However, current online learning solutions do not fully exploit the potential of online communities. This included studying the concept of instant online communities, learning communities and how online learning communities can support learning in university courses. Based on this, an idea of instant online learning communities was described with the features it should support.
Introduction
The purpose of the literature review in chapter 2 is to form a very basic concept of instant online learning communities (IOLC) and to determine its main factors in improving perceived learning. This preliminary description of IOLC can be used as a starting point for creating online learning communities. The conclusion includes the evaluation of the study and suggests future research objectives to expand and refine the idea of online instant learning communities.
Theoretical Background
Internet as a Platform for Communities
- Definition of Online Communities
- Online Community Software
- Instant Online Communities
- Sociability and Usability in Online Communities
- Awareness and Social Presence
Policies also change as the community develops, which should also be considered in software design. Another aspect of online community software is the limitations it places on the community running online. The community then really focuses on the shared common theme, the community's purpose.

Online Learning Communities
- Online Learning
- Learning Communities
- Defining Online Learning Communities
- Online Learning Community Software
- Interaction and Social Presence in Online Learning Communities
- Perceived Learning
- Role of the Students and the Instructor
- Establishing OLC in Educational Settings
- Online Learning Environments In TUT
- Instant Online Learning Community
Studies show that social presence has a positive impact on perceived learning in online learning communities (e.g. Interaction support can be seen as the most relevant aspect of online learning community software in the context of awareness and social presence. Both types of interaction rely on instructors, since facilitating productive interaction can be seen as the most important responsibility of the instructor in online learning communities.
Summary and Study Objectives
Therefore, this study seeks to answer the following question: what are the advantages that instant online learning communities offer over existing online learning solutions. While it is common for the software to focus on a single site offered by a service provider, this limits community interaction to that specific site. 2009) introduces an idea of instant online communities that easily enables online community on any desired website. Instant online communities could be used to raise awareness and support interaction in online learning communities, thereby improving social presence.
This study aims to examine how the idea of instant online communities can be used to enhance perceived learning. This study focuses on these aspects and aims to define the idea of an instant online learning community. Instant Online Learning Communities (IOLCs) are an adaptation of Instant Online Communities in the context of learning communities.
In addition, the reader gains knowledge about the common features of instant online communities today and how well they support the central functions of IOLC. As the first stage, this chapter examined the literature to determine the key factors for instant online communities that would enhance perceived learning. This is based on both the theoretical background from the first phase and the features offered by current online communities.
After these three phases, the study concludes by presenting the idea of instant online learning communities, constructed and improved through the three phases.
Features of Instant Online Learning Communities
Features of Instant Online Communities
- Creating and Managing a Community
- Integration
- Awareness
- Communication
- Content Aggregation
- Authentication
Setting the name of the community is only feature expected to be found on any service. The actual integration of the interface of the website and the online community is performed by a JavaScript code provided by the IOC service, separate from the widget code. Just like the integration of widgets, the API is also integrated by linking a JavaScript code in the HTML of the website.
These widgets can be integrated into the website at the desired location, better serving the purpose of functionality and simultaneous use of the widget and the host website. This can be seen as a way to improve the social presence of community members. Friends can be users who are members of the current community, but can also be members of other communities.
It can be used to make the online community a combined source of information on the topics of interest to the members of the community. The malicious user does not need to have any kind of community membership or access to it. It is also common for the user to log in using one of the popular services such as Google, Twitter or Facebook.
The problem there is that the user of the IOC service cannot be matched with the user of the hosting website.
IOC Services
- Livecommunity
- Friend Connect
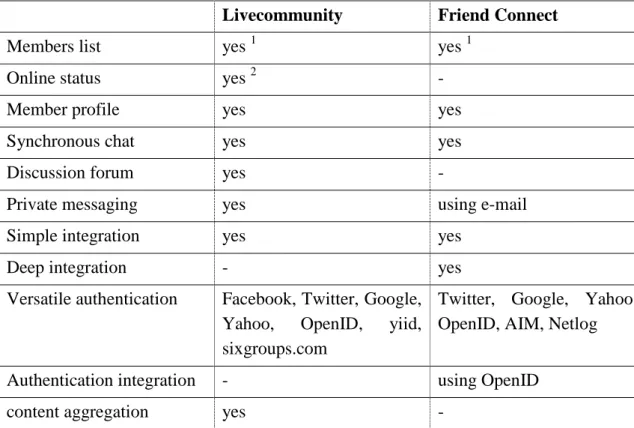
Live Community was included in the study because it is a service that intentionally follows the principles of IOC's idea. By default, the Live Community widget is a small bar at the top of the website and can be opened by the user. Members, a list of community members and status indicators that show which of them are online.
Most of the lines of code in the Members widget snippet in Program 3.1 are used to display a static link to the community website at Sixgroups.com and to the website of the company that provides the IOC service. This is done by providing developers with extensive documentation of the widget API that Friend Connect uses (Google 2010). All gadgets use the same API, regardless of the community they present or the site they are integrated into.
One major difference to Livecommunity's member widget is that Friend Connect has no online status of the members displayed in this or any other widget. Additionally, parameters for customizing the gadget's interface are included in the integration code. This allows each widget to be customized separately, which also allows for integration of the gadget view into the hosting website.
When creating a community using the admin tools, the admin must enter the address of the website the community is using.
Building an Instant Online Learning Community
- Awareness and Social Presence
- Discussion
- Supporting Features
- Summary of the Features
Both have the support for OpenID, which makes it possible to integrate authentication with the one that the host website can use. However, the fact that API is documented and open to developers allows very deep integration with the host website, although it requires expertise in some of the supported web development techniques. For this study, only the features devices were investigated. awareness information is clearly displayed to the student so that he or she can interact as a member of the online community.
The listing may use members' names, their profile picture, or any combination of information available, selected for each instance of the listing separately. Using these features, members are aware of each other and the existence of the community. Additionally, some support features can efficiently improve the functionality of the service with little effort required by the administrator.
Deep integration, which offers the possibility to integrate the interface and the functionality of the hosting website into the functionality provided by the IOLC service, if a decent level of expertise is available. These features allow the integration of the IOLC service into a website with good usability and visibility from the online community. As a conclusion of the described IOLC service and the two IOC services examined, the Livecommunity and Friend Connect functions are summarized in relation to the functions that an ideal IOLC service should have.
Using the information gathered, he then described an online instant learning community service by defining some of the most central features.
Studen Inquiry
- Goal
- Method
- Role-Playing Method
- Story Frames
- Execution
- Analysis
- Results
- Social Presence of Other Students
- Social Presence of the Instructor
- Discussion
- Ideas for IOLC Implementation
- Other Relevant Notions
- Assessments and Reliability of the Results
- Story Frames
- Respondents Background
- Summary of the Student Inquiry
Through the analysis, the results reflect examples of the opinions and ideas the students have. Central to using the method is observing the differences in the answers when different respondents are given slightly different variations of the story frame. This is due to the different variations of the story frames, which are described in the next section.
The story frames of the investigation were compiled based on the objectives described in section 4.1. The exact content of the message, including story frame variation B, is contained in appendix 1 (in Finnish). Theory-origin analysis was a natural choice as the aims of the investigation were to compare the responses with the theory.
The presence of teachers in the discussion was emphasized in variant B of the story frame, as opposed to the social presence of other students. However, this is most likely due to the choice of words in the story frame. First, the topic of discussion was seen by most respondents as strictly focused on the course topic.
The responses were analyzed using three theory-based concepts: the social presence of other students, the social presence of the teacher, and discussion.
Conclusion
- Improving Perceived Learning
- Instant Online Learning Community
- Assessment of the Study
- Unsolved Issues and Proposals for Future Study
In addition to the social presence of other students, the presence of the instructor is also an aspect that can be improved by using direct online communities. By promoting the social presence of the instructor in an online learning community, instant online communities can certainly improve perceived learning, but this is as much a matter of instructional design and pedagogy as it is a technological issue. It also makes interaction better possible when the participants of the discussion are not online at the same time.
The student survey confirmed that teacher presence is very important in online learning communities. The IOLC can facilitate this by displaying the teacher's online status, so that the students can see if a teacher is online and participating in the discussion. This feature and its use in learning communities is one of the areas that need further study.
Software that supports the learning community is only one part of the solution for supporting learners online. Taking a more technical look at the characteristics of the two sample services in Chapter Three, a highly experimental approach was taken. It offered a good insight into the students' thinking and many new ideas for the service.
Proceedings of the 47th Annual Computer Manpower Research Conference Special Interest Group on Information System Management (pp. 63–72).
Student Inquiry Example
Studen Inquiry Responses
TTY-opiskelija näkee muiden opiskelijoiden luettavaa niiltä sivuilta, joiden nimi (etunimi + sukunimi) ja kuva näkyvät, jos opiskelija on lisännyt kuvansa palveluun. Nähdessään muiden opiskelijoiden lukevan sivuilta samaa materiaalia, hän päättää kysyä, voisiko joku löytää luentomuistiinpanoja, joita hän voisi kopioida. Jos opiskelijan lähettämään viestiin tulee vastausviesti hänen ollessaan kirjautuneena kurssisivuille, opiskelija näkee ponnahdusikkunan "Vastausviesti vastaanotettu", jota klikkaamalla opiskelija voi lukea viestin.
Jos kuuluisia ihmisiä ei löydy, opiskelija tutkii muiden opiskelijoiden profiileja löytääkseen kiinnostavia tai motivoituneita henkilöitä harjoitusryhmään. Hän voi palata myöhemmin uudelleen lukemaan keskustelun, jos hän katsoo sen parhaaksi, tai hän voi jopa itse osallistua keskusteluun, jos hänellä on jotain kysyttävää tai sanottavaa aiheesta. Vaihtoehtona voisi olla myös se, että opiskelija esittää vaihtoehtoista materiaalia, jos hän on perehtynyt siihen perusteellisesti.