Revista de Saúde Pública
I SSN 0034- 8910 versão im pressaRev Saúde Pública 2004; 38(1)
Psychoactive drugs use by school- age adolescents, Braz il
José Luiz Guim arães, Pedro Henrique Godinho, Rubens Cruz, Jair I zaías Kappann and Lairt o Alves Tost a Junior
Depart am ent o de Psicologia Experim ent al e do Tr abalho da Faculdade de Ciências e Let r as da Universidade do Est ado de São Paulo ( UNESP) . Assis, SP, Brasil
ABSTRACT
To quant ify psy choact iv e dr ug use and inv est igat e use - r elat ed v ar iables among st udent s of Assis, Br azil, a quest ionnair e w as adm inist er ed t o collect sociodem ogr aphic dat a and ident ify t he pat t er n of non- m edical use of psy choact iv e dr ugs in 20% of public and pr iv at e school st udent s. The lar gest consum pt ion indexes for lifet im e use w ere seen for alcohol ( 68.9% ) and t obacco ( 22.7% ) . Drugs m ost oft en used were: solvent s ( 10.0% ) ; m arij uana ( 6.6% ) ; benzodiazepines ( 3.8% ) ; am phet am ines ( 2.6% ) ; cocaine ( 1.6% ) ; and ant icholinergics ( 1.0% ) .
Keywords
I N TRODUCTION
Drug consum pt ion has becom e a m aj or concern in t he Brazilian societ y. Epidem iological research on psy choact iv e dr ug use is especially r elev ant for t he dev elopm ent of appr opr iat e and successful public healt h policies for pr event ing subst ance abuse ( Bucher ,2 1992).
Many st udies on psychoact ive drug use have been carried out am ong young st udent s in Brazil ( Bucher,2 1992; Muza et al,4 1997) . The m ost com prehensive ones w ere conduct ed by t he CEBRI D –
Cent r o Br asileir o de I nfor m ações sobr e Dr ogas Psicot r ópicas ( Br azilian Dat a I nst it ut e on Psy ch oact iv e Drugs) . The I nst it ut e has carried out surveys in 10 different Brazilian capit als in 1987, 1989, 1993, and 1997 ( Galduróz et al,3 1997) . The pur pose of t he pr esent st udy w as t o quant ify psy choact iv e dr ug use am ong st udent s in t he cit y of Assis, São Paulo, Br azil, and t o invest igat e dr ug use- r elat ed variables.
Methods
St udy subj ect s com pr ised m iddle and high school st udent s of Assis in t he st at e of São Paulo. Wit h a populat ion of 87,251 inhabit ant s, Assis is locat ed 450 km far fr om t he st at e’s capit al. The st udy sam ple consist ed of 20% of t ot al st udent s in 18 cit y schools and 1,803 quest ionnair es w er e adm inist ered in public schools and 320 in privat e schools.
School classes were random ly drawn at t he t im e of quest ionnaire adm inist rat ion and proport ionally t o school, t erm , and school year. Trained universit y st udent s sim ult aneously adm inist ered quest ionnaires t o all classes in t he school t o pr ev ent st udent s fr om k now ing befor ehand t he quest ionnair es’ cont ent s. St udent s w er e infor m ed on t he st udy’s pur poses and asked t o par t icipat e volunt ar ily and anonym ously. Only st udent s in class at t he t im e of quest ionnair e applicat ion w er e included in t he st udy . Teacher s w er e ask ed t o leav e t he classr oom t o av oid m ak ing st udent s uncom for t able.
I t w as applied a close anonym ous self - adm inist ered quest ionnaire, sim ilar t o t hat used by Galduróz et al1 ( 1997) , which w as developed accor ding t o Wor ld Healt h Or ganizat ion cr it er ia. Ther e w er e 43 quest ions on pat t er n of psy chot r opic use, st udent s’ school at t endance, and sociodem ographic dat a based on t he ABI PEME – Associação Br asileir a dos I nst it ut os de Pesquisa de Mer cado ( Brazilian I nst it ut e Associat ion of Mar k et Resear ch)1 socioeconom ic r at ing sy st em . A quest ion w it h fict it ious dr ug nam es w as included t o det ect inconsist encies and lack of at t ent ion w hen answ er ing t he quest ionnair e. Classificat ion cr it er ia for dr ug use fr equency w er e based on Galdur óz et al.,3 1997. These aut hor s defined five drug use pat t erns: lifet im e, yearly, m ont hly, regular, and heavy use.*
* Lifet im e use: psychoact ive dr ug use at least once in a lifet im e; year ly use: dr ug use in t he 12 m ont h- period prior t o t he st udy; m ont hly use: drug use in t he last 30 days; regular use: drug use 6 or m ore t im es in t he last 30 days, and heavy use: drug use 20 t im es or m ore in t he m ont h prior t o t he st udy .
answ er s, and t hose w her e a posit iv e answ er w as giv en t o t he fict it ious dr ug quest ion w ere excluded fr om t he analysis.
Result s
Of t ot al part icipant s, t here w ere 46.9% m ale and 48.7% fem ale st udent s aged 13- 15 years ( 36.1% ) , 16- 18 years ( 30.0% ) , and 10- 12 years ( 27.2% ) . Only 4.4% were over 18. Wit h regard t o socioeconom ic st at us, m ost belonged t o Class C ( 45.9% ) , follow ed by Class B ( 23.7% ) , Class A ( 11.5% ) , Class D ( 14.3% ) , and a m inorit y t o Class E ( 1.4% ) . Of all, 3.2% did not provide inform at ion on social class.
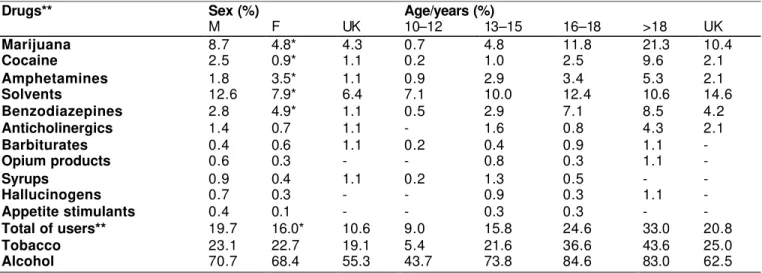
Psy choact iv e dr ugs m ost ly used in a lifet im e w er e: alcohol ( 68.9% ) , t obacco ( 2 2.7% ) , solvent s ( 10.1% ) , m arij uana ( 6.6% ) , benzodiazepines ( 3.8% ) , am phet am ines ( 2.6% ) , and cocaine ( 1.6% ) ( Table) .
St udent s who used drugs in a lifet im e showed higher school absence ( 72.5% ) t han non - users ( 58.5% ) ( p< 0.05) .
As for sex, lifet im e use of m arij uana, cocaine, and solv ent s w as higher in m ale st udent s and benzodiazepines in fem ale st udent s. The m ost ly used benzodiazepine was Diazepam ® ( 41.2% ) , followed by Lexot an® . Am ong m ost com m only referred am phet am ines were I nibex® and Hipofagin® . Th er e w as no st at ist ically significant difference in bot h sex groups regarding ot her drugs, including t obacco and alcohol.
Table - Lifetime use of psychoactive drugs by 2,123 middle and high school students of public and private schools in Assis, as a percentage, per sex, age, and drug.
Drugs** Sex (%) Age/years (%)
M F UK 10–12 13–15 16–18 >18 UK
Marijuana 8.7 4.8* 4.3 0.7 4.8 11.8 21.3 10.4
Cocaine 2.5 0.9* 1.1 0.2 1.0 2.5 9.6 2.1
Amphetamines 1.8 3.5* 1.1 0.9 2.9 3.4 5.3 2.1
Solvents 12.6 7.9* 6.4 7.1 10.0 12.4 10.6 14.6
Benzodiazepines 2.8 4.9* 1.1 0.5 2.9 7.1 8.5 4.2
Anticholinergics 1.4 0.7 1.1 - 1.6 0.8 4.3 2.1
Barbiturates 0.4 0.6 1.1 0.2 0.4 0.9 1.1 -
Opium products 0.6 0.3 - - 0.8 0.3 1.1 -
Syrups 0.9 0.4 1.1 0.2 1.3 0.5 - -
Hallucinogens 0.7 0.3 - - 0.9 0.3 1.1 -
Appetite stimulants 0.4 0.1 - - 0.3 0.3 - -
Total of users** 19.7 16.0* 10.6 9.0 15.8 24.6 33.0 20.8
Tobacco 23.1 22.7 19.1 5.4 21.6 36.6 43.6 25.0
Alcohol 70.7 68.4 55.3 43.7 73.8 84.6 83.0 62.5
*Statistically significant difference between sexes, Chi-Square test, p<0.05.
**Except for tobacco and alcohol.
Com parison bet w een public and privat e schools
Besides differ ences associat ed w it h socioeconom ic v ar iables bet w een public and pr iv at e school st u den t s, it w as fou n d t hat 16. 6% of public school st udent s hav e ev er used any dr ug ( ex cept t obacco and alcohol) and 2.4% referred regular use. Drugs m ost com m only used were: alcohol ( 67.6% ) , t obacco ( 22.2% ) , solvent s ( 8.9% ) , m arij uana ( 6.3% ) , benzodiazepines ( 3.5% ) , am phet am ines ( 2.2% ) , and cocaine ( 1.7% ) . Heavy use of m arij uana was seen in 1.0% , followed by solvent s in 0.6% .
I n privat e schools, lifet im e drug use was higher for all drugs 22.5% ( p< 0.05) , solvent s, 16.9% ( p< 0.05) , am phet am ines, 4.7% ( p< 0.05) . There was no st at ist ical significant differ ence for ot her drugs when com pared t o public schools: alcohol ( 76.2% ) , t obacco ( 25.6% ) , m arij uana ( 8.4% ) , benzodiazepines ( 5.0% ) , and cocaine ( 1.2% ) . Of t hem 1.9% referred heavy use of solvent s and 0.9% of m arij uana.
I n public schools, higher drug use w as seen am ong st udent s over 16, w hich could probably be due t o m or e av ailable r esour ces since m any public school st udent s at t his age st at ed t hey had a j ob. I n privat e schools, drug use in t he age group 16- 18 was higher in all use pat t erns. I n cont r ast , dr ug use in t he age group 10- 12 was higher in public schools.
DiscussION
Male st udent s used m or e dr ugs t han fem ale st udent s. I t is w or t h not ing t her e w as found a clear fem ale preference for licit drugs ( prescript ion drugs such as benzodiaze pines and am phet am ines) and m ale preference for illicit drugs, which corroborat es t he t rend ident ified in ot her st udies ( Bucher,2 1992; Galduróz et al,3 1997; Muza et al,4 1997; Zilberm an,5 1998) .
A com par ison bet w een public and pr iv at e schools show ed a higher prevalence of drug use in public schools, w hich could be associat ed t o t he st udent s’ higher social st at us and m or e av ailabilit y of r esour ces t o buy dr ugs.
Fur t her conclusions ar e hinder ed due t o t he scar cit y of epidem iological st udies in pr iv at e schools since r esear cher s do not hav e easy access t o dat a collect ion. ( Bucher ,2 1992) .
Drug use seen in t he schools of Assis is sim ilar t o t hat described in CEBRI D st udies in t he cit y of São Paulo ( 19% lifet im e use) but it is slight ly lower t han t hat found by t he sam e aut hors in ot her Brazilian capit als ( an average of 24.7% lifet im e use) ( Galduróz et al,3 1997) , and m uch low er t han t hat seen in dev eloped count r ies ( Muza et al4).
Psychoact ive drug use has been ubiquit ous in m an hist ory w it h varying drugs, am ount s and r out es. A m ore m arked use of a given drug at a t im e suggest s specific fact ors t o t hat t im e in hist ory. Thus, drug abuse is m or e a sy m pt om t han t he cause of pr oblem s in t oday ’s societ y and for t hat it should be t ack led t ak ing int o account it s com plex it y and m agnit ude. The m ost efficient act ion t o lessen t he dr ug pr oblem is t o develop specific pr event ion policies for each social st r at um and age gr oup focusing on healt h pr om ot ion and r espect for life.
REFEREN CES
1 . [ ABI PEME] Associação Brasileira dos I nst it ut os de Pesquisa de Mercado .Proposição para um nov o cr it ér io de classificação socioeconôm ica. São Paulo, 1978. p. 15.
2 . Bucher R. Drogas e drogadição no Brasil. Por t o Alegr e: Ar t es Médicas; 1992.
3 . Galduróz JCF, Not o AR, Carlini EA. I V levant am ent o sobre o uso de drogas ent re est udant es de 1º e 2º graus em 10 capit ais brasileiras- 1997. São Paulo: Cent ro Brasileiro de I nform ações sobre Dr ogas Psicot r ópicas / Escola Paulist a de Medicina; 1997.
4 . Muza GM, Bet t iol H, Muccillo G, Barbieri MA. Consum o de subst âncias psicoat ivas por adolescent es escolar es de Ribeir ão Pr et o, SP. I - Pr ev alência do consum o por sex o, idade e t ipo de subst ância. Rev Saúde Pública 1997; 31: 21- 9 .
5 . Zilberm an ML. Caract eríst icas clínicas da dependência de dr ogas em m ulher es [ t ese de dout orado] . São Paulo: Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo; 1998.
Address to correspondence
José Luiz Guim arães
Av. Do m Ant ônio, 2.100 Parque Universit ário Caixa Post al 65
19806 - 900 Assis, SP, Brasil E- m ail: j luiz@assis.unesp.br
Fin an ced by Fu n dação de Am par o à Pesquisa do Est ado de São Paulo ( FAPESP - Pr ocesses n s. 99/ 08304- 0 and 99/ 08305 - 6).
Received on 5/ 9/ 2002. Reviewed on 10/ 7/ 2003. Approved on 6/ 8/ 2003.
© 2 0 0 3 Fa cu lda de de Sa ú de Pú blica da U n iv e r sida de de Sã o Pa u lo Ave nida D r . Ar na ldo, 7 1 5