Title of Master's Thesis Knowledge acquisition by firms in emerging markets through M&A deals: The effect of state ownership. Discover how government ownership of companies in emerging markets affects the process of acquiring knowledge through M&A transactions. At the same time, many authors have emphasized the increasing importance of emerging market companies in M&A activities in the current globalized economy (Makino, 2002).
For example, Casciaro studied internationalization tools of companies in emerging markets, one of which is merger and acquisition tool (Casciaro, 2005). Therefore, it is necessary to examine the role of government in knowledge creation process by emerging market companies. Following the strategic motivation direction of research, we can conclude that there is a lack of studies in the field of interdependencies of government participation in M&A through emerging companies' markets and knowledge transfer through M&A.
After this, we will study the theoretical concept of knowledge and its interdependence with merger and acquisition processes. We will study the role of the state in M&A activity, specifications of M&A by companies in emerging markets and the process of knowledge transfer through M&A.
THEORETICAL BACKGROUND
Merger and acquisition transactions
- Defining M&A
- M&A rationales
- Theoretical views
Summarizing the theoretical part of the M&A type studies, we can conclude that there are several ways to distinguish types. This justification is based on increase in the company's total production with decrease in costs. In this case, two parts of the M&A transaction have a goal of complementing each other.
Scaling: Occurs when the level of executive compensation is directly related to the size of the firm. Overconfidence: It is based on the assumption by the acquirer's management that it is able to manage the target company more effectively than the previous managers (Roll, 1986). According to this concept, the company's strategic position is determined by the competitive situation in which the company operates.
Therefore, the market view is about the external influences of the company and the process of finding the best ways to adapt to the environment. The resource-based view talks about the internal processes of the company that are identified as a key driver of competitive advantage. He also argued that competitive advantage is gained through the company's resources and their manipulation.
Based on the previous chapters we can conclude that in the knowledge-based perspective, the search for knowledge is one of the rationales for merger and acquisition activity.
Knowledge acquisition
- Defining knowledge
- M&A and R&D
One of the main tools in this case is cost reduction through, for example, time, effort, space saving. In general, competitive advantage means the ability of the company to offer better products and services compared to competitors'. Instruments in achieving competitiveness are prices, quality, after-sales service, ability of the company to meet market demand, implementation of technical development results (Porter, 1996).
According to Ramos-Rodríguez and Ruíz-Navarro it has economic, sociological and psychological origins. While competitive advantage is an instrument of achieving high company performance, it can be defined as a key point in superior performance (Porter, 1985). At the same time, knowledge itself is considered as an instrument of creating competitive advantages, which is related to the concept discussed in the first chapter of creating competitive advantage under the knowledge-based perspective.
While the bulk of M&A studies focus on the economic and financial aspects of such transactions, only few papers have studied the dependence of M&A instrument and research and development activity. There are two main theoretical directions useful in this filed research: financial economic studies and industrial organization studies. According to financial economic point of view, when the acquirer conducts merger or acquisition transactions, it is able to relocate its research and development costs and use target company's resources to increase the volume of R&D investments (Braguinsky, 2015; . Maksimovic, 2011 ).
This theory was originally developed by Schumpeter and he stated that research and development activities depend on the size of the firm on the one hand and market concentration on the other (Schumpeter, 1942). After the cost shift, the acquirer is able to reduce the managers' effort, which is used in innovative activities (Hitt 1996). The main theoretical frameworks used in this case are knowledge capital model and theories of multinational enterprises.
According to them, there are different costs and quality of research and development activity in different countries and it is an efficient strategy to locate R&D subsidiaries in different countries according to buyer preferences (Markusen, 2002; . Arkolakis, 2013). In this case, the company benefits when its knowledge transfer costs are less than the internal R&D cost (Keller and Yeaple, 2013). At the same time, the buyer is able to use its own resources and assets with a combination of those of the target (Norbäck and Persson, 2007).
EMPIRICAL EVIDENCES AND HYPOTHESIS STATEMENT
- State and M&A activity
- M&A and emerging markets
- Knowledge development and transfer through M&As
- Hypothesis statement
In the research carried out by Pintoa, it was proven that the level of state participation in the capital of the acquirer is positively correlated with the possibility of profitable implementation of the M&A transaction in which the acquirer aims to acquire knowledge. Summarizing the theoretical and empirical evidence on the role of the state in mergers and acquisitions activities, we can conclude that the extent of shares in the acquirer's capital correlates with various aspects of the mergers and acquisitions process. Acquisition-merger activity is used as an instrument for the external adoption of knowledge and innovations.
However, M&A tool offers the acquirer unique features that are not available in other strategic options: the acquirer is able to achieve full control over the necessary resources, which reduces negotiation and bargaining costs, which occur in other options (Casciaro , Piskorski, 2005). There are papers that underline that knowledge acquisition and knowledge acquisition is one of the significant motivations for companies from emerging markets to use merger and acquisition tools (Jullens, 2013; Rabbiosi, 2012). To summarize, the reasons for merger and acquisition activity by companies in emerging markets are generally the same as for other companies.
This rationale, on the one hand, is seen as one of the most important factors in M&A decision-making and is considered an under-explored aspect of M&A by companies in emerging markets. With a competitive advantage creation process through a merger and acquisition tool for the purpose of receiving knowledge, we face the problem of measuring knowledge transfer. Like the concept of knowledge itself, approaches to knowledge transfer and acquisition measurement depend on specific research needs and data availability.
Other studies state that there is a neutral effect of mergers and acquisitions on research and development activity (Man, Duysters, 2005). The findings of previous research are mixed: some authors emphasize that M&A activity has a positive effect on knowledge transfer, others argue that there is a negative effect called "innovation placebo" that occurs when mergers and acquisitions are carried out with the aim innovation distribution, but results in a neutral or even slightly negative impact on knowledge transfer (Jensen, 1998). If we summarize the first and second chapters, which talk about the theoretical implications of mergers and acquisitions and the concept of knowledge acquisition, we can conclude that, firstly, knowledge is a source for creating a competitive advantage in the modern economy.
Second, merger and acquisition transactions are one of the instruments for receiving knowledge and thus creating competitive advantages. Third, this type of mergers and acquisitions from strategic groups of M&A rationales and enables transaction participants to achieve their strategic goals. Finally, mergers and acquisitions as an instrument for knowledge acquisition are widely used by companies in emerging markets.
EMPIRICAL STUDY
- Research design
- Sample selection
- Methodology and variables choice
- Regression analysis
- Results interpretation and discussions
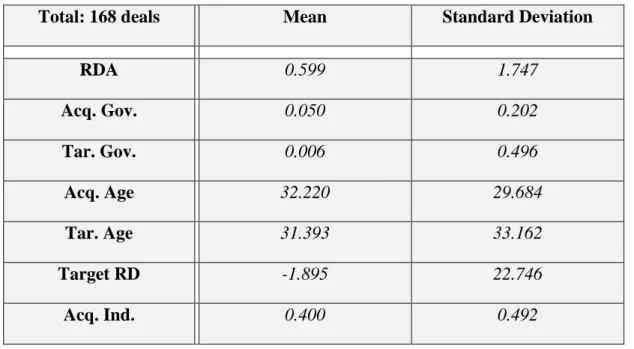
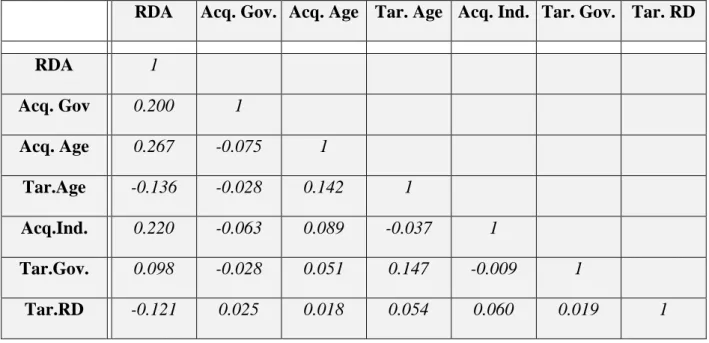
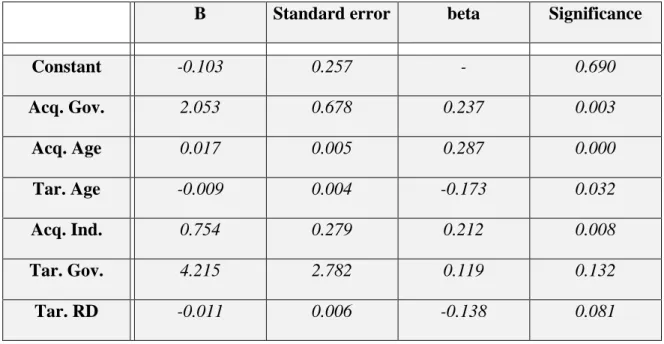
AcqGov= The government's share of the acquirer at the time of the transaction in any M&A deal;. We followed the logic that the less important the number (p), the more significant the variable has in influencing the dependent variable. The results of this review and the hypothesis can be found in chapter 2 of this paper.
Combining theoretical research and statistical results, we can explain this fact in the following way. This correlation can be used by managers of such companies in the process of defining knowledge creation strategies. Moreover, this correlation can be used in the process of such companies' activities forecasts by market experts.
Technological acquisitions and the innovation performance of acquiring firms: A longitudinal study // Strategic Management Journal – 2001 – Vol. Boeker, W., The development and institutionalization of subunit power in organizations // Administrative Science Quarterly - 1989 – Vol. Clò, S., Fiorio, C., The targets of state capitalism: evidence from M&A transactions // European Journal of Political Economy – 2017 – Vol.
Drucker, P., The New Realities: In Government and Politics/in Economics and Business/in Society and World View // 1969 – HarperCollins. Ebers, M., The Dynamics of Inter-Organizational Relationships, Research in the Sociology of Organisations // 1999 - AI Press, Stamford, Vol. Ernst, H., Vitt, J., Indflydelsen af virksomhedsopkøb på nøgleopfinderes adfærd // R&D Management – 2000 – Vol.
A content analysis of 26 years of strategic management research // International Journal Of Management Reviews – 2008 - Vol.10, Pp. Goldeng, E., Grunfeld, L., Benito, G., The Performance Differential between Private and State-owned Enterprises: The Roles of Ownership, Management and Market Structure // Journal of Management Studies – 2008 – Vol.45, pp. Mergers and acquisitions: their effect on the innovative performance of companies in high-tech industries // Research Policy – 2006 – Vol.35, pp.642-654.
Krueger, A., The Determinants of Queues for Federal Jobs // Industrial and Labor Relations Review – 1988 – Vol.XLI, p. Ramos-Rodríguez, A., Ruíz-Navarro, J., Changes in the intellectual structure of strategic management research // Strategic Management Journal – 2004 - vol.