Overview of Research on Innovation Adoption and University’s Change 9
General Discussion on University and Higher Education Transformation 9
Now, when we agree on the definition of the term, we will examine the higher education system with a focus on Universities through the theoretical application of Porter's Five Forces Analysis. The cost of switching customers is another phenomenon that keeps new entrants out of the higher education market. At that time, higher education institutions were created for a SPOD world (SPOD: stable, predictable, common, defined) [Vinogradova, Smirnova, 2020].
Now, when the motivation of Higher Education institutions to innovate and the place of EdTech startups are clear, we move to the theoretical part of the study and look at the theories of adoption.
![Figure 1. Higher Education industry through the Porter’s Five Forces Framework. [Source: author]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/pdfplayernet/420195.43349/12.918.313.666.636.975/figure-higher-education-industry-porter-forces-framework-source.webp)
Theories on Consumer Behavior Towards Innovation Adoption 30
For example, Cooper and Zmud focus on decision unit behavior during the implementation and confirmation phase [Cooper & Zmud, 1990]. By that time, a decision-making unit has obtained information about a particular innovation, but has not yet decided whether or not to use it. Considering Rogers' theory as the foundational piece for designing the adoption intent of a decision unit, we can move on to the attributes inherent in innovations.
The first method is built around the thesis that the environment affects the perception of innovative solutions, and it is possible to calculate the speed of technology application by a certain decision-making unit. The second method is focused on intrinsic characteristics of innovative solutions that influence a decision-making entity's innovation adoption. The main drawback of the Theory of Reasoned Action is its inability to include in its framework the necessary resources of a decision-making unit for an action with the product.
This model is built around a hypothesis that decision-making unit's attitude is key in understanding behavioral intention of adoption of a certain innovative and technological product. Third, compatibility - a degree to which an offered service or product matches the decision-making unit's values and past experiences [Rogers, 2003]. First, it is built around an innovation itself and concentrates on its characteristics rather than technology acceptance by decision-making agents.
![Table 3. Adoption models. [Source: Khan, 2017]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/pdfplayernet/420195.43349/32.918.114.771.178.422/table-adoption-models-source-khan.webp)
Research Gap and Hypotheses Formulation 38
Typically, EdTech solutions help expand individualized educational practices and reach new markets at a lower cost, and these are the top priorities of universities, according to Jisc, as they secure the position of higher education institutes [Jisc, 2020]. According to the head of the Department of Management Information Systems at King Khalid University Said Al-Gahtani, complexity is best described as the extent to which an innovative solution is difficult and inconvenient to use [Al-Gahtani, 2003]. As one of the key attributes of the persuasion phase, it is involved in the process when the decision-making unit tries to apply a certain innovation to its question and evaluates whether it is appropriate or not.
No matter how good an EdTech solution is at its core, it will not succeed if it is difficult to own and use [Kommuru, 2020]. It is best illustrated by the state of the accounting market, where companies spend months to years switching from one ERP system to another, as it is neither easy nor quick to become native to another programming environment [Kenge, 2020]. In this case, EdTech solutions should be compatible with existing products and, as a best-case scenario, work as an add-on or add-on module, if companies are targeting the mass market and not tailoring solutions for just one customer.
According to Rogers' study, observability does not affect much during the persuasion stage. Furthermore, software input is said to be even less visible than hardware input [Roger, 2003]. To summarize, we have formulated the following six hypotheses to test all five attributes of Rogers' innovation decision theory in accordance with a proposed relationship between the development of EdTech startups and the technological changes of Universities.
![Table 5. Formulated hypotheses. [Source: author]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/pdfplayernet/420195.43349/41.918.118.805.185.582/table-formulated-hypotheses-source-author.webp)
Research Methodology and Design 42
- Research Design 42
- Data Collection 43
- Questionnaire Design 44
- Statistical Techniques 47
And the research problem is to identify the relationship parameters between the innovation attributes of EdTech solutions and the adoption intention of University staff. The questionnaire, which was used to collect data from university staff, was made in English, as the focus was to cover respondents in several countries, and English is the best option as it is the language spoken and understood by academia around the globe. Due to the experience of working and living in the USA, the author has many contacts at the University of Pennsylvania, the University of Pittsburgh and the University of Michigan, and one of them is ranked in the top-4 in the Reuters list of the most innovative universities in the world [Ewalt, 2019].
Since 283 responses lead to quite a massive margin of error, the decision was made to reach more countries as it was an easier option for the author rather than reaching new people in the US and Russia in a "cold message" way. At this point, the questionnaire reached Peking University, Qinghua University, Yonsei University and some smaller higher education institutions in the above countries. In the previous chapter, secondary research was conducted and six hypotheses to be tested were formulated.
The designed survey allows to identify the extent to which EdTech solutions' innovation characteristics can predict University staff's adoption intention. The table below shows the list of specific variables asked in the survey. More details on each step of the statistical techniques used in this research are provided in the next chapter, when the data is analyzed and the model is calculated.
![Figure 7. Research model. [Source: author]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/pdfplayernet/420195.43349/45.918.173.740.678.1014/figure-research-model-source-author.webp)
Data Analysis 49
Descriptive Statistics 49
These results are completely consistent with the Innovation Theory, which states that the distribution of people is as follows: 2.5% innovators, 13.5% early adopters, 34% early majority, 34% late majority, 16% laggards [Rogers, 2003]. Therefore, the sample corresponds to the Diffusion of Innovation concept, represents the population of Universities' staff and with the confidence level of 95% it leads to a 4% margin of error [Page & Patton, 1991].
Reliability Analysis 50
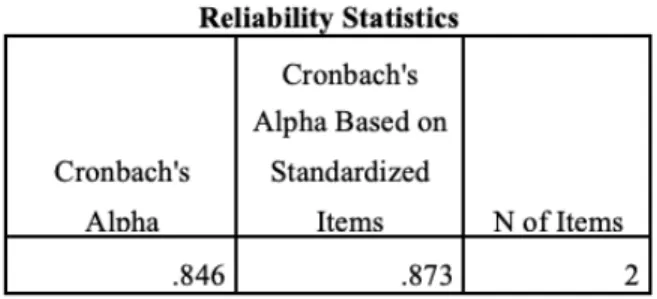
When Cronbach's alpha is below 0.5, internal consistency reliability is not acceptable, as it is quite low. When the number is more than 0.5, it is considered sufficient and the higher it is, the higher the internal consistency [Field, 2013]. For this research, internal consistency was calculated for both innovation attributes and innovation intent, where at least two questions were grouped to measure a particular parameter.
The results of reliability analyzes performed in IBM SPSS Statistics are presented below. According to the results of six separate reliability tests, the internal consistency of the survey is sufficient. In the last test, all questions of the questionnaire were included, except personal willingness to use innovative solutions and country of origin.
Cronbach's alpha for the entire data set proved to be sufficient, as it was calculated equal to 0.844.
Regression Analysis 52
Thus, the model can be used to predict a particular outcome related to the adoption intent score. To test the hypotheses, six sets of variables were created, which correspond to certain characteristics of EdTech solutions. The standardized beta coefficient is set at 0.352 with a p-value of less than 0.05, therefore the Accessibility attribute explains adoption intent quite well.
This hypothesis is rejected, as respondents expressed their willingness to pay for EdTech solutions out of pocket for work assignments. The Standard Beta coefficient is negative and does not support the hypothesis that University staff are unwilling to pay for EdTech solutions. The standardized beta coefficient is set at 0.173 with p-value less than 0.05, therefore the Complexity attribute contributes to the overall explanation of Adoption Intention.
This hypothesis is rejected, as the respondents expressed their willingness to deal with the incompatibility of EdTech solutions, if it occurs. The standard Beta coefficient is set at 0.355 with p-value less than 0.05, therefore the Trialability attribute provides the best unique explanation of Adoption Intention within the model. The standard Beta coefficient is set at 0.148 with p-value less than 0.05, therefore the Observability attribute contributes to the overall explanation of Adoption Intention.
![Table 14. Correlations table. [Source: author via IBM SPSS Statistics]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/pdfplayernet/420195.43349/53.918.108.832.480.621/table-correlations-table-source-author-ibm-spss-statistics.webp)
Conclusion 57
- Theoretical Implications 58
- Managerial Implications 59
- Limitations and Further Research 62
The research identified positive relationships between the innovation attributes of four EdTech solutions and adoption intention of University staff, and negative relationships with the other two. This research showed that cost and compatibility are not foundational attributes that negatively affect the adoption intention of university staff. The low cost barrier to entry did not result in positive adoption intention of university staff.
The research examined the relationship between the innovation characteristics of EdTech solutions and adoption intentions of university staff, and was built around Rogers' Innovation-Decision theory, which was updated by the author with insights from Kapoor, Tornatzky, and Klein. The regression model built for the research confirmed that high perceived accessibility and trialability significantly result in positive adoption intention among university staff. EdTech startups are thus advised not only to target university staff as end users, but also to collaborate with universities.
Second, compatibility is not a topic to waste time on when pitching an EdTech solution to university staff. Therefore, EdTech startups can spend less time on the cost and observability attributes of their innovative products and emphasize other attributes including accessibility, trialability, observability, and core value of the product as it results in a positive intention of university staff to adopt it. The research paved the way for EdTech startups to gain insight into how university staff decide whether or not to test a new software solution in action.
Beyond Homogenizing Global Education: Do Alternative Pedagogies Like Steiner Education Have Something to Offer an Emerging Global/Emerging World?" The Secret to Raising Brilliant Children: Part 1. Adoption of the Mobile Internet: An Empirical Study of Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS)." The International Journal of Management Science.
![Figure 2. Innovation matrix. [Source: Christensen, 2015]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/pdfplayernet/420195.43349/22.918.301.573.661.934/figure-innovation-matrix-source-christensen.webp)
![Figure 3. Ecosystem Change Model for EdTech. [Source: The Omidyar Network, 2019]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/pdfplayernet/420195.43349/23.918.130.780.463.732/figure-ecosystem-change-model-edtech-source-omidyar-network.webp)
![Table 1. EdTech startups by their focus. [Source: author]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/pdfplayernet/420195.43349/26.918.228.742.144.672/table-edtech-startups-focus-source-author.webp)
![Table 2. Incentives for companies to innovate. [Source: author]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/pdfplayernet/420195.43349/29.918.155.822.257.380/table-incentives-companies-innovate-source-author.webp)
![Figure 4. Rogers’ innovation-decision theory. [Source: Rogers, 2003]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/pdfplayernet/420195.43349/33.918.117.807.115.531/figure-rogers-innovation-decision-theory-source-rogers.webp)
![Figure 5. Theory of Planned Behavior model. [Source: Belkhamza & Niasin, 2017]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/pdfplayernet/420195.43349/34.918.163.762.610.821/figure-theory-planned-behavior-model-source-belkhamza-niasin.webp)
![Figure 6. The Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology model. [Source: Dwivedi et al]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/pdfplayernet/420195.43349/35.918.200.725.435.725/figure-unified-theory-acceptance-technology-model-source-dwivedi.webp)
![Table 4. Interconnections of innovation perception theories. [Source: author]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/pdfplayernet/420195.43349/37.918.234.682.139.611/table-interconnections-innovation-perception-theories-source-author.webp)