The key role of the 90 domains of the low-temperature P4mm phase in the stress relief is emphasized. This allows different variants of the single domain Cc phase to be present and affect the phase content [3].
Oral Presentation
Analytical Expressions for the Landau Coefficients in the Four-Particle Cluster Approximation, Critical Electric Field and Tricritical Point in KDP
First-Principles Based Study of Temperature Effects in Perovskite Ferro- electrics
Interband Theory of Ferro-Elastic Phase Transitions
The Number of Possible Orientation States in Ferroelastics and Multiaxial Ferroelectrics at Polymorphic Phase Transitions
Temperature Dependence of Raman Scattering in Rb 2 KHoF 6 and Rb 2 KDyF 6 Crystals
The Phase Diagram and the Origin of Ferroelectricity in PbTiO 3 at High Pressure
Structural changes in the triggering transition, critical and noncritical order parameters in Rb2KHoF6Elpasolite.
Structural Changes in the Trigger Transition, Critical and Noncritical Or- der Parameters in the Rb 2 KHoF 6 Elpasolite
Poster Presentation
Pretransition and Molecular Relaxation in Potassium Perchlorate
PZT System: the Real State Diagram
Temperature Raman Scattering Investigations of Rb 2 KHoF 6 and Rb 2 KDyF 6 Crystals
Order Parameter of Phase Transition, Fluctuations and Nanoclasters in Benzil Crystals
Isomorphous Phase Transitions on the Phase Diagrams of Ferroelastics
О Влиянии Механических Напряжений на Фазовый Переход в Тонкой Сегнетоэластической Плёнке
Features of Phase Transitions in Ferroelastic Thin Plates
Magnetodielectric and Magnetolosses Effects in Statistical Mixtures
Magnetodielectric Effect in Laminated Dielectric-Semiconductor Structures
Direct Magnetoelectric Effect in Layered Composites TDF – PZT
Poster presentation
Multiferroic Probed by Second Harmonic Generation
Effect of deviations from stoichiometry on the magnetic phase transition temperature in PbFe0.5Nb0.5O3Multiferroic. Studies of magnetic phase transitions in PFW-PT multiferroic solid solutions by neutron diffraction and Mössbauer spectroscopy.
Studies of Magnetic Phase Transitions in PFW-PT Multiferroic Solid So- lutions by Neutron Diffraction and Mössbauer Spectroscopy
Two-Layered Magnetoelectric Composites TDF – PZT
New Approach to Preparation and Properties
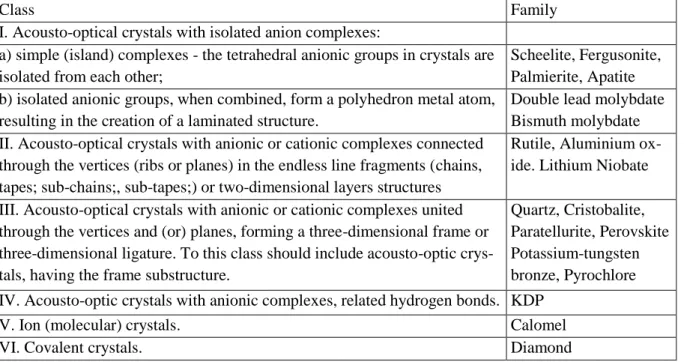
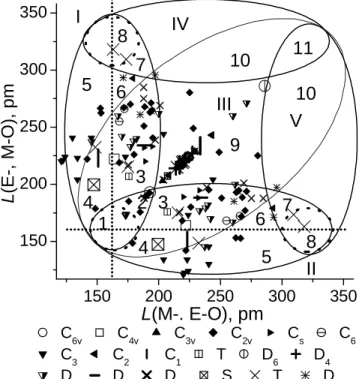
Crystals Chemistry Consideration of Acousto-Optical Ferroic Crystals
Dielectric measurements of compositions with x> 0 revealed anomalies associated with a diffuse ferroelectric phase transition. The SRFRB model parameters obtained from the best dielectric fit of the data for all studied compositions allow us to conclude that samples of the (1-x)SrTiO3-xBiScO3 system with x > 0 should transition to a spherical glass state.
Growth of Piezoelectric Potassium Bromate Crystals from Electrolyte Solutions
Interrelationship «Structure – Property» for Crystals of Non-centrosymmetric Wolframates
Orientational Order and Birefringence in Nano-Layers in Casted Polymer Films
The Growth Copper and Zinc Tartrate Crystals
Superprotonic crystals are a special class in which changes occur in the H-bond network during phase transitions, leading to radical changes in properties, in particular to the conductivity of ≈10–2Ω–1cm–1. The occurrence of high conductivity in K9H7(SO4)8∙Н2О [3] is related to the diffusion of water of crystallization and the movement of K ions, as well as to the transformation of the system of H-bonds and protonic movement. The stabilization of the superprotonic phase at high temperature and its supercooling to low temperatures are due to the presence of channels for K ions (Fig. 1.) and slow backward diffusion of water in the crystals.
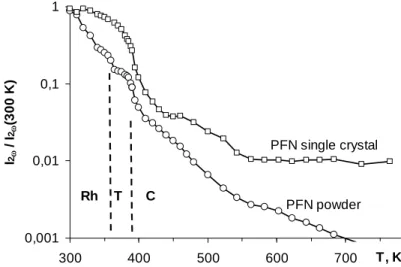
Despite the fact that ferroelectromagnetic PbFe1/2Nb1/2O3 (PFN) perovskite ceramics are well-studied so far, there are contradictions in the literature regarding their properties, which are usually related to the sensitivity of these to the ceramic manufacturing technology. A significant difference in the effect of modifiers, revealed by the analysis of cleavages, which in PFN take place both along the grain and grain boundaries, in RFNL the destruction takes place only across the grain boundaries and the presence of a "liquid phase" is observed, located between the grains in the form of a "layer" of thickness ~ 0.3 μm. The ferroelectric (FE) properties of the materials were demonstrated in the study of dielectric hysteresis loops at temperatures of C.
We believe that the observed effects indicate the localization of modifiers at grain boundaries and their partial incorporation into B-positions, which in the case of Li is attributed to the proximity of its ionic radius to that of Nb. This work was financially supported by the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation, state order. In this study, cube-shaped PFN-xPT (0≤x≤0.22) single crystals up to 3-4 mm on edge were grown by spontaneous crystallization using PbO - B2O3 as flux.

XAFS Study of Structural Position and Oxidation State of Mn Impurity in CaTiO 3
XAFS Study of Structural Position and Oxidation State of the Ni Impurity in SrTiO 3
Новая Бессвинцовая Керамика BiKScNbO 6
Optimization of technology for lead-free niobate piezoceramics
Interrelationship of micro- and macro-structure with physical properties of binary and ternary non-centrosymmetric germanate crystals.
Interrelationship of Micro- and Macro-Structure with Physical Properties of Binary and Ternary Non-centrosymmetric Germanate Crystals
Pseudosymmetry Characteristics and Nonlinear Optical Properties of Crys- tals of KTP Family
Mean-Field Method for Analysis Surface Effects in Flexible-Chain Polymer Layers
Simulation of Polarization Switching Processes in Ferro- and Liquid Crystal Polymers
Properties and Phase Diagram of Lead-Free Tetragonal Tungsten Bronze Ceramics
Special feature of the dielectric and elastic properties of the ceramic system SrTiO3-BiScO3 SrTiO3-BiScO3. Joint Research Center “Diagnostics of structure and properties of nanomaterials”, Belgorod State University, Belgorod, 308015, Russia. In this system, strontium titanate, SrTiO3, is known to be an incipient ferroelectric material that has almost reached the limit of its paraelectric phase stability [1].
Various ions replacing the host ions in both the A and B positions in ABO3 perovskite structure can induce a ferroelectric phase transition in SrTiO3. Dielectric anomalies associated with a diffuse ferroelectric phase transition were found and analyzed for these compositions. The experimental evidence of the presence of diffuse ferroelectric phase transition in SrTiO3- BiScO3 is the results of a study of the elastic properties of the samples.
It is known that the temperature dependence of the elastic modulus C at the ferroelectric phase transition in a crystal without the piezoelectric effect in the paraelectric phase is given by. Due to the electrostrictive relationship between polarization and stress in relaxor ferroelectrics below BurnsTd, elastic softening should be observed, which manifests itself as an abnormal decrease in elastic modulus with decreasing temperature. This work was financially supported by the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation under contracts no. and no. P415.
Harmonic analysis of the time evolution of the polarization components on the electric field strength in the Rb2ZnCl4 crystal near the Curie point.
Harmonic Analysis of the Time Evolution of the Polarization Components on the Electric Field Intensity in Rb 2 ZnCl 4 Crystal Near the Curie Point
Kinetics of Order Local Parameter in the Ferroelectric PLZT
Dielectric Studies of Lead-Free Relaxor Ceramics and Single Crystals with Tetragonal Tungsten Bronze Structure
Electromechanical Properties of Relaxor Ferroelectrics Ceramics in Differ- ent Regimes Supply of the Electric Field
Процессы Релаксации Поляризации при Освещении Монокристалла SBN-75+Cr
Влияние Освещения на Процессы Низко - и Инфранизкочастотной Релаксации Поляризации в Сегнетокерамике SBN
Процессы Релаксации Поляризации в Сегнетокерамике PMN+2%Li 2 O в Области Размытого Фазового Перехода
A New Description Method of Oxygen-Octahedral Systems’ Deformations in the Crystal Structures of Functional Materials
Oral presentation
Structural and Dielectric Properties of Glycine Phosphite Thin Films
Пироэлектрический Эффект в Слоистых Магнитоэлектрических Композитах Связности 2-2
Диэлектрические Свойства Пористых Оксидов Алюминия и Кремния с Сегнетоэлектрическими Включениями
Transition Temperatures of Oriented Rochelle Salt Nanorods, Confined in Porous Alumina Films
Пироэлектрические Свойства Пленочных Композитных Материалов на Основе Сополимера P(VDF-TrFE)
Сильные и Слабые Релаксационные Поляризации в Гетерогенных Диэлектриках
Метод Экстраполяции для Определения Вида Распределения Релакса- торов в Диэлектриках
Electric Properties of Heterogeneous Со x (PZT) 100-x Nanocomposites
Conductivity and Barrier Effects in PZT-Based Thin Film Heterostructures According to Synthesis Conditions
Sr 0.2 TiO 3 Films Crystallized at Room Temperature by Laser Assisted Annealing
The use of laser-assisted annealing (LAA)1 can help avoid many technological problems. By adjusting the fluence and frequency of the laser, a temperature profile can be created in such a way that the crystallization of the film is accompanied by minimal heating of the substrate. These make LAA an attractive and versatile crystallization method, and crystallization of FETF on substrates such as platinized silicon and polyethylene terephthalate was demonstrated2-4.
In this work, the Ba0.8Sr0.2TiO3 films were grown by PLD on platinized silicon, glass, and ITO-coated glass substrates. The previous study showed that Pt/Si substrate acts as a heat sink causing the temperature profile to be non-uniform and the use of high energy density and repetition rate was required to crystallize the BST films, which caused cracking and surface damage. facial layer2. By adjusting the annealing conditions, we were able to grow the well-crystalline, crack-free BST films with pure perovskite phase on bare glass substrate using LAL.
For electrical and electro-optical characterization, BST films were grown on an ITO-coated glass substrate. In order to improve the adhesion and surface of the BST films, the initial and cover layers are La0.5Sr0.5CoO3. The optimization of the growth process and the comparison of the physical properties of LAL treated films will be presented.
Диэлектрические Характеристики Композитных Структур на Основе Сополимера P(VDF-TrFE) с Включениями Сегнетоэлектрической Ке-
The Mutual inFluence of Components in Ferroelectric Composites
Electrical Conductivity of NaNO 2 –SiO 2 Matrix Composites
Механические, Диэлектрические и Магнитные Свойства Гранулиро- ванных Нанокомпозитов Co x (PZT) 100-x
Особенности Инфранизкочастотных Процессов Релаксации Поляри- зации в Монокристаллах LiNbO 3
Щелочно-Боросиликатные Стекла с Магнитной Фазой
Переключение Доменов в Доменных Границах Сегнетоэлектриков
Температурная Зависимость и Релаксация Доменного Вклада в Диэлектрическую Проницаемость Сегнетовой Соли
Усталостные явления в тонких сегнетоэлектрических пленках, стиму- лированные многократным переключением поляризации
Investigation of the Single-Domain State Disintegration in Ferroelectrics
The formation of the stable dendritic domain structures during polarization reversal in a uniform electric field at elevated temperatures (above 250oC) in single crystals of stoichiometric lithium niobate LiNbO3 was revealed and investigated. The dendritic domain structures consisting of the stable non-through domains appeared on the Z+ polar surface as a result of the application of triangular electric field pulses (field increasing rate 500 V/s) using uniform solid-state electrodes. The analysis of the series of RCM images (Figure 1), obtained by scanning at different depths, made it possible to reveal the main stages of the evolution of the dendrite structure.
It was shown that the process of the domain structure formation for application of the single pulse is composed of five successive stages. The first stage represents the appearance of the single isolated nanodomain – the center of the dendrite. The second stage represents the formation of the three isolated nanodomains equidistant from the first one at the vertices of an equilateral triangle oriented along Y directions, suppressing the growth of the first domain.
The third phase represents the oriented growth of the nanodomain chains with sub-micron period in six Y directions. The main stages in the formation of five-ray stars have resembled the domain structure evolution at the first pulse. The equipment of the Ural Center for Shared Use "Modern Nanotechnology", Department of Natural Sciences, Ural Federal University has been used.
Induced By Pulsed Laser Heating
Kinetics of Domain Structure in SBN Single Crystals Using Electrodes Based on Stable Suspension of Silver Nanoparticles
On the Nuclear Magnetoelectric Resonance in Potassium Niobate
Role of Domain Orientations in Forming the Hydrostatic Performance of Novel 2–2 Single Crystal / Polymer Composites
Field and Deformational Effects in Quasi-one-Dimensional
PO 4 Type Ferroelectrics
Additional Terahertz Light Waves in SrTiO 3 Crystal
On the Converse Flexoelectric Effect
Диэлектрические Свойства Перовскитовых Сегнетоэлектриков при Неравновесной Концентрации Точечных Дефектов
Atomic Structure Of Hf-W Non-crystalline Alloys
Влияние Фазового Состава Керамических Висмутовых ВТСП на их Критические Параметры
Динамика Абрикосовских Вихрей Вблизи Первого Критического Поля Текстурированных Сверхпроводников на Основе Иттрия
Frequency dependence of polarization hysteresis loops in Pb(Fe1/2Nb1/2)O3–PbTiO3Ceramic materials Pb(Fe1/2Nb1/2)O3–PbTiO3Ceramic materials. For lead-iron niobate-lead titanate ceramics in solid solution (1-x)PbFe1/2Nb1/2O3– xPbTiO3 (PFN-xPT), it is experimentally observed that the shape of the polarization hysteresis loops depends on the frequency of the external electric field (Fig. 1a ). As the field frequency decreases, the value of the residual polarization increases. Experimental (points) and theoretical (lines) differences between P(E) dependence measured at low (0.33 Hz and 2 Hz) and high (20 Hz) frequencies.
Theoretical curves were obtained within the framework of the proposed model using the same value of the relaxation time ф~ 1.2 s. We propose a model that explains this phenomenon by the relaxation of the charge localized on the grain boundary surface states. At sufficiently high values of the frequency of the external field (х . ~ 20Hz), this charge does not have enough time to relax, and the spontaneous polarization in the part of the grain adjacent to the grain boundary fails to switch.
An attempt was made to estimate the contribution of this polarization to the LMN part of the loop (Fig.1.a.) by subtracting the values of polarization obtained at 20Hz from the values obtained at low frequencies of the external field. . The model gives good agreement with experiment for different frequencies of the external field (Fig.1.b) at the same value of the relaxation time ± 1.2 s.

Piezoelectric Resonance in Rochelle Salt: the Contribution of Diagonal Strains
Bending Vibrations of the Screw Dislocation in the Vicinity of a Structural Phase Transition Point
The Temperature Dependences of Acoustic Waves Velocities and Elastic Constants in Ferroelastics KPb 2 Br 5 and RbPb 2 Br 5
Intelligent System For Decision-Making Processes in the Investigation of the Parameters of Ferroelectrics and Semiconductors
Models of the Dielectric Parameters of Ferroelectrics
Metrological Aspects
Temperature Hysteresis and Frequency Dispersion of Dielectric Permittivity in Рb 2 МоО 5 Crystal
Features of the Dielectric Spectra of Solid Solutions Based on Alkali Metal Niobates
Cтруктура и Электрические Свойства Новых Гетерогенных Систем Cu-Pd-In-Y-O
Зависимость Электрического Сопротивления Компактированных Нанодисперсных Углеродных Материалов от Магнитного Поля
Эффект Зеебека в Компактированных Нанодисперсных Углеродных Материалах
Диэлектрические Свойства Пленочных Структур «Желатин- Триглицинсульфат»
Релаксационное Поведение Кристаллов ТГС в Окрестности Фазового Перехода
Диэлектрические Свойства Кристалла ТГС, Выращенного с Переводом Через Точку Кюри
Влияние электронного облучения на диэлектрические свойства монокристаллов TlInS2, TlInSe2, TlGaS2 и TlGaTe2 Монокристаллы TlInS2, TlInSe2, TlGaS2 и TlGaTe2. Кристаллы TlInS2, TlInSe2, TlGaS2 и TlGaTe2 относятся к группе халькогенидных соединений таллия типа AIIIBIIICVI2 с выраженной слоистой структурой. Данная работа посвящена изучению закономерностей изменения диэлектрической проницаемости и электропроводности монокристаллов TlInS2, TlInSe2, TlGaS2 и TlGaTe2 под воздействием температуры и электронного излучения.
В результате исследования диэлектрических свойств слоистых монокристаллов TlInS2, TlInSe2, TlGaS2 и TlGaTe2 установлено, что с повышением температуры электропроводность и диэлектрическая проницаемость исследованных кристаллов увеличиваются. Облучение кристаллов электронами дозами 1015 и 1016 см-2 приводит к частичному сглаживанию пиков, соответствующих фазовым переходам, но не влияет на их температуру.
Dielectric Relaxation in SBN and BaTiO 3 Monocrystals
Фон Внутреннего Трения в Нанокомпозиционном Материале Металл-Диэлектрик и его Связь с Диффузионными Характери-
Dielectric Properties of Monoclinic RbD 2 PO 4 the Effect of Hydrostatic Pressure
Термополяризационный Эффект в Полостных Структурах Гетерогенных Систем
Электрическая Проводимость и Плотность Спиртовых Суспензий Уг- леролных Нановолокон
Роль Кристаллитов Целлюлозы в Поляризации Биополимерного Композита - Древесины в Неоднородном Температурном Поле
Properties of TGS Crystals Grown From Aqueous Solution with Isopropanol
Поглощение Ультразвука в Биополимерах
Dielectric Properties of SrTiO 3 Doped with Pr
Трансформация Геликоидальной Спиновой Структуры в Многослой- ной Системе Ho/Y
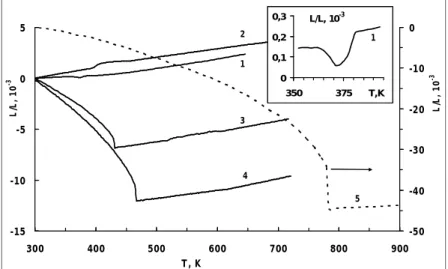
The great interest in the study of crystals with hydrogen bonds is related to the problem of structural phase transitions and transitions between phases with ordered and disordered hydrogen bonds due to symmetry change [1]. Although attention to these objects was directed for a long time, but there is some inconsistency in the results obtained (С2/сcubic [1] or m. Thus, the purpose of this work was to study various physical properties of ferroelastic-superionic single crystal Rb3H( SO4)2.
In the maximum capacitance region, the activation energy of the resistivity varies from 0.6 eV to 1.3 eV. The smearing of the internal friction peak is apparently explained by the fact that it represents a superposition of two peaks at 375 K and at 420 K. This is evident from the temperature dependence of the capacitance and a loss tangent (Fig. 1), and also of the resistance. (fig. 2) clearer.

Сопоставление Оптических Спектров Скандониобата и Скандотанталата Свинца
Диэлектрическая Релаксация В Кристалле Несобственного Сег- нетоэлектрика–Сегнетоэластика Молибдата Тербия
AUTHOR INDEX