Time Trends in Incidence and Mortality of Acute Myocardial Infarction, and All-Cause Mortality following a Cardiovascular Prevention Program in Sweden.
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
Objective: Despite the decline in the incidence of tetanus, this disease is still neglected in the developing world and remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality.
In adults, an active lifestyle is associated to a reduction in the incidence of many chronic diseases, and a reduction in cardiovascular and all-cause mortality. In children
Mortality time trends and the incidence and mortality estimation and projection for lung cancer in China. Available from:
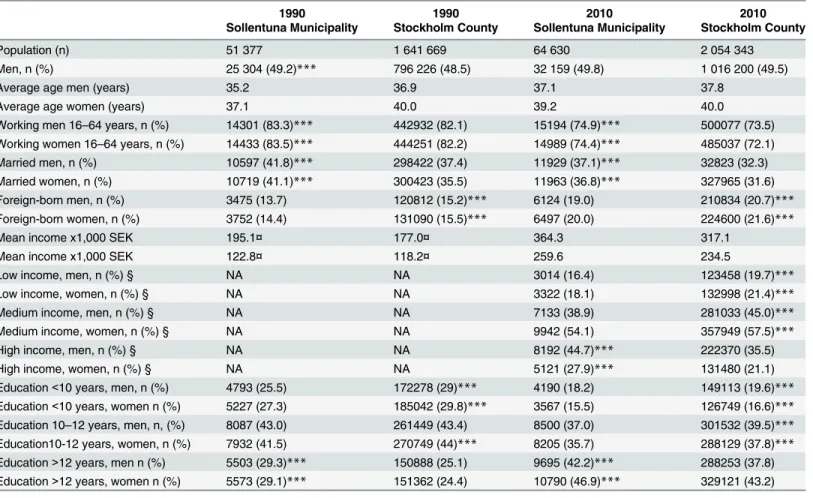
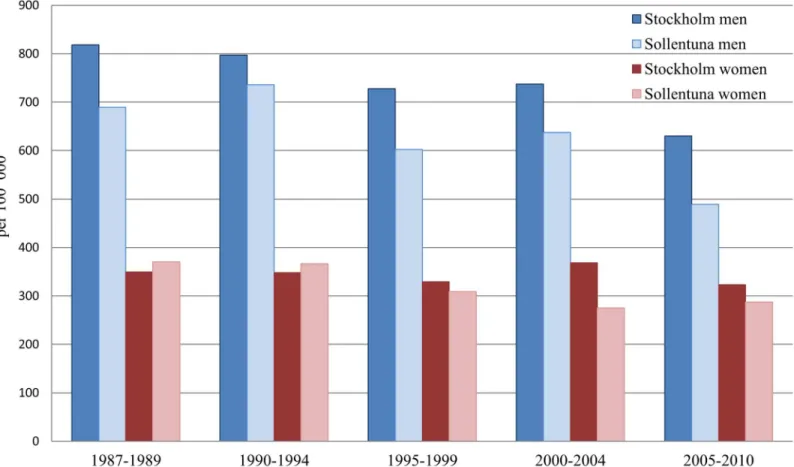
The aim of this study was to assess the rate of mortality from acute myocardial infarction in the period from 1998 to 2009 in Curitiba, as well as the distribution of mortality
The purpose of the work being partially reported here was to define the role of acute myocardial in- farction as a health problem in the city of Salvador, Bahia,
This study aimed at assessing the impact of smoking on in-hospital morbidity and mortality of patients experien- cing acute myocardial infarction and to assess the associa- tion
To identify the incidence, risk factors, and mortality of acute renal failure (ARF) in patients undergoing myocardial coronary artery bypass surgery with extracorporeal
On the other hand, cause- specific mortality analysis showed that both AF groups had proportionally significantly higher cardiovascular (especially acute myocardial infarction and
