% work as commercial employees, 19% work as senior employees, 9% of the respondents have projects. managers.
Data analysis
- Descriptive analysis
- Reliability Analysis
- Factor analysis
- Regression analysis
For reliability analysis, Cronbach's alpha (Cronbach, 1951) was used to assess the reliability of a summary rating scale (Likert, 1932) composed of the variables. Four regression models were calculated, one for each of the absorptive capacity skills in the four dimensions of organizational culture. The R² of acquisition ability is 0.609 and therefore, indicates that the model predicts the outcome variable satisfactorily.
The values of B indicate that the gradient of all the various dimensions of organizational culture is positive and that the strength of the relationship between a predictor and the outcome variable is between a minimum absolute value of .050 (care) and a maximum absolute value is. of ,272 (collaboration). The R² of the acquisition ability is .651 and thus indicates that the model satisfactorily predicts the outcome variable. The R² of the acquisition ability is .530 and thus indicates that the model satisfactorily predicts the outcome variable.
Discussion of the results
- Organizational culture and acquisition capability
- Organizational culture and assimilation capability
- Organizational culture and transformation capability
- Organizational culture and exploitation capability
This chapter aims to discuss the results of the regression analysis and their consistency with other research papers. However, this fact only means that the relationship between independent and independent variable was not proven, and does not mean that the relationship does not exist. Choi (2002) pointed out that trust increased knowledge transfers, and knowledge transfers increase knowledge creation and utilization. 2011) argued that the more knowledge is transferred, the more it can be exploited by companies.
To summarize, the results show that the absorptive capacity of SMEs is influenced by organizational culture. Furthermore, it is in accordance with the insights of the literature that the absorptive capacity of SMEs is positively influenced by the organizational culture. Since the literature identified the generally positive influence of organizational culture on absorptive capacity, with due regard to the theoretical concepts at the beginning of this thesis, a positive relationship between the dimensions of organizational culture and the capabilities of absorptive capacity was hypothesized and confirmed.
Theoretical and Practical contribution
Theoretical Contribution
This thesis presents a design of a model that allows an assessment of the role of organizational culture in ensuring the absorption of external knowledge. It is possible both to prove positive correlations between the determinants of the organizational culture and the dimensions of absorptive capacity by applying this original model of external knowledge absorption and to distinguish principles of a design concept for an external absorption-supporting organizational culture and thus to close the research gap to a certain extent. In conclusion, this research makes a significant contribution to the research area of organizational culture and absorptive capacity, from a theoretical point of view.
The attempt to substantially define the phenomenon of organizational culture to enable both an empirical research and a practical utilization of organizational culture as an absorptive-capacity-influencing ingredient has been satisfied. Organizational culture does not, as expected at the beginning of this thesis, appear to be usually positively correlated with the abilities of absorptive capacity, but rather is a specific differentiation of the different dimensions of organizational culture that are necessary to intelligently implement principles of the design concept used to promote. external knowledge absorption in an appropriate corporate culture. This thesis's main contribution to theory is that the sheath image of organizational culture is differentiated and that the outcomes for how a knowledge-oriented culture should be designed to promote the absorption of external knowledge are described.
Practical contribution
Sollberger is the only author who focused on those dimensions of organizational culture that are closely related to knowledge absorption and accordingly, the current research used Sollberger's model to conduct empirical research on the relationship of organizational culture on absorptive capacity. For the study of a company's organizational culture, it is important to fundamentally define the organizational culture within a firm in order to operationalize it. The following implications include recommendations for business practices that refer to a knowledge-oriented organizational culture that affects absorptive capacity capabilities.
The implications of designing a knowledge-oriented organizational culture to support the absorption of external knowledge, described subsequently, are structured along the several important dimensions of organizational culture that have shown the strongest influence on the absorptive capacity of Russian SMEs: trust, cooperation, openness . To create an organizational culture that promotes trust, Davenport & Prusak (1998) developed three ways in which trust must be built for the knowledge market to function in an organization: Trust must be visible and universal, and credibility must begin at the top (Davenport & Prusak, 1998). If Not-My-Jobers find training and development opportunities and are involved in a company's entire work process, they will seek growth and progression instead of losing their passion for work and trying to accomplish as little as possible. In other words, to develop and design a knowledge-friendly, absorptive capacity-supporting organizational culture that will contribute to achieving a higher level of absorptive capacity, management must create trust, openness and cooperation in their companies.