CLINICAL SCIENCE
Instituto de Ortopedia e Traumatologia, Hospital das Clinicas, Faculdade de Medicina, Universidade de São Paulo - São Paulo/SP, B rasil.
E mail: rmotaa@ uol. com. b r Tel. : 5 5 1 1 3 2 1 4 -4 4 2 2
R eceived f or pub lication on Feb ruary 1 8 , 2 0 1 0 First review completed on March 0 3 , 2 0 1 0 A ccepted f or pub lication on A pril 1 4 , 2 0 1 0
COMPARATIVE STUDY ON ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION:
DETERMINATION OF ISOMETRIC POINTS WITH AND WITHOUT NAVIGATION
Fab io J . A ngelini, R ob erto F. M. A lb uq uerq ue, Sandra U. Sasak i, G ilb erto L . Camanh o, A rnaldo J . Hernandez
doi: 1 0 . 1 5 9 0 /S1 8 0 7 -5 9 3 2 2 0 1 0 0 0 0 7 0 0 0 0 6
Angelini FJ, Albuquerque RFM, Sasaki SU, Camanho GL, Hernandez AJ. Comp arat iv e st udy on ant erior c ruc iat e ligament
rec onst ruc t ion: det erminat ion of isomet ric p oint s w it h and w it hout nav igat ion. Clinic s. 2 0 1 0 ; 6 5 ( 7 ) : 6 8 3 - 8 .
OB J E CTIV E S: T o c omp are t he ac c urac y of t unnel p lac ement and graf t isomet ry f or ant erior c ruc iat e ligament rec onst ruc t ion p erf ormed using a c omp ut er- assist ed nav igat ion sy st em ( O rt hop ilot ) and using t radit ional inst rument s.
ME THOD S: T he ant erior c ruc iat e ligament w as remov ed int ac t f rom 3 6 p airs of human c adav er knees. From eac h p air, one knee w as randomized t o Group 1 ( c onv ent ional) and t he ot her t oGroup 2 ( O rt hop ilot ) . An inelast ic sut ure w as t hen p assed t hrough t he c ent ral p oint s of t he t ibial and f emoral t unnels. N eit her of t he t unnels w as drilled. All knees w ere t hen dissec t ed, and six p aramet ers w ere obt ained: dist anc es f rom t he t ibial t unnel c ent er t o t he 1 ) p ost erior c ruc iat e ligament , 2 ) ant erior horn of t he lat eral menisc us and 3 ) medial t ibial sp ine; 4 ) dist anc e f rom t he f emoral t unnel c ent er t o t he p ost erior f emoral c ort ex ; 5 ) f emoral t unnel c oronal angle; and 6 ) v ariat ion of t he dist anc e f rom t he f emoral t o t he t ibial t unnel w it h t he knee ex t ended and at 9 0 degrees of lex ion. R E SUL TS: T he v ariat ion of t he dist anc e f rom t he f emoral t o t he t ibial t unnel during lex ion and ex t ension w as smaller in t he O
r-t hop ilor-t group ( ber-t r-t er isomer-t ry ) c omp ared r-t o r-t he c onv enr-t ional group . T here w ere no sr-t ar-t isr-t ic al dif f erenc es in any or-t her p aramer-t ers bet w een t he group s, and all t unnels w ere c onsidered t o be in sat isf ac t ory p osit ions.
D ISCUSSION : T he result s obt ained f or ant erior c ruc iat e ligament rec onst ruc t ion dep end on p rec ise isomet ric p oint p osit ioning, and a nav igat ion sy st em is a p rec ision t ool t hat c an assist surgeons in t unnel p osit ioning.
CON CL USION : N o dif f erenc es in t unnel p osit ion w ere observ ed bet w een t he group s. N onet heless, bet t er isomet ry w as ac hiev ed in t he O rt hop ilot group t han w it h c onv ent ional inst rument s.
K E Y W K nee; Ant erior c ruc iat e ligament ; B iomec hanic s; N av igat ion.OR D S:
IN TR OD UCTION
T raumat ic inj ury t o t he ant erior c ruc iat e ligament ( ACL) of t he knee p resent s w it h inc reasing f requenc y and is a c ommon p roblem among t he at hlet ic ally ac t iv e p op ulat ion. P at ient s w ho suf f er t his inj ury of t en dev elop c linic al inst abilit y of t he knee. Alt hough c onserv at iv e t reat ment has it s indic at ions, surgic al t reat ment f or ACL inj uries is t he
ideal c hoic e f or y oung and ac t iv e p at ient s bec ause it allow s t hem t o ret urn t o sp ort s but p rev ent s t he onset of addit ional knee inj uries.1
Surgic al t ec hniques hav e ev olv ed ov er rec ent dec ades, and t he c urrent gold st andard t reat ment is art hroscop ic
int ra- art ic ular ACL rec onst ruc t ion w it h aut ogenous graf t s. T he main asp ec t s of t he surgic al t ec hnique required t o ac hiev e f av orable c linic al result s inc lude graf t qualit y , t unnel p osit ioning and ef ic ient graf t ix at ion, w it h suf ic ient
t ension t o p rov ide j oint st abilit y and a p hy siologic al range of mot ion w it h normal lex ion and ex t ension.2 , 3 Along w it h
t he inc reasing number of indic at ions f or surgery , inc reases in t he f requenc y of rev ision surgery hav e also been rep ort ed.
Rev ision surgery is now p erf ormed in 1 0 - 4 0 % of c ases.4
T he main c ause of surgic al f ailure and ACL rev ision is inadequat e t unnel p osit ioning.5 , 6 Anat omic al st udies hav e
rep ort ed t hat t he anat omic al ACL origin and insert ion is t he most isomet ric graf t p osit ion7 - 1 0. How ev er, it is know n t hat
ev en senior surgeons using c onv ent ional guides f requent ly f ail t o p lac e t he t unnels in t he desired p osit ions.1 1 , 1 2
surgery p rec ision is t he Comp ut er Assist ed O rt hop edic Surgery ( CAO S) sy st em.1 3 N av igat ion sy st ems f or ACL
rec onst ruc t ion hav e been dev elop ed,1 4 - 1 8 but no c omp arat iv e
c linic al st udies hav e unequiv oc ally demonst rat ed t heir sup eriorit y in relat ion t o c onv ent ional guides. I n addit ion t o enhanc ement of p rec ision, suc h nav igat ion sy st ems can also f ac ilit at e c hoosing t he loc at ion f or bony t unnels based on t he
new isomet ry c rit erion. B ef ore t he adv ent of suc h sy st ems, t hese dat a c ould not be sup p lied t o surgeons int raop erat iv ely .
T he p urp ose of t he p resent st udy w as t o c omp are isomet ry and t unnel p osit ioning using t he CAO S sy st em and using
c onv ent ional guides.
MA TE R IA L S A N D ME THOD S
T he inc lusion c rit eria f or t he knee sp ec imens used w ere t hat t he c ause of deat h w as not t raumat ic or due t o inf ec t ious disease and t hat t here w ere no sc ars, hemat omas or def ormit ies in t he low er limbs. T he ex c lusion c rit eria diagnosed during art hrosc op y w ere t he p resenc e of any ligament lesions, menisc al lesions or degenerat iv e j oint disease. N one of t he sp ec imens ex amined w as ex c luded.
Specimen Preparation
T hirt y - six f reshly f rozen, undamaged human knees f rom c adav ers ( 1 8 p airs f rom 1 8 c adav ers) w ere used in t his st udy . Four of t he c adav ers w ere f emale and 1 4 w ere male, ranging in age f rom 3 8 t o 7 6 y ears ( mean, 5 1 .9 ;
st andard dev iat ion ( SD ) , 1 1 .9 ) . T he f emur w as c ut 2 0 c m and t he t ibia 3 0 c m f rom t he j oint line. T he iliot ibial t rac t up t o mid- t high, t he p op lit eus musc ulot endinous unit and
t he j oint c ap sule w ere lef t int ac t . T he knees w ere st ored at - 2 0 °C and t haw ed f or 1 2 hours at room t emp erat ure bef ore t est ing. P rior t o t he p roc edures, t he knees w ere subj ec t ed t o an init ial art hrosc op ic insp ec t ion t o rule out any p rev ious int ra- art ic ular lesions.
G roups
T he sp ec imens w ere div ided in t w o group s, eac h c omp rising one knee of eac h p air ( randomized side dist ribut ion by means of lip p ing a c oin) . T hese group s w ere named Group 1 , w hic h c onsist ed of 1 8 knees t hat underw ent ACL rec onst ruc t ion using c onv ent ional guides, and Group 2 , w hic h c onsist ed of t he 1 8 op p osit e- side knees t hat underw ent ACL rec onst ruc t ion assist ed by t he CAO S sy st em and nav igat ion inst rument s. All p roc edures were p erf ormed by t he same surgeon, w ho had p rior ex p erienc e in ACL rec onst ruc t ion and nav igat ion.
Surgical tech niq ue
Group 1: Conventional guide technique
I n Group 1 , guide w ire p osit ioning w as p erf ormed using c onv ent ional surgic al inst rument s. For t he t ibial tunnel, an Ac uf ex t ibial guide w as used ( D irec t or model; Smit h
& N ep hew , I nc ., U.S.A.) w it h 5 5 ° sagit t al angulat ion and 1 5 ° lat eral inc linat ion and w it h t he t ip of t he guide direc t ed t ow ard t he int erc ondy lar eminenc e of t he t ibia, half w ay
bet w een t he ant erior horn of t he lat eral menisc us and t he medial t ibial int erc ondy lar t uberc le. I n t his p osit ion, a f our-hole w ire guide w as drilled f rom t he ant eromedial surf ac e of
t he t ibia t o t he t ip of t he guide inside t he j oint . T he p osit ion of t he guide w ire w as c hec ked using an art hrosc op e. A p oly est er sut ure w ire ( E t hibond® 5 ) w as t hen p ulled by
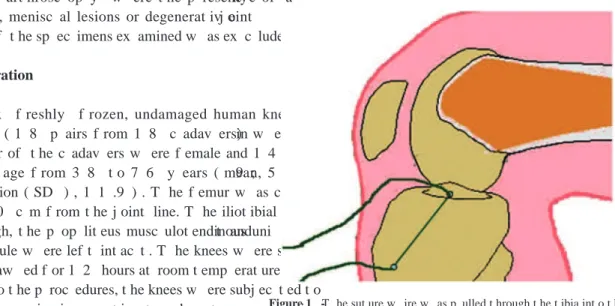
t he met al guide w ire f rom t he ex t ra- art ic ular ant eromedial c ort ic al surf ac e of t he t ibia t o t he inside of t he j oint , ex it ing f rom t he c ent ral p oint of t he t ibial t unnel, w hic h w as not drilled ( Figure 1 ) .
For t he f emoral t unnel, a 7 - mm of f set Ac uf ex f emoral guide w as int roduc ed t hrough t he ant eromedial p ort al and p osit ioned at t he f emoral int erc ondy lar not c h, w it h t he t ip of t he guide on t he p ost erior w all at elev en o’c loc k f or t he right knee and one o’c loc k f or t he lef t knee. I n t his p osit ion,
t he f our- hole w ire guide w as drilled f rom t he medial surf ac e
of t he lat eral f emoral c ondy le t o t he ant erolat eral surf ac e of t he t high of t he sp ec imen. T he end of t he sut ure w ire t hat had been lef t inside t he j oint w as t hen p ulled t hrough t he ant eromedial p ort al and w as led by t he f our- hole w ire guide
t hrough t he f emur ( Figure 2 ) . I n t his w ay , t he sut ure w ire w as p osit ioned at t he c ent ral p oint of t he f emoral t unnel,
w hic h w as also not drilled.
Group 2 – Navigation technique
Group 2 guide w ires w ere p osit ioned w it h assist anc e f rom t he O rt hop ilot nav igat ion sy st em. O rt hop ilotR ( Aesc ulap ,
T ut t lingen, Germany ) is a c omp ut er sy st em t hat p rovides t hree- dimensional ( 3 D ) real- t ime t rac king of sp ec iic surgic al inst rument s in relat ion t o anat omic al ref erenc e p oint s t hat are ac quired during surgery . T he 3 D t rac king is p erf ormed w it hout t he need f or addit ional p reop erat iv e p lanning or imaging suc h as t omograp hy . T he ant erior c ruc iat e ligament
rep lac ement sof t w are, v ersion 1 .1 ( 2 0 0 2 ) w as used toget her w it h it s sp ec iic surgic al inst rument s. T o p rov ide trac king, t w o p assiv e rigid bodies w it h f our relec t iv e sp heres eac h w ere at t ac hed using K - w ires t o t he f emur and t ibia. I nf rared ray s w ere p rov ided by a sourc e at t he side of t he cameras. T he hardw ired c ameras det ec t ed t he signals relec t ed by t he sp heres and det ermined t heir sp at ial p osit ion. A t hird p assiv e rigid body w as c onnec t ed t o t he sp ec iic inst rument s f or eac h st ep of t he surgery .
I n t he O rt hop ilot set up , t he graf t diamet er w as set t o 1 0 mm f or all knees. T he anat omic al ref erenc e p oint s and kinemat ic s of t he knee w ere ent ered and regist ered by t he O rt hop ilot sof t w are, t hus allow ing it t o c alc ulat e t he relat iv e p osit ions bet w een t he ix ed sensors and anat omic al landmarks.
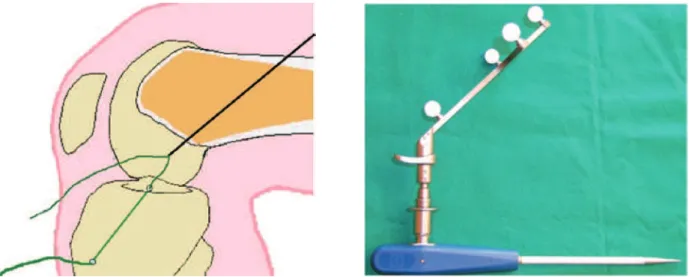
T he anat omic al ref erenc e p oint s inp ut t o t he sy st em w ere obt ained using a p oint er c onnec t ed t o t he mobile and p assiv e rigid bodies ( Figure 3 ) . Sup eric ial anat omic al landmarks w ere regist ered in sequenc e, st art ing w it h t he ant erior t ibial t uberosit y and ex t ending t o t he ant erior, medial and lat eral t ibial p lat eau borders. T he f ollow ing int ra- art ic ular st ruc t ures w ere v iew ed by means of art hrosc op y and regist ered w it h t he p oint er t hrough t he ant eromedial p ort al: p ost erior c ruc iat e ligament ( P CL) , ant erior t ibial insert ion, medial int erc ondy lar t uberc le, p ost eromedial margin of t he
ant erior horn of t he lat eral menisc us, at least iv e p oint s of t he ant erior border of t he f emoral int erc ondy lar not c h at it s t ransit ion w it h t he j oint c art ilage and at least iv e p oint s on t he medial surf ac e of t he f emoral lat eral c ondy le.
Subsequent p alp at ion of t he p ost erior w all of t he femoral int erc ondy lar not c h in t w o p osit ions, elev en and t welv e o’c loc k f or t he right knee and t w elv e and one o’c loc k f or t he lef t knee, w as c arried out w it h a nav igat ion- linked p oint er.
T he irst st ep in t he nav igat ion w as t he p osit ioning of t he t ibial t unnel; a sp ec iic t ibial guide c onnec t ed t o t he mobile and p assiv e rigid bodies w as t rac ked, and it s p osition w as monit ored on t he c omp ut er sc reen ( Figure 4 ) . T he t arget p aramet ers used w ere t he same as t hose desc ribed f or Group 1 . As soon as t he desired p osit ion of t he t ibial guide w as ac hiev ed, t he guide w ire w as drilled t hrough t he guide f rom t he t ibial ant eromedial surf ac e t o t he guide t ip inside t he j oint . A p oly est er sut ure w ire ( E t hibondR 5 ) w as p ulled t hrough t he
f our- hole w ire guide along t he drilled p at h. T he w ire remained f ree inside t he j oint at t he c ent er of w hat w ould be t he t ibial t unnel, w hic h w as not drilled as in Group 1 .
Figure 2 - T he sut ure w ire w as p ulled t hrough t he f emur by t he guide w ire out t o t he ant eromedial f emoral met ap hy seal surf ac e.
Figure 3 - Rigid body w it h relec t iv e sp heres f or t he nav igat ion–linked p oint er.
T he dat a f or t he t ibial t unnel w ere st ored in t he comp ut er and used t o c alc ulat e t he op t imum ent ry p oint f or the f emoral t unnel in relat ion t o t hat sp ec iic t ibial t unnel.
A nav igat ed f emoral guide w as int roduc ed t hrough t he ant eromedial p ort al and w as t rac ked by t he nav igat ion sy st em, allow ing t he guide p osit ion on t he medial w all of t he lat eral f emoral c ondy le t o be f ollow ed on t he c omp ut er sc reen. I n addit ion, it p ermit t ed t he c alc ulat ion of t he f ollow ing p aramet ers: c oronal angulat ion, dist anc e f rom t he f emur p ost erior w all and graf t isomet ry .
T he p oint selec t ed f or t he c ent er of t he f emoral t unnel resp ec t ed t he p rev iously deined p aramet ers and p rovided t he
best isomet ry . I n t his p osit ion, t he f our- hole w ire guide w as drilled f rom t he medial surf ac e of t he lat eral f emur c ondy le t o t he ant erolat eral surf ac e of t he t high of t he spec imen. T he
same p roc edures as f ollow ed f or Group 1 w ere p erf ormed in relat ion t o t he sut ure w ire, and t he f emoral t unnel w as not drilled. T hus, no t unnel w as drilled, but t he sut ure w ire w as p osit ioned inside t he knees, t hrough t he c ent ers of w hat w ould be t he f emoral and t ibial t unnels.
T he isomet ry measurement met hods w ere based on t hose desc ribed by Hernandez et al. ( 1 9 9 5 ) . A knot w as made at
t he end of t he sut ure w ire, p rox imally t o t he f emur. T his knot had a diamet er larger t han 2 .5 mm, and t heref ore, when t he op p osit e end emerging f rom t he t ibia w as p ulled, it c ould not migrat e bey ond t he f emoral c ort ex . Anot her knot w as made
at t he ex t ra- art ic ular t ibial end of t he w ire at an arbit rary dist anc e f rom it s t ibial ex it . T he w ire lengt h bet ween t he
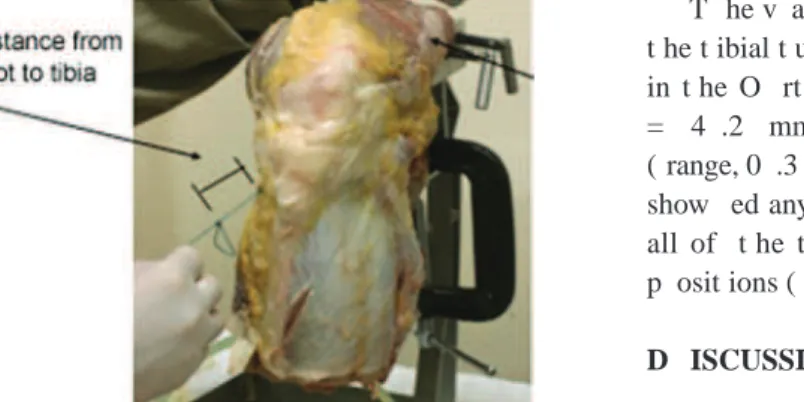
t ibial ex it and t he dist al knot , w it h t he knee at 90 ° of lex ion and t ot al ex t ension ( Figure 5 ) , w as measured using a manual
p ac hy met er. T he dif f erenc e bet w een t hese measurement s c orresp onded t o t he dif f erenc e bet w een t he dist anc es f rom t he f emoral t unnel t o t he t ibial t unnel at t hese p osit ions. T he graf t w as c onsidered isomet ric if t he lengt h v ariation w as zero.
T hrough art hrot omy , t he dist anc es t o t he P CL, medial int erc ondy lar t uberc le and margin of t he ant erior horn of t he
lat eral menisc us relat iv e t o t he guide w ire ex it on t he t ibial
j oint surf ac e w ere c ollec t ed using a manual p ac hy met er. T he p ost erior w all t hic kness w as measured on t he f emur.
A digit al p hot ograp h of t he f ront al v iew of t he f emoral int erc ondy lar not c h w as t aken w it h 9 0 ° knee lex ion. A line p erp endic ular t o t he t ibial j oint surf ac e w as draw n t hrough t he c ent er of t he int erc ondy lar not c h ( t w elv e o’c loc k) . T he int ersec t ion of t his st raight line w it h t he image of t he c ranial
edge of t he t ibia det ermined t he p oint t hat w as c onsidered t he angular v ert ex . From t his p oint , a sec ond st raight line w as draw n t hrough t he c ent er of t he f emoral t unnel. T he angle f ormed by t hese t w o st raight lines w as measured by t he sof t w are ( Figure 6 ) .
Statistics
T he dat a w ere analy zed using t he W ilc ox on t est f or c omp arisons bet w een t w o p aired samp les. A signiic anc e lev el of 0 .0 5 w as used ( p≤0 .0 5 ) .
R E SUL TS
T he v ariat ion of t he dist anc e f rom t he f emoral t unnel t o t he t ibial t unnel bet w een lex ion and ex t ension w as smaller in t he O rt hop ilot group [ bet t er isomet ry ; Group 1 , mean
= 4 .2 mm ( range, 1 .1 - 9 .4 mm) ; Group 2 , mean = 2 .8 mm ( range, 0 .3 - 6 .7 mm) ; p < 0 .0 5 ] . N one of t he ot her paramet ers
show ed any signiic ant dif f erenc e bet w een t he group s, and all of t he t unnels w ere c onsidered t o be in sat isf ac t ory
p osit ions ( T able 1 ) .
D ISCUSSION
T he design of t his st udy aimed t o make simp le c omp arisons using direc t measurement s bet w een t he Figure 5 - Sut ure w ire lengt h v ariat ion. D if f erenc e in w ire lengt h bet w een
t he t ibial ex it and t he dist al knot , w it h t he knee at 9 0 ° of lex ion and at t ot al ex t ension.
p osit ions of t he ACL rec onst ruc t ion t unnels ac hiev ed using t he O rt hop ilot nav igat ion sy st em and using c onv ent ional guides. Furt hermore, and p erhap s more imp ort ant ly , t his st udy aimed t o det ermine w hic h of t hese t ec hniques p rov ided bet t er isomet ry .
T he knees used in t his st udy did not p resent any ACL inj ury , and t he ACLs w ere art hrosc op ic ally remov ed. T he resec t ion inv ariably leav es c lear signs of t he anatomic al
origin and insert ion of t he ACL, and t his may hav e assist ed in p osit ioning t he guides, t hereby p ot ent ially imp rov ing t he result s in bot h group s.
D irec t measurement s using a manual p ac hy met er hav e t he adv ant age of being simp le and rep roduc ible, p art ic ularly w hen p erf ormed by a single surgeon. T he measurements w ere based on absolut e p oint s t hat w ere c ov ered by radioluc ent st ruc t ures, inc luding c art ilage and ot her t issues. T hus, our dat a c annot be c omp ared w it h radiograp hic dat a.1 9 , 2 0 T he measurement s of t he dist anc e f rom t he t ibial tunnel t o
t he P CL show ed av erages c lose t o 1 0 .2 mm in bot h group s. T his result w as higher t han t he ex p ec t ed result of 7 mm,
p ot ent ially indic at ing t hat t his w as not a reliable ref erenc e p oint f or t unnel p osit ioning.
Measurement ( in degrees) of t he c oronal angle of t he f emoral t unnel using digit al p hot ograp hy has not been
rep ort ed p rev iously in t he lit erat ure. W e c hose t o use t his measurement bec ause of it s rep roduc ibilit y and bec ause it is easy t o p erf orm.
T heref ore, it w as surp rising t hat t he t w o group s, w hic h demonst rat ed no signif ic ant dif f erenc es in any anat omic al p aramet ers, had dif f erent isomet ric behav iors.
T he O rt hop ilot group not only had a low er av erage but also a low er int erv al bet w een t he minimum and max imum v alues,
and t his result w as v ery c onsist ent .
O ur int erp ret at ion of t his f inding is t hat t here is a relat iv ely broad ac c ep t able area f or p osit ioning t he c ent ers of t he t ibial and f emoral t unnels. P osit ioning t he c ent er of t he t unnel at any of t he ininit e number of p oint s inside t hese
areas w ould be ap p rop riat e. T heref ore, an ininit e number of p ossible c ombinat ions of ap p rop riat e t ibial t unnels w it h ap p rop riat e f emoral t unnels f or eac h knee are p ossible. E ac h
of t hese c ombinat ions det ermines dif f erent mec hanical graf t behav ior and dif f erent isomet ry .
T he nav igat ion sy st em seemed t o p rov ide us w it h a f emoral t unnel loc at ion ( c hosen af t er p osit ioning t he t ibial t unnel) in an ac c ep t able area of t he f emur in relation t o
t he selec t ed t ibial p osit ion, t hereby p rov iding decreased v ariat ion of t he graf t lengt h or bet t er isomet ry . How ev er, t he nav igat ion sy st em p resent s some p ot ent ial inc onv enienc es, suc h as t he longer t ime required f or t he p roc edure2 1 and
morbidit y relat ed t o t he ix at ion of rigid bodies t o bones. T hese f ac t ors w ere not ev aluat ed in t he p resent st udy .
T he result s of t his st udy suggest ed t hat t here w as no dif f erenc e in t he anat omic al t unnel p osit ion bet w een t he group s. How ev er, f urt her st udies w it h a larger number of c ases are needed t o c onirm t hese result s. Finally , t he result s of our st udy enc ourage us t o c ont inue ev aluat ing t he use of nav igat ion f or t he imp rov ement of knee surgery .
CON CL USION
T here w as no dif f erenc e in anat omic al t unnel p osit ion bet w een t he group s. B et t er isomet ry w as ac hiev ed using t he nav igat ion t ec hnique ( Group 2 ) c omp ared t o t he c onv ent ional t ec hnique ( Group 1 ) .
Tab le 1 - Result s
Group 1 Group 2 W ilc ox on
Mean St andard dev iat ion Mean St andard dev iat ion
∆ T T - LM 7 .2 4 2 .3 4 7 .5 6 2 .5 3 P = 0 .7 5 6
∆ T T - MI T 7 .1 5 2 .4 2 6 .5 8 2 .3 5 P = 0 .4 5 9
∆ T T - P CL 1 0 .2 4 3 .5 8 1 0 .1 6 3 .5 8 P = 0 .9 3 1
∆ FT - P W 4 .5 6 2 .5 4 4 .2 6 3 .5 9 P = 0 .8 6 8
< FT 1 9 .1 8 5 .7 0 1 4 .1 6 8 .9 8 P = 0 .0 6 3
≠∆ FT - T T 0 °- 9 0 ° 4 .2 5 .4 5 2 .8 4 3 .3 8 P = 0 .0 2 8 *
∆- dist anc e; T T - t ibial t unnel; LM- lat eral menisc us; MI E - medial int erc ondy lar t uberc le; P CL- p ost erior c ruc iat e ligament ; FT - f emoral t unnel; P W - p ost erior f emoral w all; < FT - f emoral t unnel angular p osit ion in t he not c h; ≠- v ariat ion
R E FE R E N CE S
1 . K urzw eil P R, Jac kson D W . Chronic ant erior c ruc iat e ligament inj uries. I n Fu FH, Harner CD , V inc e K G. K nee surgery . B alt imore: W illiams & W ilkins; 1 9 9 4 . p . 7 3 1 - 4 7 .
2 . Hoogland T , Hillen B . I nt ra- art ic ular rec onst ruc tion of t he ant erior
3 . K half ay an E E , Sharkey P F, Alex ander AH, B ruc kner JD , B y num E B . T he relat ionship bet w een t unnel p lac ement and c linic al result s af t er ant erior
c ruc iat e ligament rec onst ruc t ion. Am J Sp ort s Med. 1 9 9 6 ; 2 4 : 3 3 5 - 4 1 .
4 . Sat i M, St aubli H, B ourquin Y , K unz M, N olt e LP . Realt ime c omp ut erized in sit u guidanc e sy st em f or ACL graf t p lac ement . Comp ut Aided Surg. 2 0 0 2 ; 7 : 2 5 - 4 0 .
5 . Get elman MH, Friedman MJ. Rev ision ant erior c ruc iat e ligament rec onst ruc t ion surgery . J Am Ac ad O rt hop Surg.1 9 9 9 ; 7 : 1 8 9 - 9 8 .
6 . Gali JC, Adad MAH, Mod MSB . Causas p ot enc iais de rec idiv a da inst abilidade ap ós rec onst rução do ligament o c ruzado ant erior. Rev B ras O rt op . 2 0 0 5 ; 4 0 : 5 2 - 9 .
7 . O denst en M, Gillquist J. Func t ion anat omy of t he ant erior c ruc iat e ligament and a rat ionale f or rec onst ruc t ion. J B one Joint Surg Am. 1 9 8 5 ,6 7 : 2 5 7 - 6 2 .
8 . P enner D A, D aniel D M, W ood P , Mishira D . An in v it ro st udy of ant erior c ruc iat e ligament and isomet ry . Am J Sp ort s Med. 1 9 8 8 ; 1 6 : 2 3 8 - 4 3 .
9 . Sc hut zer SF, Christ en S, Jakob RP . Furt her observat ions on t he
isomet ric it y of t he ant erior c ruc iat e ligament . Clin O rt hop Relat Res. 1 9 8 9 ; 2 4 2 : 2 4 7 - 5 5 .
1 0 . Hef zy MS, Grood E S, N oy es FR. Fac t ors af f ec t ing t he region of most isomet ric f emoral at t ac hment s. Am J Sp ort s Med. 1 9 8 9 ; 1 7 : 2 0 8 - 1 6 .
1 1 . E riksson E . How good are t he result s of ACL rec onst ruc t ion? K nee Surg Sp ort s T raumat ol Art hrosc. 1 9 9 7 ; 5 : 1 3 7 .
1 2 . Sudhahar T A, Glasgow MMS, D onell ST . Comp arison of ex p ec t ed v s. ac t ual t unnel p osit ion in ant erior c ruc iat e ligament rec onst ruc t ion. K nee.
2 0 0 4 ; 1 1 : 1 5 - 8 .
1 3 . Albuquerque RFM, Angelini FJ, P éc ora JR, Amat uzzi MM, Sasaki SU. Comp ut er- assist ed knee t ot al art hrop last y . Ac t a O rt op B ras.
2 0 0 6 ; 1 4 : 1 9 9 - 2 0 2 .
1 4 . D essenne V , Lav allée S, Julliard R, O rt i R, Martelli S, Cinquin P .
Comp ut er- assist ed knee ant erior c ruc iat e ligament rec onst ruc t ion: irst c linic al t est s. J I mage Guid Surg. 1 9 9 5 ; 1 : 5 9 - 6 4 .
1 5 . Julliard R, Lav allee S, D essenne V . Comp ut er assist ed rec onst ruc t ion of t he ant erior c ruc iat e ligament . Clin O rt hop Relat Res. 1 9 9 8 ; 3 5 4 : 5 7 - 6 4 .
1 6 . Sat i M, St aubli H, B ourquin Y , K unz M, N olt e LP . Realt ime c omp ut erized in sit u guidanc e sy st em f or ACL graf t p lac ement . Comp ut Aided Surg. 2 0 0 2 ; 7 : 2 5 - 4 0
1 7 . Müller- Alsbac h UW , St aubli AE . Comp ut er aided ACL rec onst ruc t ion. I nj ury . 2 0 0 4 ; 3 5 : S- A6 5 - 7 .
1 8 . Sc hep N W L, St av enuit er HJ, D iekerhof CH, Mart ens E P , v an Haef f CM, B roeders I A, et al. I nt ersurgeon v arianc e in c omp ut er- assist ed p lanning of ant erior c ruc iat e ligament rec onst ruc t ion. Art hrosc op y . 2 0 0 5 ; 2 1 : 9 4 2 -7 .
1 9 . K oh J, K oo SS, Leonard J, K odali P . Ant erior c ruc iat e ligament ( ACL) t unnel p lac ement : a radiograp hic c omp arison bet w een nav igat ed v ersus
manual ACL rec onst ruc t ion. O rt hop edic s. 2 0 0 6 ; 2 9 : S1 2 2 - 4 .
2 0 . P anisset JC, B oux D e Casson F. N av igat ed ant erior c ruc iat e ligament rec onst ruc t ion: c orrelat ion bet w een c omp ut er dat a and radiograp hic
measurement s. O rt hop edic s. 2 0 0 6 ; 2 9 : S1 3 3 - 6 .
2 1 . K oh J. Comp ut er- assist ed nav igat ion and ant erior c ruc iat e ligament