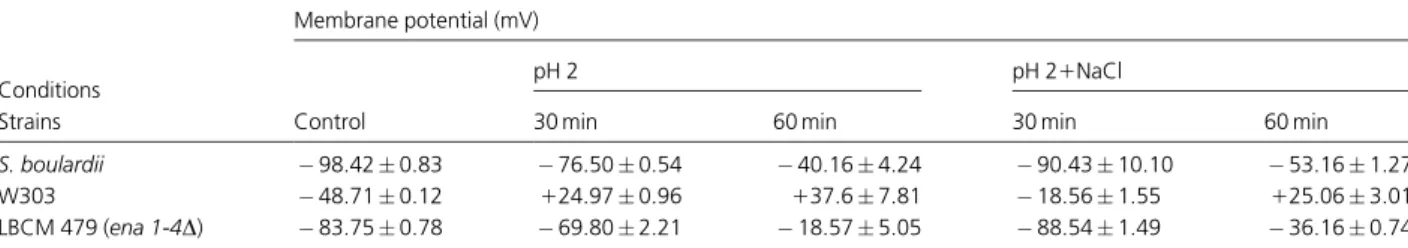
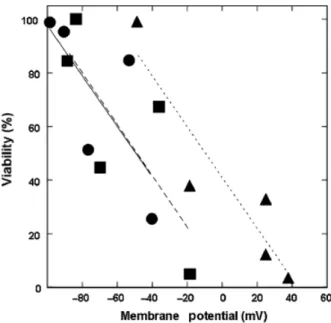
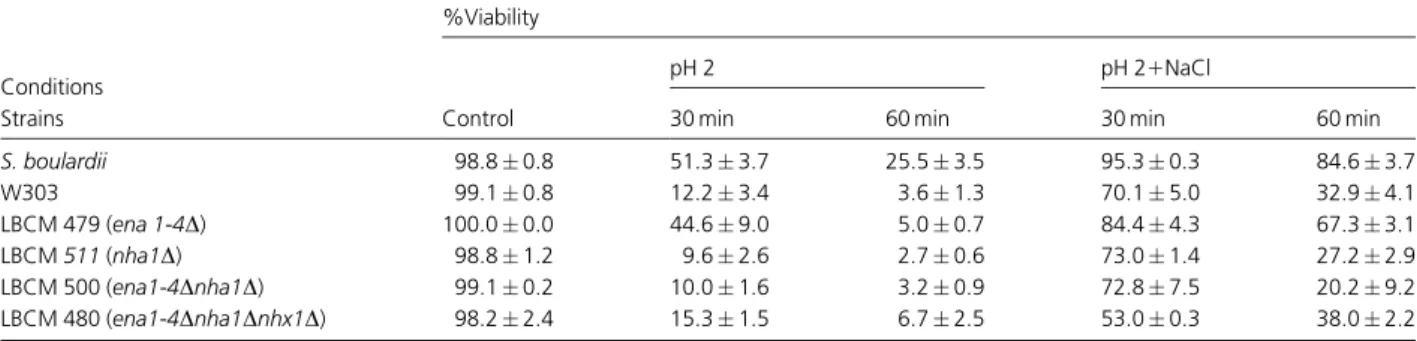
REPOSITORIO INSTITUCIONAL DA UFOP: Protective effect of ions against cell death induced by acid stress in Saccharomyces.
Texto
Imagem



Documentos relacionados
Confirmando muitas pesquisas sobre o ensino da Anatomia Humana na formação do profissional em saúde, os estudantes deste estudo relataram que os conhecimentos
Desse modo, a concorrência necessariamente produz perdedores assim como ganhadores: “trata-se, portanto, de uma medida de resultado final, interpretada em uma perspectiva
O foco deste trabalho é o desenvolvimento de blenda de polietileno de baixa densidade/amido termoplástico (PEBD/ATP) com característica biodegradável e atividade
The aim of the present study was to elucidate the possible protective role of vitamin E and / or sodium selenite on mercuric chloride-induced oxidative stress and
In experiments of nociception induced by acetic acid, formalin and capsaicin in mice, the HE Mv evidenced an antinociceptive effect, being active against both inlammatory
Considerando os objetivos definidos anteriormente que passam pela (i) análise das dimensões que definem o envolvimento do consumidor, em diferentes níveis como o
The present study was conducted to study the effect of the addition of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell wall (0.2%) in broiler feeds on the performance, morphometric parameters
Objectives/Hypothesis: Evaluate the effect of in vitro exposure of mice laryngeal mucosa to solutions that simulated human gastric juice and to assess the topical protective effect